Warehouse Management System (WMS)
Warehouse Management System revolutionizes the warehouse & order fulfillment processes and empowers you with automation, accuracy & cost-efficiency
What is Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a software that allows businesses to intelligently execute and administer various warehouse-specific operations such as receiving, put-away, inventory management, allocation, replenishment, yard management, order picking, and delivery shipment.
As an essential module within the ERP Software, it plays a critical role in the supply chain process. It automates a multitude of warehouse operations, thereby avoiding potential disruptions. It facilitates up-to-the-minute insights into how quickly your warehouse inventory is collected, located, packaged, and sold in the market. By building a highly efficient Warehouse Management System, companies can better respond to changing market dynamics and improve their competitiveness.
Why Choose Sage Warehouse Management Module?
In today’s era, businesses need deeper insights into their warehouse operations while keeping their warehouse costs at lower. Sage X3 is the best-in-class extended warehouse management solution that handles your warehouse complexities, and provides complete control over the movement of your inventory.
Here’s how Sage X3 helps leading Indian companies drive efficiency and gain competitive advantage in the market-
- Lot & serial number tracking, and expiration management
- Streamline inbound & outbound processes and reduce waste
- Optimize warehouse storage and reduce operating expenses
- Advanced risk evaluation and reporting capabilities
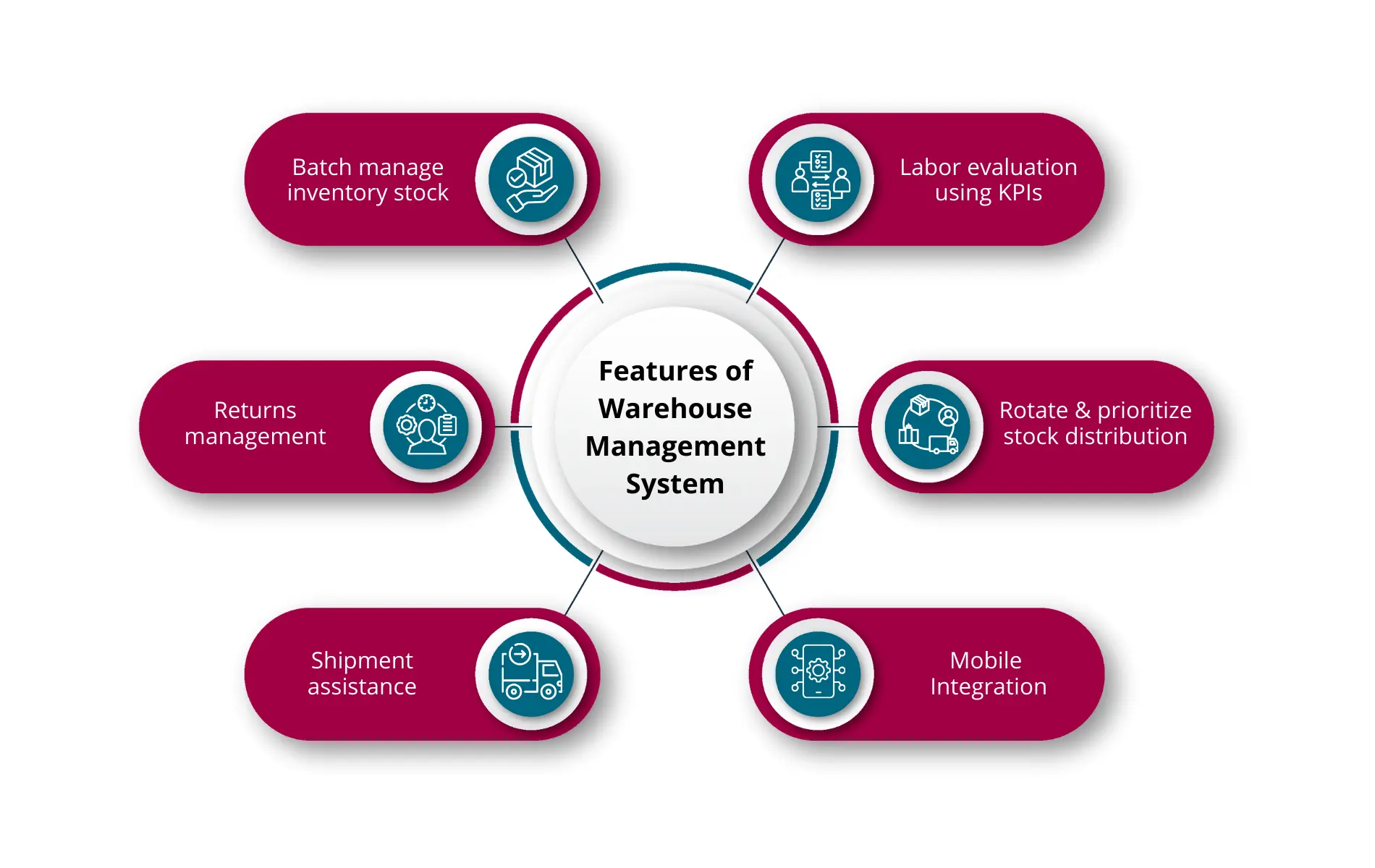
What are the Features of a Warehouse Management System?
The are many distinct characteristics of a Warehouse Management System (WMS). We’ll discuss them one by one:
1. Batch Management
A WMS System plays a vital role in increasing the efficiency of the customer’s inventory handling. It allows businesses to batch manage the stock of inventory based on their unique characteristics such as color, size, type, ingredients, and usability. It reduces the time required to locate and fulfill customer orders.
2. Stock Rotation
Stock rotation is an effective technique used to fight stock obsolescence or expiration. WMS Software enables businesses to perform stock rotation by prioritizing the stock distribution that is expiring earlier. It is extremely important for businesses that deal with perishable products such as food, dairy products, fish, eggs, cooked foods, and so on.
3. Returns Management
In today’s highly competitive world, businesses have to provide a seamless Returns Policy to ensure customers get what they have paid for, and they don’t hold negative perceptions about the brand or product. A Warehouse Management System (WMS) automates various processes in the returns from restocking, and reverse logistics, to managing loyalty points.
4. Product Shipment Management
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) streamlines various processes in product shipment from invoice generation to automated shipment notifications. Furthermore, before a shipment is shipped, it drafts and automatically sends a Bill of Landing, which is required to prove the ownership of the cargo.
5. Labor Management
Another important feature of the Warehouse Management System is its ability to monitor labor performance and allow decision-makers to evaluate it. They can use various Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to assess labor performance and make decisions to improve their productivity, reduce inefficiency, and ensure smooth continuity in the warehouse operations.
6. Mobile Integration
Sage X3, A Warehouse Management System enables your employees from scanning scan barcodes, access historical data, and perform quality inspections to check inbound trailer information, everything using their mobiles. The employee’s mobile app is connected to a centralized cloud server to ensure the transmission of up-to-date and accurate information.
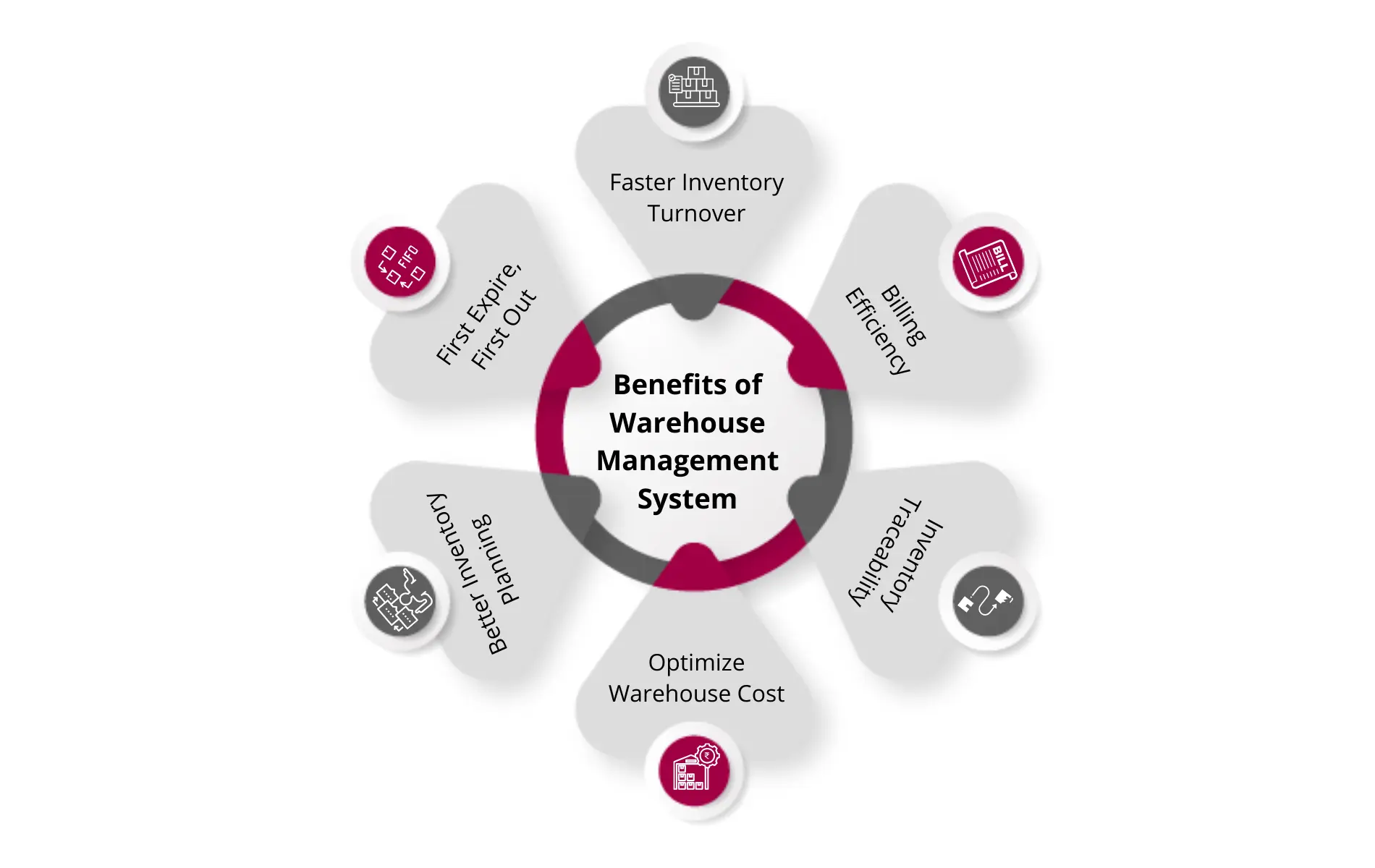
Benefits of Using a Warehouse Management Software (WMS)
An increasing number of businesses are deploying a Warehouse Management System to unlock the following benefits:
1. Expedite Movement of Goods
Warehouse Management System empowers businesses with automation to improve their volume handling capability and boost the movement of goods. Business owners can get a 360-degree view of their business processes to identify discrepancies and make strategic decisions to overcome them. Moreover, the use of automation reduces human errors and brings in accuracy.
2. Automated Replenishment System
WMS Software keeps a complete record of product expiries so that you can sell sooner-expiring products first. The “First Expired, First Out (FEFO)” method lets you re-arrange your inventory in such a way that you will save your warehouse storage space and lower the time it takes to locate your inventory.
3. Reduce Inventory Misplacement
The use of a Warehouse Management System aids with inventory planning and forecasting, WMS System provides real-time tracking of the inventory movement and lowers the instances of misplacement & miscalculation. Not only that, decision-makers can understand how certain products are performing and use powerful forecasting tools to make accurate forecasts.
4. Limit Warehouse Costs
We all know the manufacturing cost, but we often neglect the warehouse storage costs. Businesses incur a significant amount on the rental of the warehouse premises, stock maintenance, labor, and taxes. Deploying a Warehouse Management System (WMS) allows you to maintain optimum inventory levels, reduce over-stocking, and save the cost of warehouse operations.
5. Inventory Traceability
Warehouse Management Software keeps a complete record of the inventory along with its Serial Number, Batch Code, and Lot Number, and provides decision-makers with comprehensive reports and analysis. It groups inventory by its distinct characteristics such as color, size, and ingredients. Not only does it reduce a lot of manual work, but also paves the path for aggregate planning and forecasting of inventory.
6. Efficiency in Billing Operations
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) comes with an accounts receivable automation which reduces human errors, miscommunications, and time delays in the billing process. It makes the billing process faster, more accurate, and transparent, thereby increasing customer trust, ensuring stricter regulatory compliance, and seamless order fulfillment.
Boost Your Warehouse Efficiency with Sage X3
Scale and transform your warehouse operations with ERP software
What are the Types of Warehouse Management Systems?
The warehouse management systems can be broadly classified into four types based on their nature of operations.
1. Standalone WMS Software :
A fully standalone and independent system of warehouse management that best suits for complex businesses requiring extensive customizability.
2. ERP-integrated WMS Software:
A sub-system that is an integral part of a comprehensive ERP Software. If you’re looking for real-time insights and collaboration, go for it.
3. Cloud WMS System:
A cloud-based system with remote accessibility and no need for upfront investment. It offers more flexibility, customizability & remote accessibility.
4. Supply Chain WMS System:
A system integrated deeply into the Supply Chain Network, facilitating better coordination & strategic decision-making.
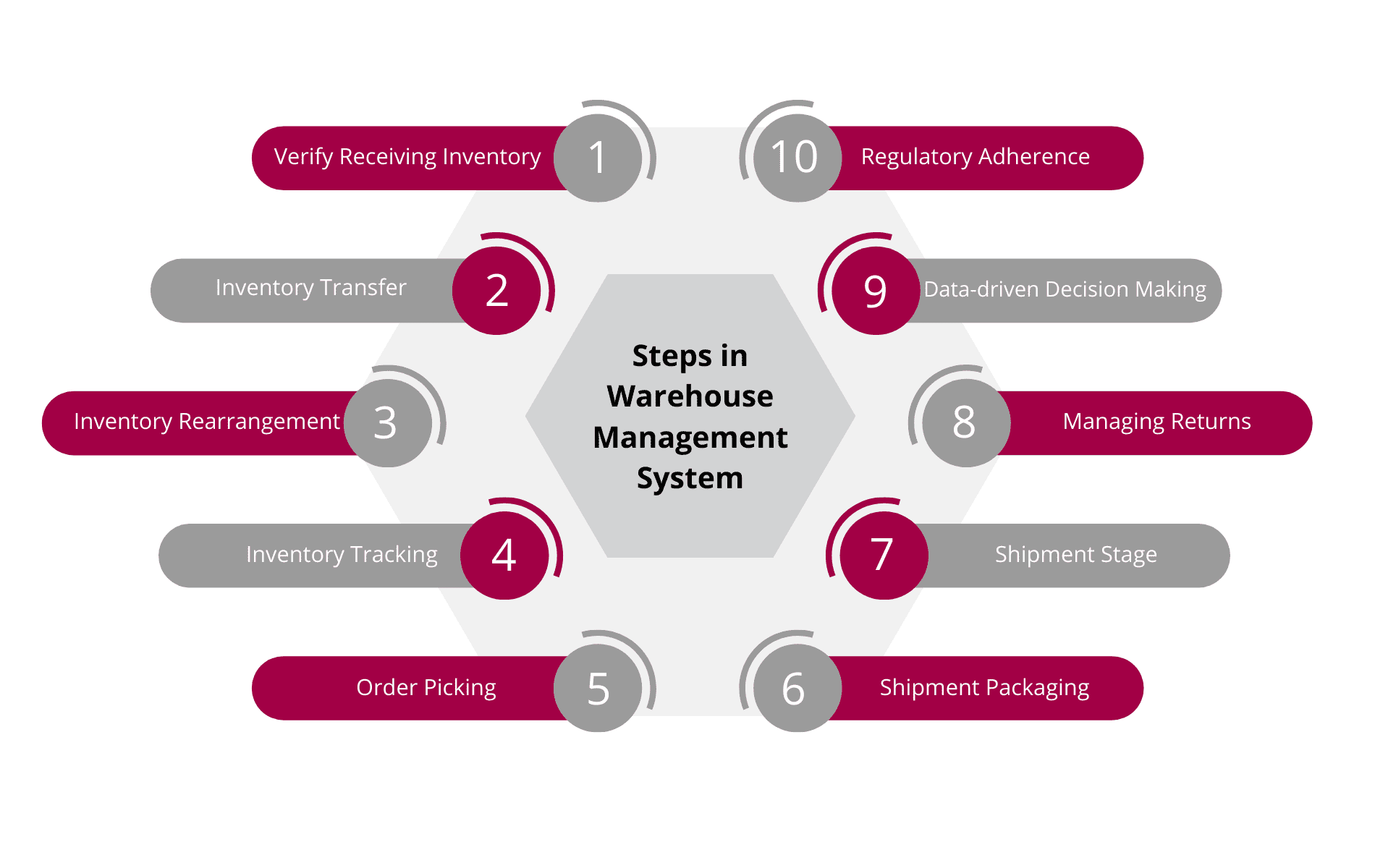
Important Steps in Warehouse Management System (WMS)
Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a comprehensive process that involves the following steps:
1. Verify Receiving Inventory
- Make sure that the inventory is received during the desired time frame
- Check the received inventory for accurate quantity
- Perform quality inspections to ensure the inventory meets the acceptable quality level
2. Inventory Transfer
- This stage involves transferring inventory from the dock to the relevant storage location
- It also involves making sure the inventory is easily accessible when required
- The exact location of the inventory is accordingly updated in the WMS System
3. Inventory Rearrangement
- The inventory is rearranged in such a manner to optimize the storage usage
- The company can implement either First-in-First-Out or Last-in-First-Out method
- The objective of this step is to enhance the inventory storage efficiency.
4. Inventory Tracking
- Classifying inventory into raw materials, ready-to-sell, and unfinished goods
- Keeping a close eye on the inventory threshold to prevent over-stocking & under-stocking
- Checking inventory catalog for potential errors & discrepancies
5. Order Picking
- This step involves the use of automated systems
- It involves bringing accuracy to order management using the automated order management system
- The system also prioritizes the client base based on their requirement type and urgency.
6. Shipment Packaging
- Preparing shipment for dispatch
- Making sure the right quantity of inventory is packaged
- Use of Safe Packaging to protect the package during transportation
7. Shipment Stage
- This phase involves coordinating with external stakeholders for smooth order shipment
- The employees make an entry into the WMS Software
- The customer receives a notification about the shipment details and tracking details
8. Managing Returns
- Managing the movement of damaged or faulty products from customers to the warehouse
- Assessing the condition of returned products
- Determining the future course of action for returned products
9. Data-driven Decision Making
- Generating inventory-specific and order-centric reports for higher-decision making
- Performing thorough data analysis to find trends, analysis, and anomalies
- The higher management takes appropriate decisions based on the submitted reports
10. Regulatory Adherence
- Keeping a close eye on the latest regulatory standards
- Drafting emergency protocols and training employees on safety standards
- Performing regular safety audits
5 Signs You Need to Deploy a WMS Software
1. Poor Warehouse Visibility
Do you rely on an outdated system that suffers from poor visibility across warehouse operations? Do other departments often complain of a lack of smooth data exchange with warehouse staff? If so, it’s time to upgrade to an Extended Warehouse Management (WMS System).
2. Frequent Returns
Do you heavily rely on manual work for tracking, counting & item placement? If so, there’s an increased potential for human errors, leading to higher returns & replacements. Frequently dispatching wrong products (different qty, size, or type) can affect your customer’s experience and damage the company’s reputation.
3. Higher Warehouse Costs
If you aren’t optimizing your warehouse storage, you’ll incur higher warehouse storage costs. Furthermore, increased instances of tracking errors and returns & replacements can lead to higher operational costs and shrink your profit margins.
4. Lower Productivity Issues
Without a Warehouse Management System, you might suffer from a lack of standardization and labor-intensive procedures. Lower warehouse productivity can delay the order fulfilment process, leading to longer wait times for the customer and a lower revenue stream in the long term.
5. Lack of Scalability
Over-reliance on outdated systems can hamper your ability to process increased order volumes. As you don’t optimize your warehouse storage, meeting sudden demand spikes and dealing with market uncertainties can be difficult.
Important Factors to Consider While Choosing the Best Warehouse Management System
1. Centralized View of Inventory
Make sure that your warehouse management system provides a centralized overview of your inventory across multiple branches and units.
2. Track Demand Variations
Look for customized dashboards and intelligently crafted reports to understand your current demand patterns, seasonal trends, and fluctuations.
3. Post-deployment Support
For smooth deployment and post-implementation support, buy a system from a reputed vendor offering regular support.
4. Cloud Storage
By storing data on the cloud, you can eliminate server set up, maintenance and repair costs, and achieve cost efficiency.
5. Third-party Integration
Make sure your new system offers robust integration with legacy tools to minimize the potential for data obsolescence.
6. Adapt to Growing Needs
Choose an Enterprise Resource Planning system that adapts to your growing needs as your business expands in size and operations, and captures new markets.
Difference Between Warehouse Management System vs. Inventory Management System
Warehouse Management System and Inventory Management System are two highly interlinked, yet distinct concepts. Here’s the fundamental difference between them:
| Category | WMS (Warehouse Management System) | IMS (Inventory Management System) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The Warehouse Management System is an integral module of ERP that provides complete control over warehouse operations and optimizes warehouse-specific tasks. | The Inventory Management System is an integral module of ERP that provides real-time visibility into the inventory levels, alongside superior inventory tracking and forecasting. |
| Objectives | • Warehouse storage optimization • Cost-efficiency • Expedite the physical movement of goods within the warehouse • Track warehouse operations • Track the productivity of warehouse staff | • Seamless inventory tracking • Inventory counting • Inventory forecasting • Mitigate inventory-specific challenges (stock-outs & surplus stock) |
| Common Technological Integration | • RFID Tags • Internet of Things (IoT) devices • Barcodes • Light Fidelity (LiFi) • Blockchain | • RFID Tags • Internet of Things (IoT) devices • Barcodes • Light Fidelity (LiFi) • Blockchain |
| Scope | Single warehouse | Multiple locations across different units or branches |
| Commonly Used Accounting Ratios | • Warehouse Cost to Sales Ratio • Order Picking Accuracy Rate • Labor Productivity Rate • Inventory Carrying Cost Ratio • Inventory Turnover Ratio | • Inventory Turnover Ratio • Gross Margin Return on Inventory • Days Sales of Inventory (DSI) • Stockout Rate • Inventory Cost • Inventory Valuation • Inventory Holding Cost Ratio • Backorder Rate • Excess Inventory Ratio |
Future-Proof Your Business with Sage X3
Modernize your business operations and drive precision & growth
What are the Limitations of the Warehouse Management System?
1. Upfront Investment
Many businesses, especially smaller ones, lack sufficient financial capital to invest in modern technologies such as WMS software. Thankfully, it is no longer a concern with the introduction of Cloud ERP.
2. Basic Functionality
Selecting the best ERP software in India requires extensive planning & analysis. It can be a time-consuming procedure.
3. Limited Scalability
Some low-quality ERPs may not be scalable. Thus, you may risk running their functional limits occasionally and not being able to adapt to new market dynamics.
4. Data Security Concerns
ERPs from unreliable vendors may lack strong data security measures (such as encryption) and expose your confidential business data to cyber criminals, thus resulting in significant losses and disruptions.
Optimize Your Warehouse Management Using Sage X3
Do you frequently experience inventory shortages & over-stocking problems? Is your business unable to cope with the growing demand for your products due to the slow & tedious order fulfillment process? If so, it’s time to invest in a warehouse management system. In today’s fast-paced and highly complex business environment, it serves as the central orchestrator for optimizing your warehouse activities & order fulfillment process.
Sage X3 is a high-end solution that completely revamps the traditional process of warehouse management and addresses a myriad of issues faced by modern-day businesses. Businesses can leverage their technological capabilities to use their warehouse storage more efficiently, better coordinate between different departments, minimize errors, and fulfill customer orders quickly & efficiently
Top Industries Leveraging ERP Software
Food & Beverage
Alcohol
Pharmaceuticals
Advertising
IT Services
Furniture
Manufacturing
Auto Ancillary
Pharma Trading
Packaging
Medical Device
Chemical
Plastic
Brewery
Logistics
Automotive
FAQ of Warehouse Management System
What is the Warehouse management system?
Warehouse Management System meaning is a platform that helps businesses manage their everyday warehouse operations, from tracking inventory to streamlining order picking & shipment procedures. It plays a crucial role in the order fulfillment process and enables decision-makers to respond swiftly to sudden market trends & changes.
Who uses a WMS?
A WMS System is used by manufacturers, retailers, and wholesale distributors to get vital information about their warehouse operations and reduce errors in order processing. It is a vital tool that helps businesses harness the power of modern technology to improve efficiency, become responsive, and face challenges efficiently.
What are the most popular WMS?
Here are the top 5 WMS system used across the world:
- Sage X3: A highly flexible & customizable solution with robust analytical features and workflow automation
- Zoho: A cloud-based system supporting multiple sales channel and locations
- NetSuite: A single system that provides 360-degree overview of warehouse operations
- SAP: Offers better integration across departments and improved decision-making
- Unicommerce: Better shipping integration and supply chain visibility
Which software is best for warehouse management?
Sage X3 is a comprehensive suite that aligns with evolving needs of modern-day businesses across different industries. It provides advanced analytical insights, real-time reporting, SKU level traceability, multi-location warehouse management, and dynamic stock replenishment.
What are the four types of WMS?
The four types of Warehouse Management System are:
- Standalone Warehouse Management Software
- ERP-integrated WMS System
- Cloud WMS System
- Supply Chain WMS Software
What are the 5 principles of Extended Warehouse Management?
The following are the principles of extended warehouse management:
- Ideal Inventory Levels: A business must maintain ideal inventory levels to mitigate the risks of over-stocking and under-stocking.
- Faster Transaction Processing: Digitize the manual invoice-generation process and improve your transaction processing speed.
- Regular Employee Training: Conduct regular employee training sessions to ensure they are productive and efficient.
- Process Optimization: Analyze existing business processes, fix discrepancies, and simplify complexities.
- Regular Performance Audits: Regularly analyze the effectiveness of your organizational performance through 360-degree performance audits.
Is WMS an ERP system?
Many people use the terms WMS and ERP interchangeably. However, the WMS is an integrated module within a broader ERP system. While an ERP takes care of your organization-wide operations, the WMS provides intelligent reporting, precise tracking of stock, and cross-docking abilities. It is an important module that works in conjunction with your ERP to facilitate smooth flow of information for better decision-making and warehouse efficiency.
Schedule Product Tour
"*" indicates required fields