What is Breakeven Point?
The Breakeven Point is the point at which the cost of production and sale of products equals the revenues, or the market price of an asset or security equals its total cost, and the seller incurs neither profit nor loss. It is an important formula that helps businesses limit financial strain, make data-backed decisions, and set revenue targets to increase their profit margins.
The concept of Breakeven Point is often used in the context of the production and sale of goods, sale of assets, and securities. When it is used in the context of an asset, it indicates the point at which the revenue from the sale of the asset equals the original acquisition cost of the asset, alongside repair, and maintenance charges. In the context of securities, it takes into consideration the original purchasing cost of the security, alongside any brokerage charges, and taxes incurred.
Why is the Breakeven Point Important for Businesses?
Now that we’ve discussed the breakeven point meaning, let us understand its importance for businesses of all scales.
1. Financial Stability
As we’ve learned in the break even definition, the breakeven point identifies the level of sales where revenues cover all costs, ensuring a business reaches financial stability. This knowledge aids in planning and decision-making, helping to avoid losses and maintain a healthy bottom line.
- Budget Precision: Breakeven analysis ensures accurate budgeting, preventing shortfalls and enabling effective resource allocation.
- Debt Servicing Assurance: It instills confidence in creditors by assuring the ability to cover fixed and variable costs.
- Cost Control Strategies: Identifying and controlling costs promotes financial stability.
- Sustainable Growth: The break-even point is helpful in various activities meant to grow and expand the business operations.
- Cash Flow Predictability: A break-even analysis is helpful in various business processes such as predicting cash flow effectively.
- Profitability Analysis: Understanding the breakeven point enables businesses to assess profitability thresholds. It guides pricing strategies, ensuring that prices set above the breakeven point contribute to profits, promoting sustained growth and competitiveness.
- Optimized Pricing: Guides setting prices for products or services to exceed the breakeven point.
- Product Mix Evaluation: Assesses the profitability of different products, optimizing the product mix.
- Margin Improvement: Identifies opportunities to enhance the contribution margin for higher profits.
- Cost Efficiency: Promotes cost-conscious decisions, improving overall cost efficiency.
- Scenario Planning: Allows businesses to assess profitability under different scenarios for proactive decision-making.
2. Risk Management
Businesses face uncertainties, but knowing the breakeven point formula allows for effective risk assessment. Identifying the sales required to cover costs provides a safety net, helping businesses navigate economic downturns or unexpected challenges.
- Contingency Planning: Facilitates effective planning for unexpected challenges, minimizing risks.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Helps assess the impact of variable changes, enhancing risk mitigation.
- Liquidity Management: Supports managing liquidity by ensuring cash flow covers costs.
- Volatility Preparedness: Prepares businesses to navigate market volatility with resilience.
- Insurance Adequacy: Assesses and ensures adequate insurance coverage for comprehensive protection.
3. Operational Efficiency
The breakeven analysis highlights the efficiency of operations. By striving to operate below the breakeven point, businesses can optimize processes, reduce costs, and enhance productivity, contributing to long-term success and competitiveness.
- Resource Optimization: Guides businesses to allocate resources efficiently for maximum productivity.
- Process Streamlining: Identifies and streamlines processes to enhance operational efficiency.
- Benchmarking Performance: Serves as a benchmark for evaluating and improving operational performance.
- Employee Productivity: Aligns financial goals, encouraging employees to contribute to operational efficiency.
- Technology Integration: Encourages leveraging technology for enhanced efficiency through automation and analytics.
4. Investment Decision Support
Investors and stakeholders often use break even analysis to evaluate the viability of a business. A clear understanding of the break-even point provides valuable insights, helping attract investors, secure funding, and build confidence in the business’s financial sustainability.
- Risk Assessment: Investors assess risk through a clear breakeven point, supporting investment decisions.
- Valuation Enhancement: Contributes to business valuation, attracting potential investors with a favorable perception.
- Financial Forecasting: Aids in accurate forecasting, allowing investors to anticipate returns and evaluate risks.
- Capital Allocation Guidance: The break-even point is important for businesses to guide Guides strategic capital allocation for investors based on profitability prospects.
- Due Diligence Facilitation: Simplifies due diligence by providing insights into a business’s financial health for confident investment decisions.
What are the Components of Break even analysis?
The concept of Break even analysis involves the following components:
1. Fixed Costs
Total fixed costs are constant expenses that don’t vary with production levels, such as rent and salaries. Identifying and totaling fixed costs is crucial in break even analysis, serving as a baseline for determining the minimum revenue needed to cover expenses.
2. Variable Costs
Variable costs fluctuate with production or sales volume, including materials and direct labor. Calculating these costs per unit is essential in break even analysis, as they directly impact the overall cost structure and influence the break-even point.
3. Sales Revenue
Revenue represents the income generated from selling goods or services. In break even analysis, understanding the relationship between revenue and costs is vital. The break-even point occurs when revenue equals total costs, marking the threshold for profitability.
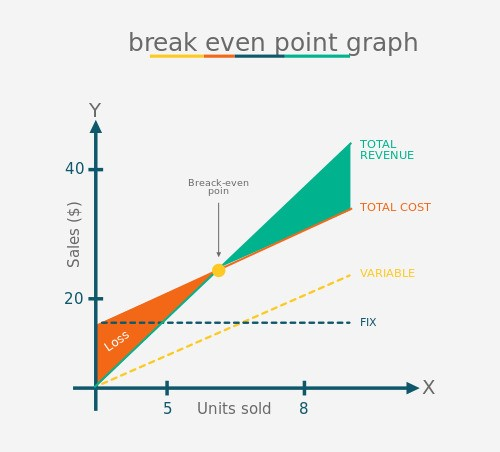
4. Break-even Point
The break-even point is the sales level where the revenue generated from the asset equals its costs, resulting in no profit & no loss. Determining this point is a fundamental aspect of breakeven analysis, guiding businesses in setting pricing strategies and making informed decisions.
5. Contribution Margin
The contribution margin is said to be the difference between the selling price and variable cost, both defined in the cost per unit. Calculating the contribution margin aids in assessing the financial health of a business.
How to Calculate the Breakeven Point?
Now that we’ve discussed everything theoretical such as the break even analysis meaning, let us find out how to calculate the break-even point.
1. Breakeven Point Formula
Breakeven Point (in units) = Total Fixed Costs / (Selling Price per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit)
Here’s a breakdown of the components in the above break even analysis formula:
- Fixed Costs: In the break even formula, these are the constant expenses that a business incurs, such as rent, salaries, and insurance. Fixed costs remain the same regardless of the level of production or sales.
- Selling Price per Unit: In the break even analysis formula, it represents the amount for which a single unit of a product or service is sold. It is the revenue generated from each unit sold.
- Variable Cost per Unit: These are the expenditures that differ with the production and sales level. The variable cost per unit includes costs like raw materials, direct labor, and other variable production expenses.
As we’ve covered in the break even analysis explanation, the formula for calculating break even analysis essentially calculates the number of units a business needs to sell to cover its fixed costs and variable costs, resulting in a break-even scenario where total revenue equals total costs. Knowing the break-even point is crucial for businesses as it helps set pricing strategies, make informed decisions, and assess the financial health of the operations.
Which Factors Influence the Breakeven Point?
As previously stated in the What is breakeven point section above, the break-even analysis can be influenced by various factors. Some of the factors that influence it are given below:
1. Variable Costs
As clear from our break even point formula, the Variable costs include raw materials and labor, which directly impact the break-even point. Higher variable costs per unit necessitate more sales to cover expenses, influencing pricing strategies and overall cost management.
2. Selling Price per Unit
The selling price per unit in the breakeven point formula significantly affects the break-even point. A lower selling price requires higher sales volume to cover fixed and variable costs, impacting revenue generation and the business’s financial viability.
3. Market Demand
Fluctuations in market demand directly influence the break-even point. High demand reduces the threshold, while decreased demand raises it. Businesses must analyze and adapt to market dynamics to maintain a sustainable break-even.
4. Operational Efficiency
Improved operational efficiency lowers variable costs per unit, positively impacting the break-even point. Streamlined operations enhance cost-effectiveness, promoting sustainable profitability and financial stability by achieving economies of scale and optimizing resource utilization.
5. Fixed Costs
As per our break even point formula, fixed costs include rent and salaries, which play a crucial role in determining the break-even point. Higher fixed costs require a greater sales volume to cover, influencing overall financial stability and the minimum sales threshold for profitability.
Popular Strategies for Improving Breakeven Point
Here are some popular strategies that businesses use for improved break-even analysis:
1. Cost Reduction Initiatives
Implementing cost reduction strategies, such as negotiating supplier contracts or optimizing operational processes, can lower both fixed and variable costs. This, in turn, improves the break-even point by requiring fewer sales to cover expenses and achieve profitability.
2. Price Optimization
Carefully analyzing market conditions and competitors allows businesses to set optimal prices. Strategic pricing above the breakeven point ensures that each sale contributes positively to covering costs, improving overall profitability, and reducing the breakeven threshold.
3. Operational Efficiency Enhancements
Focusing on operational efficiency through technology adoption and streamlined processes can lower variable costs per unit. Efficient operations contribute to achieving economies of scale, positively impacting the breakeven point by reducing the sales volume required for profitability.
4. Product Mix Adjustment
Evaluating the profitability of different products and adjusting the product mix to emphasize high-margin offerings can positively impact the breakeven point. A strategic product mix ensures that each sale contributes more towards covering fixed costs, improving overall financial performance.
5. Market Expansion
Exploring new markets or expanding product/service offerings can increase revenue streams, lowering the breakeven point. Diversification reduces reliance on a single market or product, enhancing overall financial stability and creating opportunities to achieve profitability with a broader customer base.
Real-life Challenges in Achieving Breakeven Point
1. High Fixed Costs
Elevated fixed costs create a higher breakeven point, requiring a substantial sales volume to cover these constant expenses. Managing and reducing fixed costs pose challenges, impacting the feasibility of reaching breakeven quickly.
2. Intense Competition
In competitive markets, pricing pressure may limit the ability to set profitable prices. This poses a challenge in achieving breakeven, as the business may need higher sales volumes to cover costs.
3. Variable Cost Fluctuations
Fluctuations in variable costs, such as raw materials or labor, challenge businesses in predicting and managing breakeven. Unforeseen changes can impact profit margins and increase the sales volume needed to break even.
4. Market Volatility
Economic uncertainties and market volatility can disrupt demand and pricing strategies, making it challenging to predict and achieve the breakeven point. Businesses must navigate dynamic conditions, that affect overall profitability.
5. Slow Revenue Generation
Generating revenue at a slower pace than anticipated hinders breakeven achievement. This challenge may arise due to factors like delayed market adoption, marketing inefficiencies, or unexpected external factors affecting customer acquisition and sales growth.
FAQ’s
1. Is Breakeven Point the Same as Profitability?
No, the break even meaning is a point where total revenue equals total costs, resulting in no profit or loss. In contrast to the break even definition, profitability occurs when revenue exceeds costs.
2. How Does Market Demand Affect the Breakeven Point?
Higher market demand positively impacts the breakeven point formula by spreading fixed costs over a larger sales volume, making it easier to cover costs and achieve profitability.
3. What Role Do Fixed Costs Play in Determining the Breakeven Point?
As understood by the break even analysis meaning, fixed costs set the minimum sales volume required to cover all expenses at the breakeven point. Lower fixed costs contribute to a lower breakeven threshold, enhancing financial feasibility.