Summary: Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) refers to the management of processes and data used in the engineering, design, manufacturing, service, and sales of products throughout its entire lifecycle and supply chain. It has played a pivotal role in the manufacturing sector, but PLM is quickly gaining attention in the software solution market.

Why is PLM essential for companies?
Manufacturing companies face myriad challenges apart from designing and engineering products. PLM provides viable solutions to those challenges by distributing resources and making business-critical information freely accessible to all relevant stakeholders.
PLM was originally designed to enable engineers to securely share information and collaborate on the latest product designs across a product’s lifecycle. But earlier, companies usually used On-premise systems that focused solely on the company’s internal employees. Today, PLM solutions cover a more significant portion of the organization — marketing, supply chain partners, customer service, and sales executives.
Legacy PLM systems were built to help engineers enhance productivity, reduce time to market, and decrease final product costs. On the other hand, today’s PLM solutions are primarily made for:
- Enhancing quality of complicated products
- Quick and efficient response to customer queries
- Launching products in the market at a fast pace
- Improving revenues
What is cloud-based PLM?
Cloud-based PLM systems provide a single source of truth that allows relevant stakeholders to access, share, and track crucial processes and information at a moment’s notice. Moreover, it also allows different departments to update product changes in real-time and keep a tab on any new revisions in industry compliance norms and regulations.
Employees require a more collaborative work environment in today’s business landscape. PLM systems have adjusted to this need by offering multi-layered communication and process management solutions that enable employees and third-party vendors to collaborate efficiently from anywhere in the world.
Why do you need a PLM system?
PLM organizes and integrates data across various touchpoints, providing a 360-degree view of each manufactured product and forecasting their market performance. This feature helps enhance profitability and maximize efficiency in the following areas:
- Product rollouts across the globe: PLM enables global rollout of products by providing various services such as process governance, document management, and instantly sharing reliable data with multiple stakeholders. Collaborative workflows ensure business activities run smoothly and that teams respond to challenges at an accelerated pace.
- Destroys information silos: Traditional companies have information silos that restrict critical business data flow from one department to another. PLM systems provide a single source of truth that allows relevant stakeholders to create, use, and retrieve crucial information from anywhere and at any time.
- Integrating design and manufacturing processes: The two most important departments of a typical manufacturing company are design and manufacturing. PLM solutions enable them to optimize production processes in real-time by integrating disparate information systems and forming a standard communication bridge between all stakeholders.
- A standard system for all: PLM solutions have a central Product Data Management (PDM) repository that provides a common platform to all subsidiaries, employees, third-party vendors, and other stakeholders.
The Product Lifecycle Management Process
Conceptualization & ideation is the first stage of the PLM process. The following stages include designing, manufacturing, and supplying the product to the final customer. But other non-core activities such as service, purchase, repair, and disposal also play an essential role in enhancing the company’s reputation.
There are primarily four stages in a product’s lifecycle:
- Introduction: New products require a massive investment of resources during the R&D stages. Companies often lack concrete data regarding consumer reaction, market performance, and sales of a new product, making them risky.
- Growth: After the successful launch of a new product, it receives popularity, and the sales start growing. At this stage, marketing activities help maximize profits.
- Maturity and plateauing: Marketing professionals brainstorm better marketing strategies when they receive concrete data about the new product. Moreover, the product design team also tweaks the production process accordingly.
- Decline/Replacement: The product popularity gradually declines with increased market competitiveness or due to non-returning customers. At this stage, companies either introduce the product in less popular markets or gradually decrease the production rate.
PLM is essentially the collaboration, alignment, and management of resources, employees, third-party vendors, business systems, data, and processes that help make the entire product portfolio a success.
Now, let’s dive deep into the lifecycle stages one by one.
1. Design
PLM allows manufacturing companies to control, monitor, and run multiple processes together, including design, simulation, engineering, marketing, and manufacturing. As a result, you can also make changes in the product during the design and engineering phase that significantly reduces the time taken to complete a final product. This feature helps to quicken time-to-market and eventually enhances the overall profit.
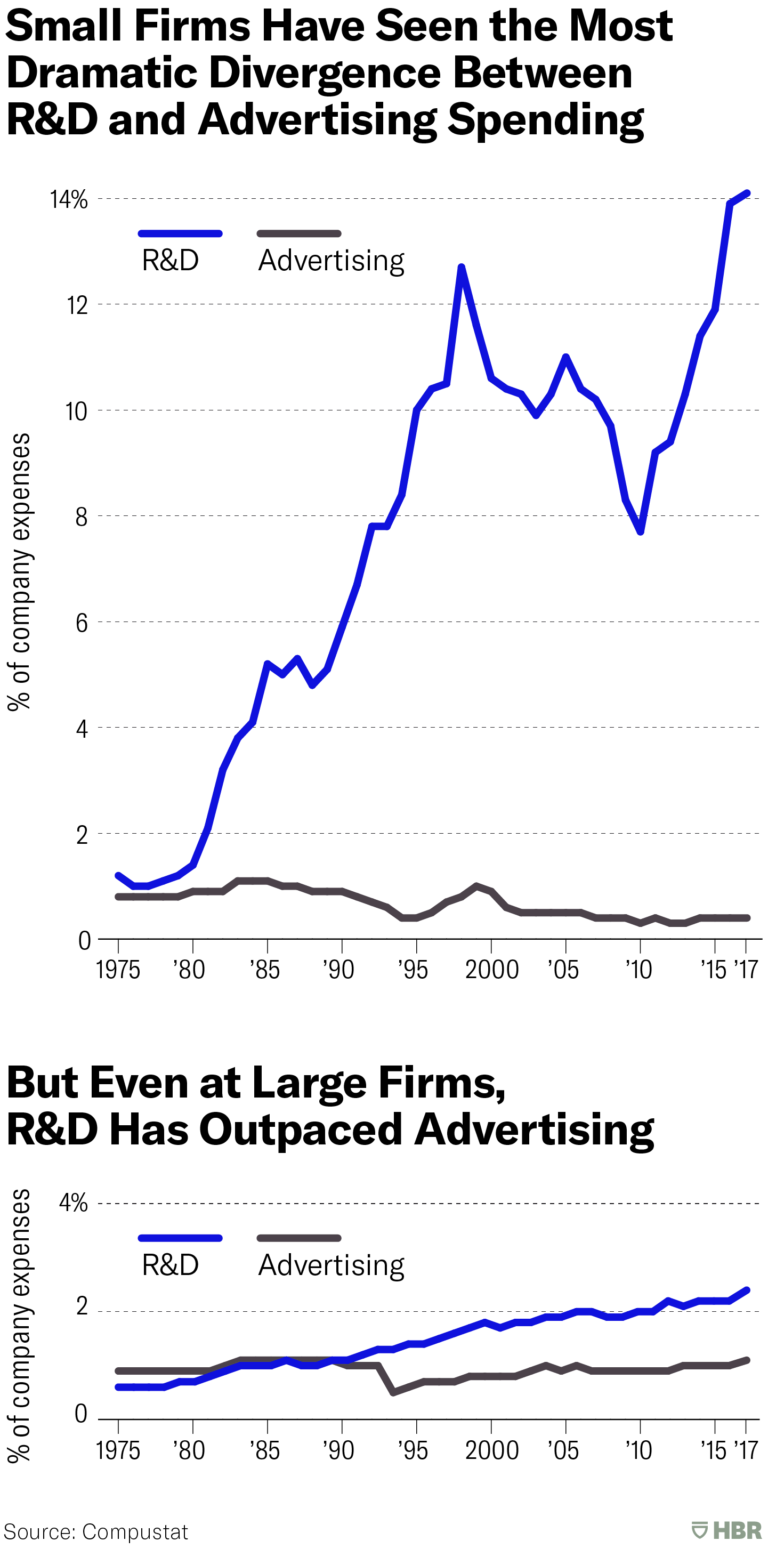
Do you know that the manufacturing industry has changed its business model?
Research shows that the manufacturing industry spends 5% of its total expenses on R&D. The following two graphs show a dramatic divergence between R&D and advertising spending since the 1970s’.
The best part about PLM software is that it allows companies to deliver high-tech innovation, track customer feedback, and provide solutions to customer queries in real-time.
2. BOM management
Managing Bill of Materials (BOM) is undoubtedly an essential function of PLM. It integrates BOMs with the following important data points:
- Manufacturing data
- Source information
- Product definitions
- Pricing
- Documentation
BOM management is a collective process that involves sourcing and procurement, engineering design, go-to-market strategy, and design collaboration. Moreover, companies need to ensure that BOM management includes fruitful partnerships with third-party vendors, such as suppliers, partners, and sales channels. Change management is also an essential feature of BOM management. It helps different departments — manufacturing, engineering, and marketing — collaborate and exchange real-time updates for the product to become sales-ready.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) systems allow synchronization between engineers and the non-technical staff during the product designing stage. Companies attain enhanced accuracy, better collaboration, and faster time-to-market when CAD systems exchange information through PLM software.
3. Distribution and Service
Companies need an efficient way to ensure that their sales channels receive and display the correct product information that eventually helps market and sell their products. Product Information Management (PIM) plays an essential role over here. It allows companies to share critical product data with various sales channels, including direct sales, e-Commerce, and distributors. The best part is that modern PLM systems have an in-built PLM module that provides a single data repository accessible by engineering, manufacturing, sales, and marketing departments. Let’s understand this with the help of a few examples.
The PIM module allows the sales team to collect product information from the engineering department and extract data — pricing, product attributes, and SKUs — that helps sell the product.
Similarly, the marketing department can gather real-time information throughout the product lifecycle that helps create marketing collaterals, such as statistics, infographics, ebooks, guidebooks, whitepapers, case studies, solution briefs, and product manuals that help market products on e-Commerce and distributor portals.
Customer satisfaction plays an essential role once the product is available for sale. It helps understand what customers feel about the product and create new product versions that are better than the initial prototypes.
4. Production
The two most crucial outcomes of implementing PLM systems are decreasing time-to-market and reducing product development costs. And these are achieved by cost management, change management, and supplier qualifications.
Change management deals with the systems and processes that enable a company to keep track of different product versions, perform cancellations and revisions, and stick to a workflow pattern.
Similarly, cost management allows companies to monitor and control the cost of components and tools used while developing the finished product. Modern PLM software provides cost transparency, allowing manufacturers to solve cost- and delivery-related challenges and eliminate product launch problems.
>>>Also Read: Top 6 Ways Furniture Manufacturing Industry Can Boost Productivity Using ERP Software With Enhanced Integration<<<
How Sage X3 is the best Production Lifecycle Management (PLM) software in the market?
Sage X3 is the best ERP software for production management. It enables planning, controlling, and scheduling quality control, thereby helping you get your products to the market quickly and efficiently.
The following features explain in greater detail how Sage X3 is the most preferred PLM software in the market.
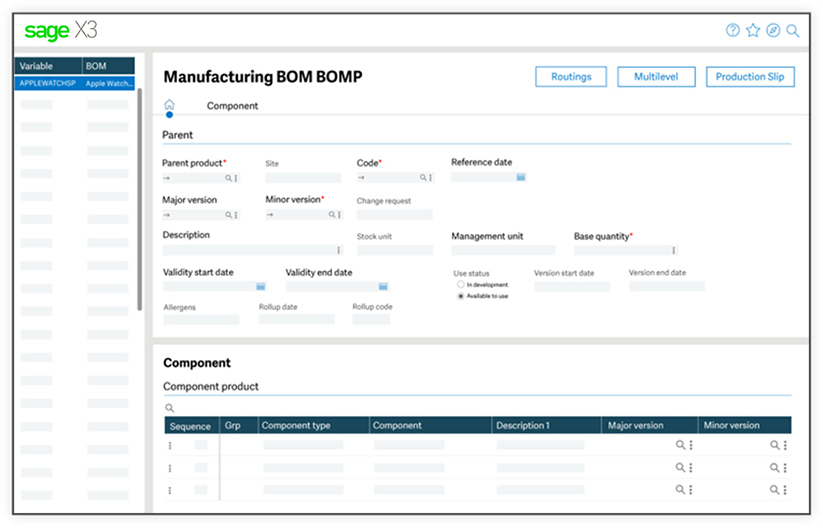
1. BOM Planning
Sage X3 ensures the highest levels of product quality, consistency, and collaboration by delivering a world-class single and multi-level Bill of Materials (BOM).
- Current bills of material
- Multi-bill of materials — production, commercial, sub-contracting, and much more.
- Version number management — minor and major versions
- Mass maintenance
- Bill of materials and product change management
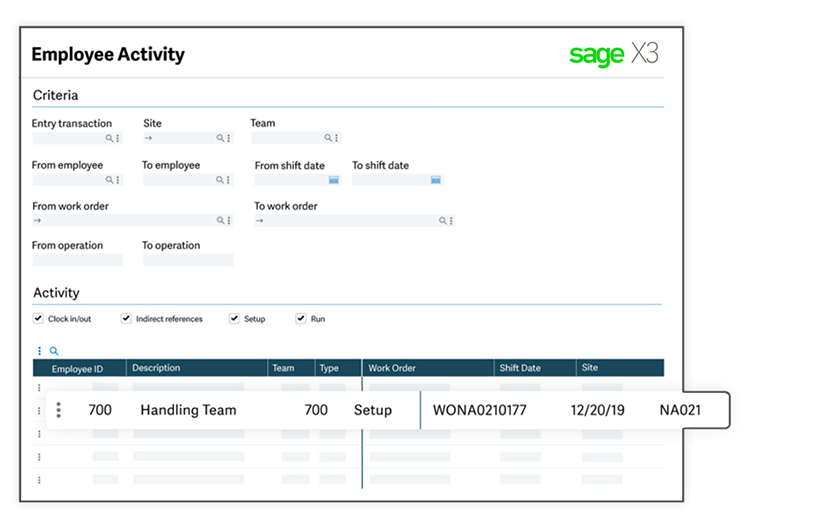
2. Shop floor control
Sage X3 excels in tracking, prioritizing, and managing each aspect of your production — scheduling, planning, and costing.
- Synchronized and unsynchronized multi-tasking
- Indirect time entry
- Collection of labor time
- Actual and elapsed time
- Team entry
- Shop floor tracking workbench
- Break time entry (clock in/out)
- Automatic breaks
- Indirect labor (breaks and indirect time)
- Direct labor (breaks and indirect time)
- Time and attendance (clock in/out)
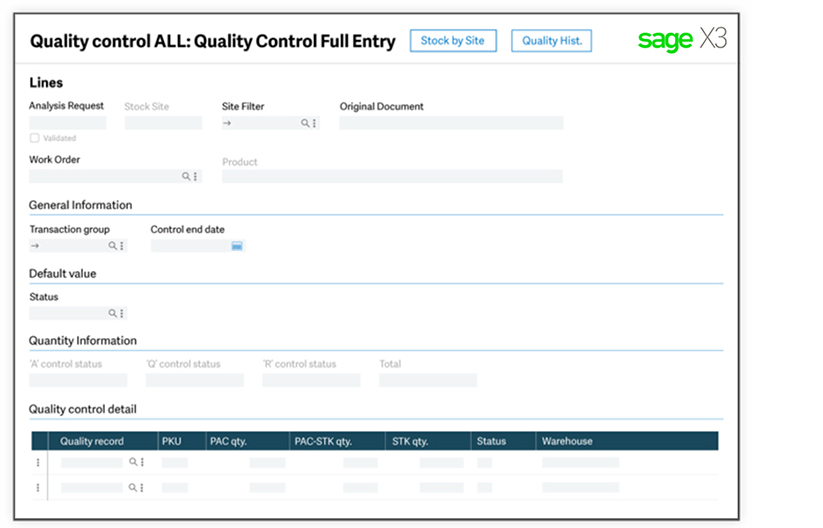
3. Quality Control
Sage X3 has all the tools and workflow capabilities that ensure top-notch quality standards by monitoring and performing complete product traceability.
- Re-inspection date management
- Batch and sub-batch number management
- Use-by date management
- Quality control record creation
- Expiry date management
- Upstream and downstream traceability management
- Stock status management — accepted, inspected, rejected
- Serial number management
- Quality control procedures with analysis request
- Stock sub-status management
>>>Also Read: Efficient Quality Management in Sage X3<<<
4. Project Management
- A multi-level description of the tasks, preparing the operational and manufacturing process
- Advanced project duplication function
- Time entries to enter the time consumed by a project at the task, operation, and budget level
- Employee assignments to various operations
- Financial follow-up function to track the budget and expenses of projects
- Project cost breakdown structure (CBS)
- Project work and product breakdown structures (PBS and WBS)
- A multi-level description of budgets, facilitating project cost follow-up
>>>Also Read: Project Management in Sage X3<<<
STAY UPDATED
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
At Sage Software Solutions (P) Ltd., we are home to world-class ERP software and CRM software that will solidify your business tech support fundamentals and enable you to build a customer-centric organization. You can also write to us at sales@sagesoftware.co.in.
Disclaimer: All the information, views, and opinions expressed in this blog are those of the authors and their respective web sources and in no way reflect the principles, views, or objectives of Sage Software Solutions (P) Ltd.