What is the Reorder Point (ROP)?
A Reorder Point (ROP) is the minimum threshold of stock at which the business initiates the inventory replenishment process to avoid running out of stock and ensure smooth & timely customer order fulfillment.
ERP Software offers superior inventory management capabilities to ensure you don’t face discrepancies in inventory management, and your customers will have a positive experience.
What is the Reorder Point Formula?
The Reorder Point Formula is pretty much straightforward.
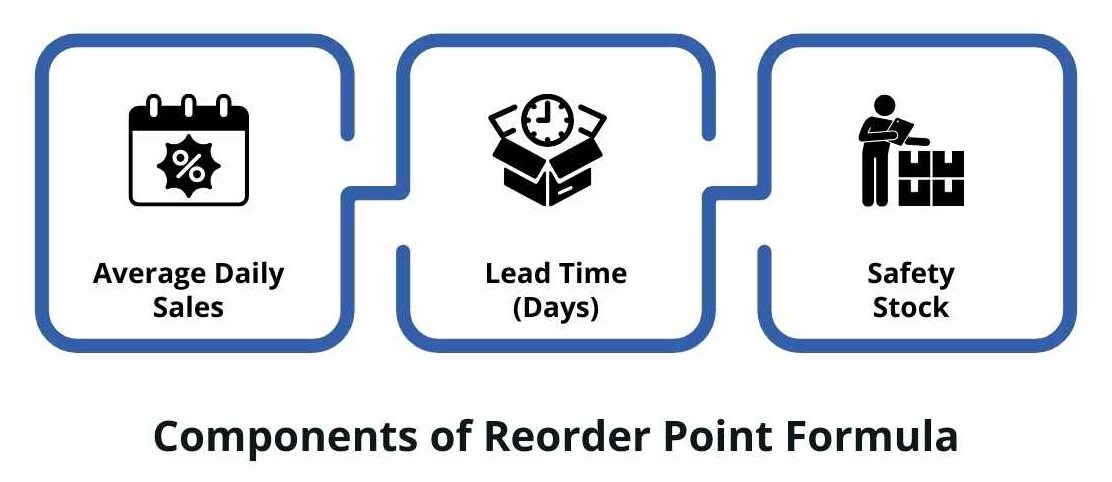
Reorder Point = (Average Daily Sales × Lead Time in Days) + Safety Stock
Components of Formula for Reorder Quantity
Now, let us discuss each of the important components:
1. Average Daily Sales
Average Daily Sales denotes the average number of products sold each day during a specific period (such as a month). It’s easy to calculate the Average Daily Sales. For example, ABC Ltd is a manufacturer of computer peripherals. During 2023-24, it sold 7,00,000 quantities of peripheral devices. The Average Daily Sales will be 7,00,000 / 365, i.e. 1917 average number of sales per day.
Average Daily Sales Formula:
Average Daily Sales = Total Sales During a Specific Timeframe / Number of Days
2. Lead Time (Days)
Lead Time is the amount of time in days it takes to deliver a customer’s order after its order placement. The shorter the lead time, the better it is. Many food businesses nowadays use an ERP for Food Industry to benefit from shorter lead time, i.e. higher efficiency in different aspects of the supply chain including pre-processing, processing, and post-processing. In contrast, a longer lead time will result in poor customer experience.
3. Safety Stock
Let’s say, you’re a manufacturing company. A Manufacturing ERP will provide you with a variety of measures to prevent stock-outs and ensure on-time order fulfillment. One such measure is the additional stock of items reserved to be used in the event the regular stock is exhausted. The amount of Safety Stock may differ from industry to industry and business to business. Business Intelligence Tools are commonly used to tackle the challenge of manually analyzing market trends & patterns, and historical demand for products.
Example of Formula for Reorder Quantity
A chemical manufacturer sells 10 tons of chemicals on a daily basis. It takes about a week to deliver each batch of the chemical. The manufacturer keeps an excess stock for 10 days.
In order to calculate the Reorder Point, let’s first find out the Safety Stock for 10 days.
Safety Stock = 10 tons * 10 days = 100 tons
Now, let’s calculate the Reorder Point.
Reorder Point = (10 tons × 7 days) + 100 tons = 170 tons
The chemical manufacturer should configure his ERP for Chemical Industry to place new orders every time the stock dips below 170 tons.
Which Factors Affect the Reorder Point?
Now, let’s discuss which factors affect your Reorder Point.
1. Demand Patterns
Sudden spikes or drops in demands can require adjustments to your Reorder Point. For example, a sudden spike in demand may require reserving a larger stock of inventory.
2. Supplier Efficiency
Does your supplier fulfill raw materials in a timely manner? If not, longer delays in the procurement of raw materials may increase the need for additional Safety Stock, and vice versa.
3. Stockout Costs
Stockout Costs are direct and indirect consequences of running out of inventory. Stockout costs can have negative consequences on your company’s profit margins. The intensity of the Stockout Costs significantly affects your Reorder Point.
4. Production Efficiency
Production Efficiency measures how well your company manages to produce goods. The unavailability of sufficient storage, skilled labor, and finances can impact the Stockout Costs.
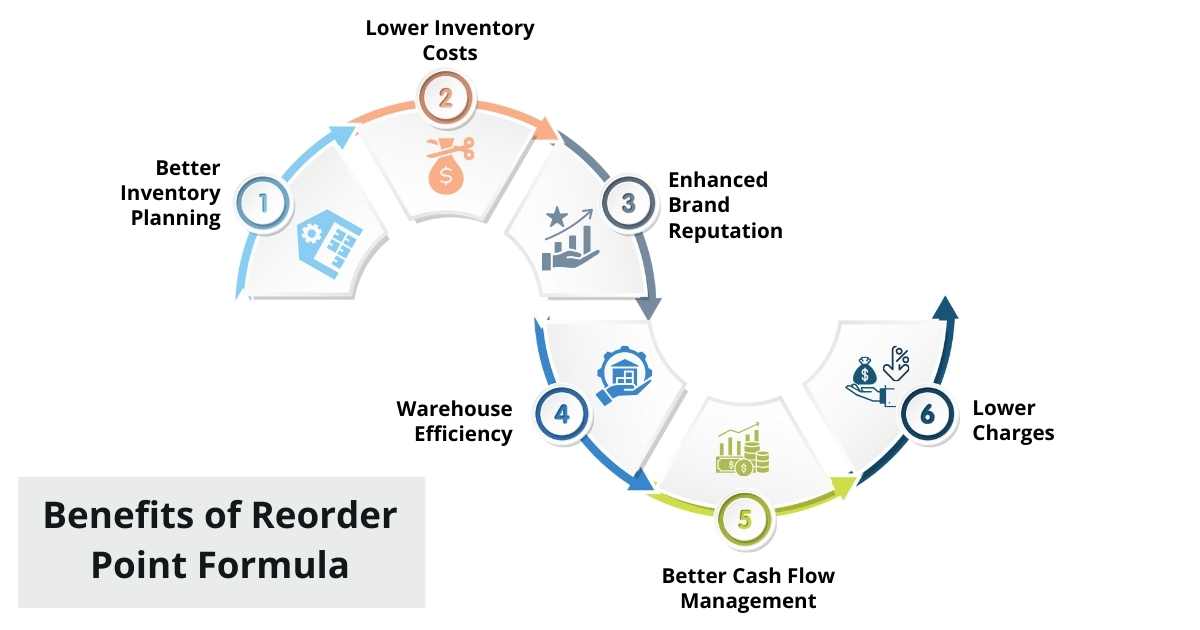
Benefits of Calculating Reorder Point Formula
First things first, why calculate the Reorder Point? The formula for Reorder Quantity helps businesses in numerous ways from better inventory management, accurate Demand Forecasting, and higher operational efficiency to better financial management.
1. Better Inventory Planning
The formula provides you with a realistic view of the current inventory levels and the amount of inventory you will need to fulfill demand spikes. Use an Inventory Management System to gain an accurate understanding and make better decisions pertaining to inventory planning and forecasting.
2. Lower Inventory Costs
Surplus inventory can lead to higher inventory storage costs. In contrast, the lack of enough inventory can force you to replenish it at higher-than-normal rates. Let’s take a simple example: Pharma ERP Software helps maintain an optimum reorder point for pharmaceutical products so that you gain a higher financial flexibility and lower inventory costs.
3. Enhanced Brand Reputation
Minimal or no stockouts directly translate into better customer experience. By regularly maintaining adequate stock of inventory with a Cloud ERP, you will be able to retain the trust & confidence of your customers and avoid forcing them to switch to your competitors.
4. Warehouse Efficiency
Avoid misplacement of warehouse items, store more items in limited storage, bring efficiency into items sorting & picking, and optimize the shipment process. A Warehouse Management System also helps prioritize warehouse items based on their value and turnover time.
5. Better Cash Flow Management
Managing your inventory efficiently results in better cash flow. Excess stock of inventory ties up your business capital unnecessarily and leads to cash crunch issues. In contrast, the optimum level of inventory strengthens your company’s Cash Flow Statement.
6. Lower Charges
Carry the replenishment at the right time and prevent rush orders of inventory. With an inventory reordering system in place, you can avoid the subsequent rush hour delivery fees.
Limitations of Formula for Reorder Quantity
The Inventory Reorder Point formula serves an important role in tackling various inventory-specific challenges. However, it has certain limitations too.
1. Manufacturing Complexities
Reorder Points can be ineffective for some large ERP for chemical manufacturing companies with complex operations and a diverse range of products requiring parallel production lines.
2. Demand Fluctuations
The demand for some products may be stable while that for other products may fluctuate a lot. Reorder Points are often ineffective for the latter types of products.
3. Reliance on Historical Data
Reorder Point heavily relies on historical data. As markets are dynamic, over-reliance on historical data may lead to inaccuracies and terrible financial losses.
4. Overlook Production Facility’s Capacity
Reorder Points overlook one of the important factors, i.e. capacity of your production facility.
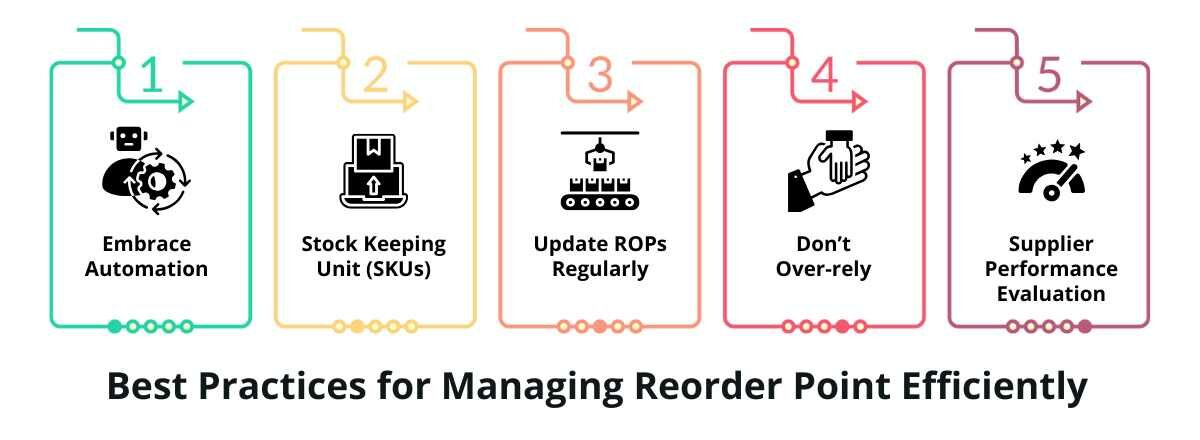
Best Practices for Managing Reorder Points Efficiently
Let’s discuss some of the best practices for effectively managing your Reorder Points.
1. Embrace Automation
Implementing robust automation strategies will help you not only gain efficiency in the entire procedure but also reduce the potential for errors & discrepancies. ERP implementation will help you standardize & centralize the procedure and ensure regulatory compliance.
2. Stock Keeping Units (SKUs)
Make use of the Stock Keeping Unit. SKUs are alphanumeric codes that act as unique identifiers and facilitate easy identification and locating of your inventory, optimizing inventory levels, monitoring product supplies, identifying market trends, and formulating effective business strategies.
3. Update ROPs Regularly
A strategy that worked years ago may not necessarily work in today’s business landscape. Try not to use the same formula for Reorder Quantity for a longer time. Perform an A&B testing strategy to regularly update your ROPs on changing times, circumstances, and business needs. Also, different inventory methods such as the FIFO Method and LIFO method should be considered.
4. Don’t Over-rely
Avoid over-relying on the formula for Reorder Quantity. While the formula may be useful, it’s not the one and only focus of inventory management. Over-reliance on the Inventory Reorder Point formula can lead to various problems from rigidity to misinformed decision-making.
5. Supplier Performance Evaluation
Last but not least, evaluate the responsiveness and quality of your supplier using robust Supply Chain Management Tools. It’s important to choose a supplier who delivers fast and on-time delivery of materials. You can also make agreements with multiple suppliers to minimize the impact of shortages and supply chain disruptions.
Summing Up…
Reorder Point Formula is an important formula that assists businesses with informed decision-making, managing their inventory, and cutting down on costs. It’s not a “set it and forget it” thing. It’s crucial to update it from time-to-time as the demand for your products fluctuates and the market conditions change.
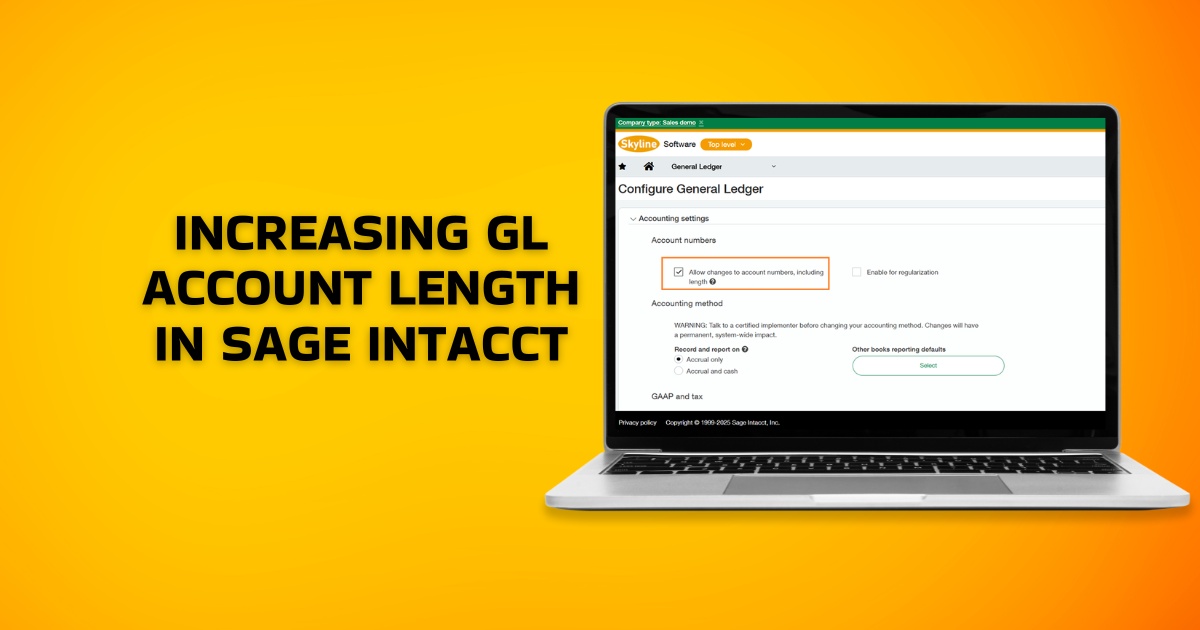
Sage X3 is a multi-language, multi-currency, and multi-site ERP that comes with built-in data analysis, reporting, and visualization capabilities. It offers a wide range of modules that empower your business with smart planning, inventory management, budgeting, and advanced production scheduling functionalities.
FAQs
1. What is an Ideal Reorder Point?
There is no one-size-fits-all ideal Reorder Point that works for every business regardless of its size and type. Each business is unique, and so are its requirements. It’s a good idea to test your Reorder Point from time-to-time so that you will never have to dip into your safety stock or deal with excess stock that ends up with increased storage costs & wastage of perishable goods.
2. What is the Purpose of Reorder Point Formula?
The purpose of calculating the formula for Reorder Quantity is to set a minimal stock level and avoid the potential risk of running out of inventory. Whenever your stock level reaches below this threshold, your Business Management Software will automatically give a replenishment order to ensure you have sufficient stock to fulfill your customer’s expectations.
3. How Do You Calculate the Reorder Point?
The Reorder Point is calculated using the Reorder Point formula. The formula takes different factors into consideration such as the Average Daily Sales, Lead Time, and Safety Stock. It is vital to bring efficiency into the inventory operations, maintain ideal inventory levels, and avoid over/ under-stocking situations.
4. Are Reorder Point and Safety Stock the Same Thing?
No, the Reorder Point and Safety Stock are not the same thing. Safety Stock acts as an emergency stock that a business uses whenever it runs out of the normal stock of inventory. In contrast, a Reorder Point is the minimum inventory threshold level. Whenever your inventory level falls below this level, a replenishment order is generated. Both Safety Stock and Reorder Point are important tools available in the Best ERP Software in India to avoid running out-of-stock or excess inventory problems.
5. Which Tools Are Used for Calculating Reorder Points?
Reorder Point is an important aspect of inventory management. It can be calculated using different tools:
- Manual Method: Here, the company uses the Reorder Point formula to manually calculate it without using any tools.
- Excel Spreadsheets: The company may also use a variety of software such as Microsoft Office Excel, LibreOffice Calc, or Google Sheets.
- Legacy Tools: Dedicated legacy tools also automate the calculation of Reorder Point, and eliminate the need for manual intervention.
- ERP Tools: A comprehensive ERP Application provides deeper functionality than a legacy tool. It automates & consolidates your business operations & improves agility.
6. Is Reorder Point a Must for Every SKU?
It’s recommended to set a Reorder Point for every item in your Stock Keeping Unit (SKU). The exact point may vary from product to product depending on several factors such as the historical demand & salability of each item. The scalability is an important factor that lets you know whether a stock is under-performing or over-performing.