What is Production Management?
Production management is a process of organizing and planning the manufacturing activities in a factory to transform input resources like raw material, machinery and manpower into finished goods in a controlled manner and maintaining the quality levels set by the organization.
Simply put, the production department supervises smooth shop floor operations to produce the right quantity of goods efficiently and cost-effectively. Production management is responsible for running and scheduling production lines and ensuring effective utilization of resources and production capacity.
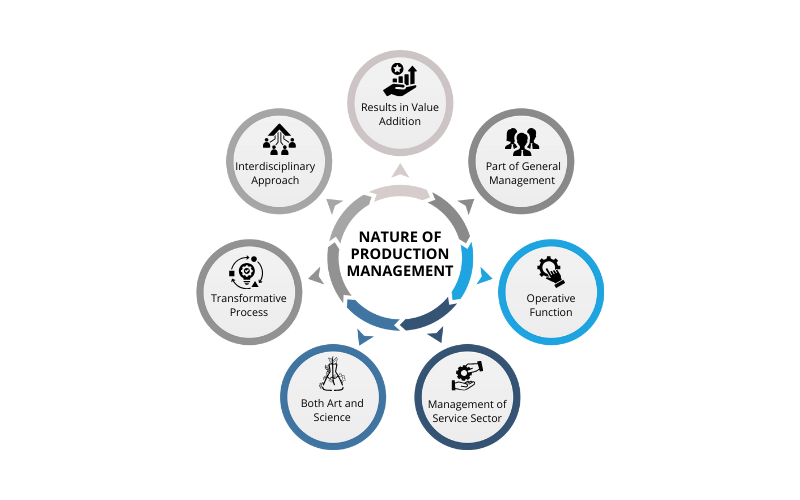
Understanding the Nature of Production Management
The production management encompasses several parameters that help to understand its essence. Here are the defining parameters of its nature:
1. Results in Value Addition
The production activities add incremental value to raw material at every stage of production. The resulting value added in terms of price and benefits is nothing short of production excellence.
2. Interdisciplinary Approach
At its core, production management may seem to be just concerned with manufacturing. On the contrary, it spans multiple disciplines, including statistics, science, mathematics, and economics.
3. Part of General Management
Production management is not an isolated activity. General administrative functions like planning, organizing and scheduling operations and services fall well within the ambit of production management.
4. Transformative Process
Production leads to the transformation of raw materials into finished goods through processes like cutting, drilling, and punching that may change the shape, size, and property of raw materials.
5. Operative Function
Sustaining and managing the routine operations of the business like people management, machinery maintenance, inventory, procurement and warehouse operations with a long-term focus using ERP solution is an essential part of production management.
6. Both Art and Science
Understanding customer sentiments, handling the workforce and taking all stakeholders along the production journey is an art that needs mastery. Meeting the technical specifications of the product and driving innovation make it a scientific field.
7. Management of Service Sector
Production operations are incomplete without service components. Equipment installation and maintenance, employee training, and customer service are central to production management.
What is the Importance of Production Management?
The manufacturing sector has witnessed rapid growth in recent years with India fast becoming a global production hub. According to Statista, the manufacturing industry grew at 4.7% in the financial year 2023 due to strong consumer demand. Production management is the core function of a manufacturing company, surrounding which all other operations are aligned. Ensuring its success using advanced tools like ERP software is pivotal to the company’s growth for various reasons.
1. Resource Utilization
Resources are always limited. The real skill of the production department is showcased through building efficiencies in raw material consumption, labor distribution, and optimizing outputs at every work center.
2. Quality Assurance
Quality is a hallmark of most manufacturing corporations. Many take years of perfection to excel at their processes and refine products to get top-notch results.
3. Market Changes
Clients always demand improvements in products. If you don’t evolve and keep up with the changing trends, someone else will take your place. Responding quickly to market changes is key here.
4. Operational Safety
Eliminating occupational hazards during production and maintaining product use safety is the foremost concern for manufacturers to prevent accidents and adhere to government regulations.
5. Unique Selling Proposition
At the heart of market leadership is constant product innovation through rigorous R&D and testing. This is only possible with a robust design team backing the production department.
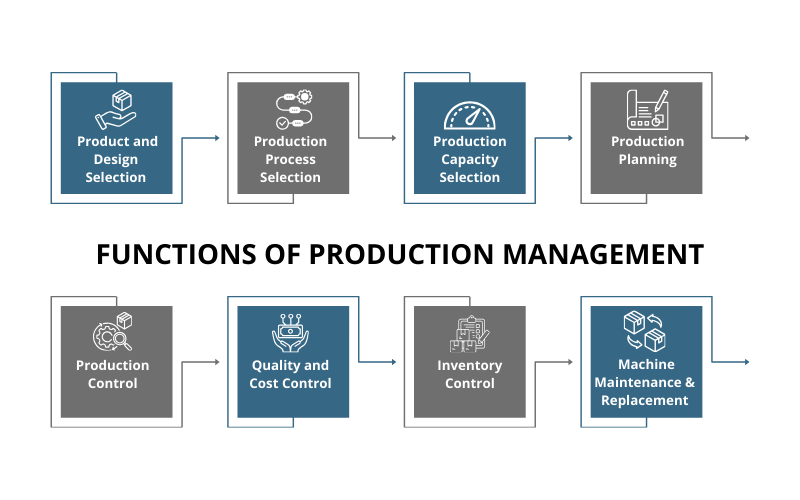
What are the Functions of Production Management?
Production management is the process that involves a range of functions to fulfil an organization’s production and business objectives. They are as follows:
1. Product and Design Selection
Your product design could be excellent. But does it fit in with customer requirements? Can you adapt and make changes to accommodate specific customer needs? Selecting the right product with the right design is important to ensure design feasibility and durability in the long run.
2. Production Process Selection
Selecting a production process depends on various factors like quality needs, customer requirements, time, funds and skills available and output levels desired. For example, a manufacturer may need to choose between hot forging and cold forging depending on the material strength desired.
3. Production Capacity Selection
Planning production capacity is a capital-intensive task, involving machinery and space requirements. It obviously cannot happen overnight. One must have long-term capacity plans according to market demands and trends.
4. Production Planning
Production planning includes all activities that enable the organization to fulfil customer orders on time and cost-effectively. Developing daily, weekly and monthly production plans using business management software ensures that resource allocation of labor and material is effectively accomplished.
5. Production Control
Another crucial function of production management is to monitor all pre-production and production tasks for the effective utilization of raw materials. Material acquisition, material handling, storage and distribution to managing the workflows – all form a part of production control.
6. Quality and Cost Control
A minor negligence can lead to tremendous cost overruns for a company. That’s why, keeping the cost of production low is always the primary focus during production management. Be it procurement, inventory or material consumption per machine cycle, low costs multiply the profits.
7. Inventory Control
Inventory control is the process of managing a company’s stock levels of raw materials and finished goods. An accurate assessment of inventory in the warehouse with inventory management software ensures that the company’s production is aligned with forecasted demand.
8. Machine Maintenance and Replacement
The machines are always expected to yield maximum output. It is only possible if a company undertakes routine check and maintenance of machines without waiting for expensive breakdowns to occur. Collecting data on parts usage helps with timely part replacement, reducing the chances of downtime.
You Might Also Like : What is Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul (MRO)?
What are the Benefits of Production Management?
In order to effectively manage production, a company must engage the necessary resources and talent at its disposal. Here are some benefits offered by streamlining the production processes.
1. Cost Reduction
A well-managed production process will ensure that all production activities are synchronized with each other. Ordering raw material on time, utilizing raw materials to prevent inventory build-up and improving machine productivity lead to low per-unit cost and high profitability for the organization.
2. Customer Satisfaction
Delivery of products and services on time and in the best quality takes effort and a lot of hard work. With a suitable ERP system, production managers can track order updates and inventory to keep customers happy and loyal to the company.
3. Shorter Lead Time
Customers may ask for design improvements or new product development. Getting the products faster to market is only possible when you follow efficient management practices to maximize the output levels.
4. Improve Supplier Relationship
Suppliers look for clients who make payments on time and give regular orders. With production process optimization, you can maintain healthy working capital and order inventory on time from trusted suppliers.
5. Employee Productivity
Every employee likes to work for an efficient and forward-looking organization that grows and improves with time. Good production management increases employee productivity and boosts their morale, improving employee retention.
What is the Scope of Production Management?
Production management is vast in scope with widespread implications for the organization. Diving into every aspect with a razor focus determines the overall success of the production strategy. Here are the key aspects to consider in production management.
1. Location of Facilities
Why would you decide to set up a new plant at a particular location? Factors like the availability of raw materials, logistics, labor availability, ancillary industry and services, and customers are decisive factors.
2. Plant Layout and Material Planning
Effective utilization of plant space can only happen by planning a step-by-step flowchart of production processes to optimize material flow & minimize slack time. Ordering the right quantity of materials that can be delivered just in time to maintain production continuity helps optimize operations.
Also Read : What is Material Management?
3. Production Management
Determining machinery and labor requirements is an essential part of production management. Besides, controlling variance in products through process improvements and statistical control tools like gauges and calipers ensures product uniformity and quality control.
4. Planning and Controlling Production
As soon as the customer order is punched in in the manufacturing ERP software, the production manager has to plan and adjust production lines to meet new and existing customer orders. Preventing overproduction and minimizing the risk of underproduction are ongoing tasks for the department.
5. Maintenance Administration
Maintenance of machines, tools, shop floor and utilities – all contribute to efficient production operations. The administration has to manage it on a priority to minimize upkeep costs and repairs.
6. Process Design
A manufacturer may have multiple ways at his disposal to develop a product. Designing a process which is efficient, cost-effective and delivers quality products is necessary for ensuring long-term success.
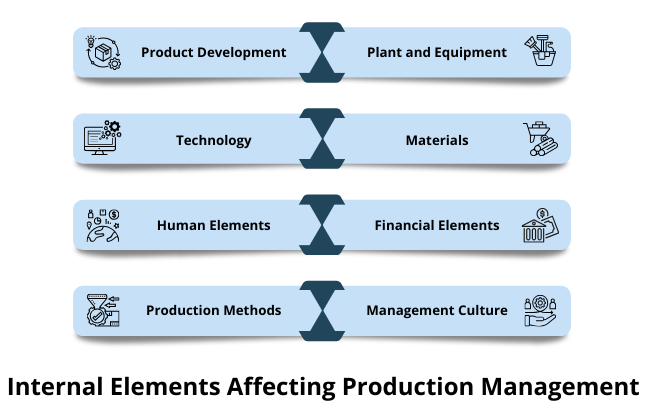
Key Elements Affecting Production Management
A number of internal and external elements affect production management. An organization does have significant control over internal elements, however, external elements are largely out of control and one needs to be quick at adjusting to the changes.
Internal Elements Affecting Production Management
a. Product Development
Product design and development are completely dependent on the internal capabilities of the organization. A robust design team develops a sturdy product that meets business goals and customer needs.
b. Plant and Equipment
What is the production capacity of the plant? What is the scope of expansion? It also matters if the machinery used for production is up-to-date.
c. Technology
New production methods are more efficient and precise. For example, using computer-integrated machinery or robotic process automation can generate unparalleled success for a business.
d. Materials
Securing the best quality of raw materials and maintaining a steady supply is crucial for high-quality production.
e. Human Elements
A skilled and experienced workforce constantly works towards process improvement and increasing output levels. They are also adept at resolving production issues.
f. Financial Elements
A strong balance sheet is reflective of healthy operations management. It offers strategic advantages for investment in new technology and capacity expansion.
g. Production Methods
There can be 10 different ways to achieve the same task. Adopting production methods that eliminate waste and improve quality can make a significant difference to the organization.
h. Management Culture
Management is responsible for the overall success of the production. If the management is only bothered about profits and not interested in knowing how the production is fairing, there is a serious issue about that.
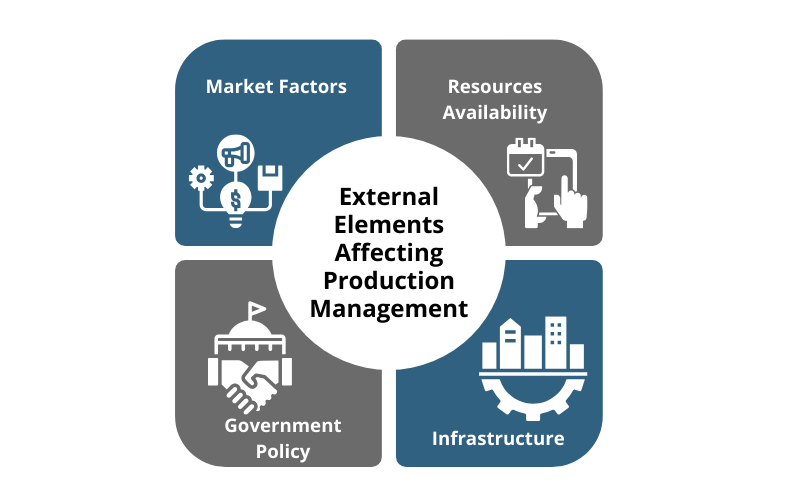
External Elements Affecting Production Management
a. Market Factors
Most businesses operate in a dynamic landscape. There can be sudden shifts in customer preferences and adoption of new technology among key players, which can make existing set-up unworthy.
b. Resources Availability
If key suppliers in the area shift base, it can put your entire business at stake due to a lack of raw materials. Finding alternatives may not be easy, hampering your production.
c. Government Policy
The government may announce changes in emission norms and impose tariffs to support domestic producers, or it may offer incentives like Production Linked Incentive (PLI) to put up plants with full value addition in India. Keeping track of policies and responding quickly is important.
d. Infrastructure
Surrounding infrastructure is crucial for an industry to function seamlessly. Availability of ancillary industry, repair and maintenance services, good roads and continuous water and power supply are crucial elements to support production.
What are the 5 M’s of Production Management?
The five M’s of manpower, machinery, methods, materials and money form the core resources to support manufacturing operations.
People drive the wheels of production. Hiring an efficient and skilled workforce to operate the machines, with production supervisors and managers at the helm forms the basis for successful manufacturing operations. Upgrading and maintaining machinery with timely predictive and preventive maintenance prevents unforeseen breakdowns. Employing efficient production techniques that minimize wasteful processes and reduce time to market is another vital differentiating characteristic. Sourcing raw materials that precisely meet customer requirements and quality guidelines promotes a culture of customer satisfaction. Ultimately, one needs ‘money’ to fund and organize everything, which is earned through profitable business managed through advanced tools like financial management software.
Difference Between Production Management and Operations Management
| Production Management | Operations Management | |
| Characteristic | Focuses on the process of transforming raw materials into finished goods | Focuses on the processes involved in both production and service delivery |
| Scope | Primarily deals with manufacturing processes | Includes both manufacturing and service processes |
| Goal | Efficiency in production processes, minimizing cost, and maximizing output | Achieving operational efficiency, customer satisfaction and resource utilization |
| Key functions | Involves planning, organizing, directing, and controlling production activities | Includes product/service design, process selection, inventory management and continuous improvement |
| Key Performance Indicators | Productivity, cost per unit, defect rates and production cycle time | Efficiency, service quality, customer satisfaction and delivery time |
| Techniques | Lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, Total Quality Management (TQM) | Lean operations, Six Sigma, Just-In-Time (JIT) and Business Process Reengineering (BPR) |
What is the Role of Production Manager?
To clearly define production management, it’s necessary to highlight the role of the production manager in streamlining production operations and accomplishing manufacturing objectives. Here are some essential duties performed by the production manager.
1. Handling Production Team
People management is a vital part of a production manager’s job. They have to handle and supervise the production team, including production engineer, foreman and quality control staff.
2. Creating Production Budget
Develop a production budget, including the cost of raw materials, machinery and equipment, and labor to function within budgetary constraints.
3. Developing Production Schedule
Efficiently plan production and assembly lines to accommodate and prioritize orders to meet customer order deadlines and minimize the cost of production.
4. Communication
Coordinate with senior management and managers of other departments to ensure that everybody works together to fulfil production objectives and business goals.
5. Requirement Planning
To manufacture a product, one may need 100 or more items in the raw material list, including metal parts, lubricants, and chemicals. A production manager has to plan for every part and authorize their purchase.
6. Production Management
Manage routine operations and resolve production issues. For example, a high-pressure die-casting machine with aluminum as a raw material may encounter 200 different defects. Finding a solution to every problem is the job of the production manager.
7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance
Using safe production methods, and safety equipment is paramount to prevent injuries at the workplace. Moreover, production is in charge of following the emission norms set by the government, effluent disposal and waste treatment.
Sage X3 ERP: Your Key to Smooth Production Management
Understanding the meaning of production management can help organizations optimize their production process and boost operational productivity. Its vast scope from a strategic perspective like selection of plant location, process and material selection makes it a crucial business activity.
As business operations scale up, so does the need to manage surging complexities. With innovative ERP tools like Sage X3 by your side, managing procurement, production, inventory, warehousing and supply chain becomes smooth and easy, thus improving your overall production efficiency.
FAQs
1. What is the Main Goal of Production Management?
The main goal of production management is planning, organizing and controlling production operations to achieve business objectives and meet customer demand.
2. What is the Difference Between Production and Operations Management?
- Production management is concerned with manufacturing operations whereas operations management covers both manufacturing and service operations.
- The objective of production management is to bring about efficiency in production processes, reduce costs and maximize output. On the other hand, operations management is focused on overall operational efficiency with lean operations throughout the organization.
3. How Does Production Management Help in Cost Reduction and Quality Improvement?
Reducing costs and ensuring continuous quality improvement is vital to the success of production in the long term. The production manager has to ensure that all work centers work in harmony, inventory is ordered as per requirement, production methods are improved and there are no wasteful processes.
4. What are the Major Challenges Faced in Production Management?
Supply chain management and meeting changing customer demands while keeping costs low and profits high are some of the key challenges faced by production managers. Use advanced tools like ERP application to swiftly manage your production.
5. What are the Risks Involved With Poor Production Management?
Poorly managed production can lead to low production output, high cost of production, reduced profits, production defects, thereby decreasing production efficiency of the organization.
6. What are the KPIs Used in Production Management?
Key performance indicators serve as a benchmark to measure production performance. Some of the important metrics used by production managers include:
- takt time
- cycle time
- changeover time
- defect rate
- capacity utilization
- production output per day