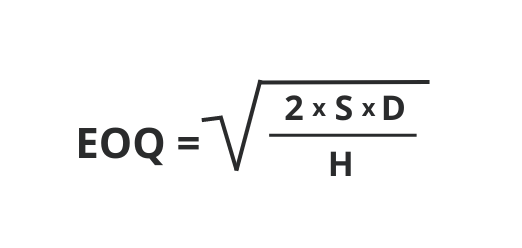What is Perpetual Inventory System?
Perpetual inventory system is an inventory management technique that enables continuous tracking and real-time updates of inventory levels following each transaction, thereby enhancing accuracy in inventory management and reporting while seamlessly integrating with sales and purchase systems.
A perpetual inventory system allows business owners to stay continually updated on inventory levels, avoid low stock situations and trigger automatic adjustments in reorder points. It significantly reduces the need for physical inventory counting, bringing inventory efficiency and greater inventory control.
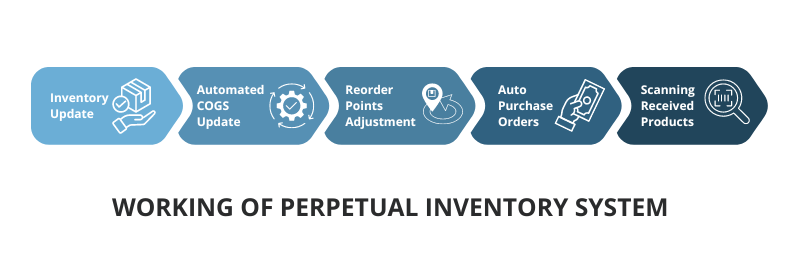
What is the Working of Perpetual Inventory System?
Step 1: Inventory Update
When a lot is sold, the point of sale system (POS) integrated with inventory system instantly updates inventory records across purchase, production, warehouse and sales departments. Barcodes or RFID scanners make this process quick and efficient.
Step 2: Automated COGS Update
COGS is automatically recalculated and updated as soon as sales occur, ensuring accurate financial reporting by adjusting the overall COGS accordingly.
Step 3: Reorder Points Adjustment
The perpetual inventory system uses historical data to auto-update reorder points, thus maintaining optimal inventory levels by anticipating sales demand.
Step 4: Auto Purchase Orders
When inventory hits reorder point, new purchase orders are automatically sent to vendors, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
Step 5: Scanning Received Products
When items are delivered to the warehouse, the staff scans them into the system, thereby updating the inventory count and making the products available for sale.
And so, the perpetual inventory cycle goes on without needing any manual intervention.
Perpetual Inventory System Method
1. FIFO Perpetual Inventory System
FIFO ( First-In, First-Out) perpetual inventory system allows you to track and record inventory levels continuously. The cost flow assumes that the oldest stock items are sold first, and the cost of goods sold is aligned with the earliest purchase prices. It grants accuracy in financial records by showing the cost of the oldest inventory sold and also providing up-to-date inventory levels. FIFO inventory system is quite useful for businesses with perishable products with an expiry date to ensure that the older inventory is consumed before it becomes obsolete.
2. LIFO Perpetual Inventory System
LIFO ( Last In, First Out) perpetual inventory system is an inventory valuation method where the last purchased items are sold first. The cost of goods sold in this case is based on the most recent purchases. Although the inventory is continuously tracked and updated with each purchase and sale, it tends to have higher COGS, thus impacting the cash flow statement. This system is often suitable during high inflation when a business wants to reduce taxable income by increasing the cost of goods sold. Also, this inventory strategy is used to match recent inventory costs with current sales revenue.
3. Weighted Average Cost
The weighted average cost is an inventory valuation method that calculates the average cost of inventory by distributing costs evenly across all units, depicting the average investment in inventory over a specific accounting period. Weighted average cost is then used to allocate a value to cost of goods sold and ending inventory.
This method ensures consistent valuation throughout the accounting period, as it adjusts price fluctuations by averaging the cost of inventory over time.
Businesses with high inventory turnover and frequently changing purchase costs often use this approach to keep their inventory records updated, providing a consistent unit cost while promoting accuracy in financial reporting.
Weighted Average Cost Formula
Weighted Average cost = Cost of Goods Available for Sale/ Units Available for Sale
| Date | Description | Quantity | Unit Cost (Rs.) | Total Cost (Rs.) | Cumulative Quantity | Cumulative Cost (Rs.) | Weighted Average Cost (Rs.) |
| 01-Jun | Opening Balance | 100 | 50 | 5000 | 100 | 5000 | 50 |
| 05-Jun | Purchase | 50 | 60 | 3000 | 150 | 8000 | 53.33 |
| 10-Jun | Sale | 70 | 53.33 | 3733 | 80 | 4267 | 53.33 |
| 15-Jun | Purchase | 40 | 55 | 2200 | 120 | 6467 | 53.89 |
| 20-Jun | Sale | 60 | 53.89 | 3233 | 60 | 3233 | 53.89 |
The table tracks inventory transactions, starting with an opening balance of 100 units at Rs.50 each. Each purchase or sale updates the quantity, unit cost and total cost. The cumulative quantity and cumulative cost are adjusted accordingly after each transaction. The weighted average cost (WAC) is calculated by dividing the cumulative cost by the cumulative quantity.
What is a Periodic Inventory System?
In contrast to a perpetual inventory system, a periodic inventory system is an inventory management technique where inventory counts are performed periodically with updates performed at specific intervals. It mandates physical counting of inventory which is conducted monthly, quarterly or at the end of a financial year to tally stocks. As periodic inventory systems offer lesser immediate visibility into the inventory levels, tracking inventory can be delayed and become challenging.
Also Read: What is a Periodic Inventory System and How Does it Work?
What is the Difference Between Perpetual Inventory System and Periodic Inventory System?
The following table illustrates the difference between the two inventory tracking systems.
| Perpetual Inventory System | Periodic Inventory System | |
| Inventory Tracking | Continuous & immediate | Periodic & delayed |
| Updates | Real-time | Specific intervals |
| Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) | Automatically updated | Manually calculated periodically |
| Methodology | Relies on technology & integration of systems | Relies on physical inventory counting |
| Accuracy | Immediate visibility & accuracy | May cause discrepancies between counts and book records |
When to Implement a Perpetual Inventory System?
Using a perpetual inventory system can deliver substantial returns for your business, offering real-time margin and profitability information. A perpetual inventory system maintains correct accounting by automatically documenting sales and purchase prices. Knowing when to implement this system in your organization is important to ensure that the investment you make gives maximum returns.
If your answer to the below-mentioned question is yes, then an automated inventory management ERP system is suitable for your organization.
- Does your business have high sales volume?
- Do you feel the need for real-time inventory updates?
- Do you want to plug the gap between sales and purchase systems?
- Do you require accurate and timely financial reporting?
- Do you want to minimize stock and overstock situations?
It is interesting to note that no matter which inventory management technique you use such as ABC analysis or FSN analysis, a perpetual inventory system can effectively be applied in any situation and steadily improve ROI in managing inventory.
Perpetual Inventory Formulas
1. EOQ
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) formula is used to calculate the optimal order quantity for reducing overall inventory expenses, which include ordering and holding charges.
Where:
D = Demand rate (units sold per accounting period)
S = Order cost (per order)
H = Holding cost (per unit per accounting period)
Calculation of EOQ is helpful for businesses in finding the ideal order size that can decrease the total costs associated with ordering and holding stock. This way, companies can make sure that inventory management is efficient and that there are no unforeseen stock out and overstocking events. Perpetual inventory system empowers you to monitor your EOQ in real time.
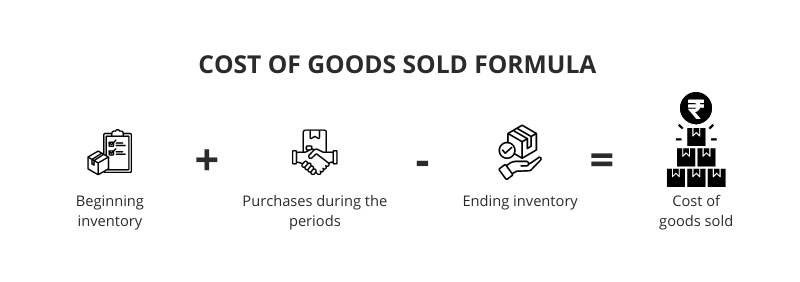
2. COGS
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) reflects the direct costs incurred by a business in producing the goods during an accounting period.
COGS Formula
COGS = Beginning Inventory + Purchases during the year – Ending Inventory
COGS includes the cost of materials and labor directly involved in producing the product, helping the business in the calculation of gross profit. In a perpetual inventory system, an update of COGS happens in real time after every sale transaction using FIFO, LIFO or any other chosen inventory valuation method.
You May Like: What are Inventory Valuation Methods and their Importance?
3. Gross Profit
Gross Profit reflects the profit a business makes from its core business operations before deducting operating costs. It is deduced by subtracting COGS from the net sales revenue earned by selling stock. Gross profit plays a vital role in evaluating how profitable are inventory management and sales operations in your business.
Gross profit formula
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
In perpetual inventory systems, the estimation of gross profit using an inventory management ERP allows you to conduct inventory valuation, make crucial decisions on pricing and product mix and gain valuable insights into the financial health of the company.
What is Perpetual Inventory System Example?
A manufacturer who supplies motorcycle brakes and handles via two business units to motorcycle OEMs – can use an ERP inventory system integrated with barcode scanners and RFID to improve operational efficiency and ensure stringent inventory control.
Every time a sale of brakes or handles happens, inventory levels are updated in real-time, triggering reorders. If there is a sudden spike in demand for a particular item, the reorder threshold for that item is automatically adjusted by analyzing historical patterns.
Perpetual inventory system gives a clear picture to the business owner of which item is selling faster. They can compare the inventory turnover ratio of brakes and handles, and focus on the sale of the item with a lower inventory turnover ratio.
Further, accurate stock monitoring across multiple businesses ensure inventory visibility and timely availability of items, thereby optimizing the supply chain.
Now let’s look at the advantages and disadvantages of perpetual inventory systems.
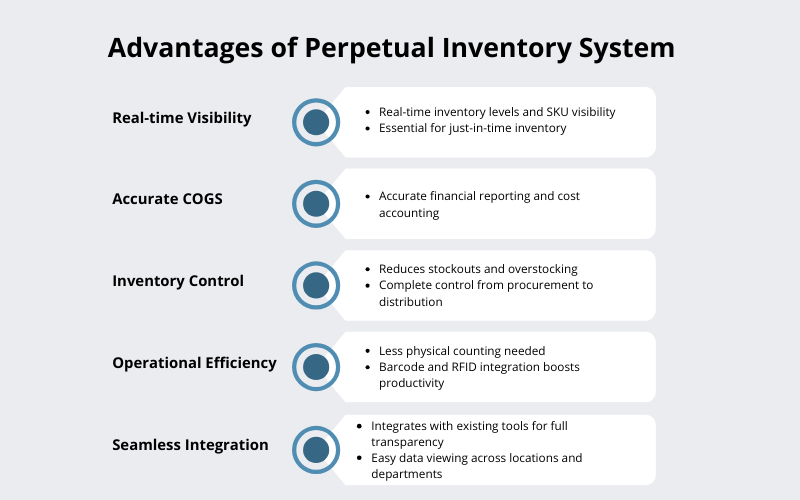
What are the Advantages of Perpetual Inventory System?
1. Real-time Visibility
Perpetual inventory system provides real-time visibility into the inventory levels and all the Stock Keeping Units (SKU), enabling business owners to forecast sales demand. Real-time visibility is of immense use in a scenario like lean manufacturing production, where inventory is ordered just in time to minimize storage costs.
2. Accurate COGS
As a perpetual inventory system automatically debits the cost of goods sold, including the cost of raw materials, labor, and overheads, it provides real-time insights crucial for informed decision-making and strategic planning in businesses.
3. Inventory Control
With this inventory system, the chances of stock outs and overstocking inventory are reduced to a bare minimum, as reorder points are triggered automatically as and when inventory fulfilment is needed. Thus, a business owner has complete control over the flow of inventory from procurement to distribution.
4. Operational Efficiency
The need for physical counting of inventory is drastically reduced with perpetual inventory systems, allowing greater efficiency in warehouse operations. The use of barcode scanners and RFID, integrated with WMS, brings operational efficiency by increasing the productivity of inventory processes and the workforce.
5. Seamless Integration
The ERP software with inventory management module can easily integrate with existing software and tools, and brings the entire data into a single source, thus, inventory managers can seamlessly view inventory data spread across multiple business locations and departments. As a result, they get complete transparency.
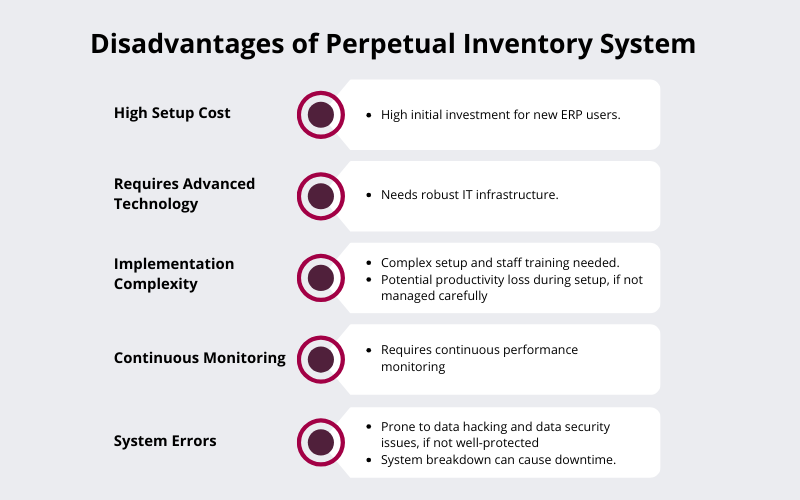
What are the Disadvantages of Perpetual Inventory System?
1. High Setup Cost
Business owners who have never installed business management ERP software to manage business and their inventory might be discouraged from investing in a perpetual inventory system driven by technology. If a business plans to invest in an on-premises ERP solution, the initial cost could be high.
2. Requires Advanced Technology
A perpetual inventory system is a technique which often requires continuous reliance on robust IT infrastructure that can control the monitoring of inventory efficiently. For the uninitiated, finding the right technology can be difficult and overwhelming.
3. Implementation Complexity
When implementing a new system, there is often a fear of productivity loss and the need for staff training to adjust to the new system. However, using an advanced and cost-effective cloud ERP solution like Sage X3, you can quickly implement the perpetual inventory system.
4. Continuous Monitoring
When installing a new inventory system in place, one has to make sure that the system is delivering the promised outcomes. For that, you need to monitor continuously and compare its performance with the existing inventory management system in place, until you find satisfactory results.
5. System Errors
IT and computerized systems are prone to errors. There can be data hacking, system downtime and data theft, which can be major cause for concern for businesses of all sizes. No business would want to suffer the loss of customer data due to security breakdowns.
Closing Thoughts
The perpetual inventory system tracks and updates inventory levels in real-time, increasing efficiency in inventory management by providing visibility into inventory levels and adjusting automatic reorder points. Perpetual inventory systems can effectively calculate COGS and gross profit, irrespective of the inventory valuation method being used.
Through advanced technology integration with ERP software and warehouse management system, a perpetual inventory system optimizes inventory control and minimizes stock outs, offering a perfect solution for growing small to mid-sized businesses to monitor inventory, improve financial reporting and reap maximum return on investment.
FAQs
1. What is the Definition of Perpetual Inventory System?
Perpetual inventory system is an inventory management method which allows you to continuously track your inventory in real-time perfectly synchronized with sales transactions.
2. What is the Meaning of Perpetual Inventory?
Perpetual inventory signifies a recurring process of monitoring inventory levels and transactions as soon as they take place.
3. Why is Perpetual Inventory Better Than Periodic?
Various reasons make perpetual inventory better than periodic inventory systems.
- Offers real-time visibility into the inventory levels
- Enables instant updates after a transaction occurs
- Allows accurate calculation of Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
- Helps timely decision-making and inventory control
- Minimizes the need for physical counting of inventory
4. What is the Definition of Perpetual Inventory?
Perpetual inventory is a system that continuously monitors inventory levels and updates them in real-time for each transaction.
5. What are the Advantages of Perpetual Inventory System?
Implementing a perpetual inventory system comes with several advantages.
- Provides real-time visibility and maintains accuracy of inventory levels
- Enables more efficient inventory management and reduces stock outs
- Enables precise financial reporting and expense control
- Works seamlessly with ERP and other management systems
- Improves overall operational efficiency
6. How Does a Perpetual Inventory System Work?
- Immediately records every inventory transaction
- Updates inventory levels in real-time after every sale
- Automatically recalculates and updates COGS and gross profit.
- Provides continuous visibility and control over inventory.
7. What Companies Use the Perpetual Inventory System?
- Retail chains
- Manufacturing companies
- Chemical companies
- Pharmaceutical companies
- E-commerce businesses