What is Opportunity Cost?
Opportunity cost is an economic decision-making approach used by business owners to determine the cost of giving up an opportunity while choosing an alternative opportunity, to allocate the limited resources for maximum return on investment.
Simply put, it is a process of comparing the costs and benefits of different alternatives available at the time of investment. From this perspective, a higher opportunity cost would mean that you are giving up on a more lucrative investment than the one in hand.
How to Determine Opportunity Cost in Business?
Consider a manufacturer who faces multiple alternatives to choose from, whether it is capacity planning for setting up a new production plant or deciding on which product to manufacture using a tool like ERP software. The choice has to be made. And there is always an opportunity cost associated with giving up the alternative not chosen. According to The Economic Times, choosing to leave money idle in the bank due to fear of a market crash creates an opportunity cost, which is the difference between the market return of 8% and the 3% earned in the bank.
Knowing opportunity cost helps you to make confident decisions and maximize your return on investment. Accurate calculation of opportunity cost through the multi-scenario planning feature of Sage X3 ERP ensures that your financial decisions are driven by data and not guesswork. The idea is to choose the option that best aligns with business goals, even though it comes with an opportunity cost.
A basic formula to calculate the opportunity cost is as follows.
Opportunity Cost Formula
Opportunity cost = Return of Next Best Option Not Chosen – Return of Option Chosen
What are Opportunity Cost Types?
Now that we’ve discussed what opportunity cost means, let’s look at two main opportunity cost types – Implicit cost and Explicit cost.
1. What is Explicit Cost?
Explicit cost is a type of opportunity cost that involves direct payment to buy resources for the business. These are typically visible expenses which have to be paid out-of-pocket and are recorded in the financial statements. A thorough understanding and calculation of explicit opportunity costs helps in controlling operational expenses and ensuring transparency in finance reporting and analysis.
Explicit costs play a vital role in business decision-making. They have to be factored in for preparing accurate budgets and financial forecasts. As explicit costs are deducted from revenue to determine net income, they significantly impact the profitability of a business. For instance, planning capacity expansion may require buying land for a new plant, new machinery and hiring more workforce.
2. What are Implicit Costs?
Implicit costs, on the other hand, are the opportunity costs involving resources for which a business has already paid and is free to further engage these resources without shelling out extra money. In other words, these resources are already owned by the business like existing machinery, manpower and land and do not involve direct monetary transactions for engaging them further.
Also referred to as implied costs, implicit cost can include the business owner’s time devoted to managing multiple companies and determining the tradeoff between focusing on one company over another. Additionally, would renting out underutilized space in the plant be a better option than increasing the production capacity? Calculating implicit costs using business intelligence software ensures that you take into account all costs, not just the explicit costs that you pay for.
What is Marginal Opportunity Cost?
Now that you know what are implicit costs and explicit costs, let’s understand marginal opportunity costs.
While explicit and implicit costs provide an overview of total costs, marginal opportunity cost determines the loss of production output of product A in producing additional units of product B, because the scarce resources of the business like machinery and manpower are diverted to producing additional units of Product B at the expense of reducing the output of Product A.
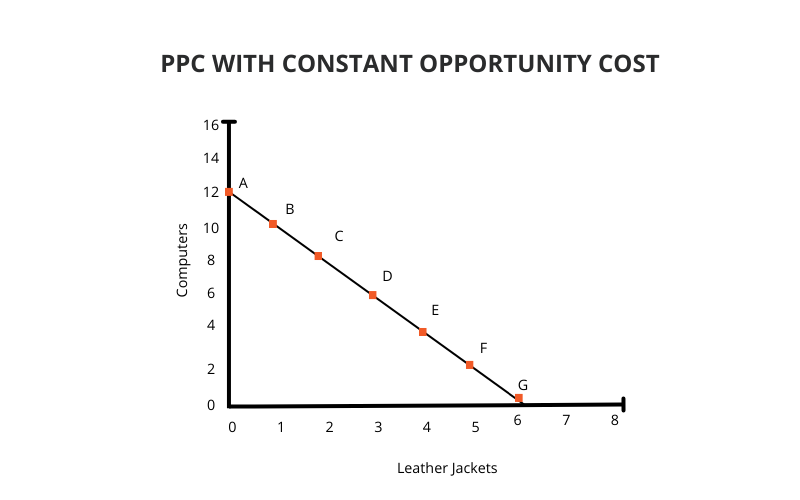
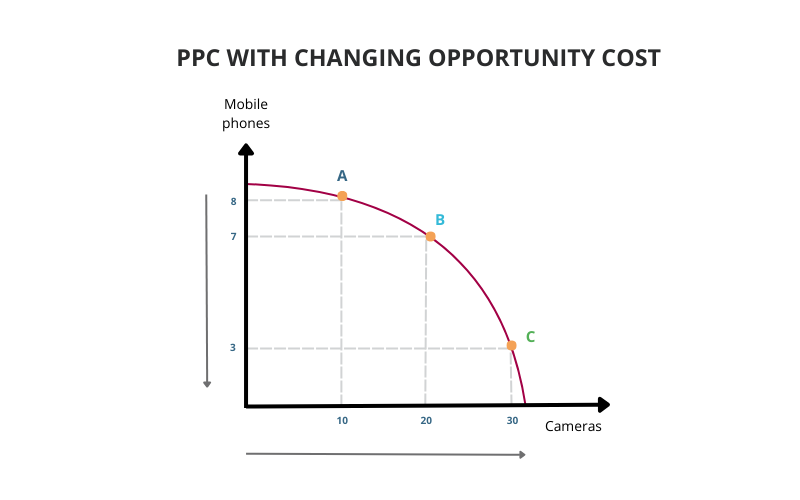
The production possibility curve is an excellent way to understand the tradeoff when allocating limited resources to the production of different goods and services, and determining the opportunity cost between producing different goods, such as deciding the right quantities of production of Product A and Product B.
A straight line PPC will indicate constant opportunity cost whereas a curved PPC points to changing opportunity costs and potentially higher economic returns in producing one product over another.
Marginal Opportunity Cost = Loss of Output of One Product/ Gain in Output of Chosen Product
Opportunity Cost vs Sunk Cost
| Opportunity Cost | Sunk Cost | |
| Definition | The value of the next best alternative forgone | Costs that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered |
| Time Frame | Relates to future decisions | Relates to past decisions |
| Relevance | Relevant for decision-making | Irrelevant for decision-making |
| Influence on Decisions | Helps in evaluating alternatives | Should be ignored when making decisions |
What is Opportunity Cost Advantage?
Here are the top advantages of knowing the opportunity cost in running a business.
1. Decision-Making Clarity
Opportunity costs are crucial for business owners in determining tradeoffs between alternatives. Deciding between hiring more workforce to meet additional production demand or outsourcing production to vendors involves gains and losses. Outsourcing might mean losing control over product quality but using procurement software for vendor management can make it a profitable decision.
2. Resource Allocation Efficiency
Accurate knowledge of opportunity costs improves resource allocation efficiency. Properly allocating capital, time and workforce maximizes profits. Alternatives with lower opportunity costs are more favorable as they better utilize resources, enhancing profit maximization.
3. Strategic Planning
From a strategic planning perspective, the significant R&D investment in new drug development lacks assurance of success. By calculating opportunity costs, a pharmaceutical entrepreneur might focus on producing generic drugs with lower R&D costs. ERP for pharma industry helps steer the business owner towards decisions that align with the company’s long-term goals.
4. Financial Management
Another major advantage of opportunity cost analysis is financial management. You can use opportunity cost to maximize ROI across the business using ERP software. Whether in financial planning or budgeting, incorporating opportunity cost improves financial decisions. It also helps manage risks, control costs, and optimize profitability.
5. Competitive Advantage
An in-depth analysis of opportunity costs helps evaluate products and production activities, focusing on those that provide the greatest value relative to their costs. Opportunity cost effectively drives R&D in the company. If analysis shows investing in a new product is worthwhile, it promotes efficiency in the design process and offers a chance to differentiate in the market.
Also Read: Costing Methods and Techniques
What is Opportunity Cost Disadvantage?
Despite the numerous advantages offered by opportunity cost, there are certain disadvantages of including opportunity cost in financial planning.
1. Inaccurate Estimation
Measurement of accurate opportunity costs can be difficult in many situations as one has to consider future returns and benefits, for which accurate data may not be available, leading to speculation. As a result, the opportunity cost estimations generated could be inaccurate.
2. Subjective
How an organization looks at opportunity cost can differ based on individual perspectives and circumstances the business is operating in. The subjective nature of the opportunity cost does not make it a standardized option to base your financial calculations.
3. Increases Complexity
As such, a business has to make various decisions based on fundamental financial metrics and KPIs like net profit margin, operating cash flow and working capital. Adding opportunity cost to standard metrics adds another layer of complexity in business, ultimately delaying key decisions.
4. Inapplicable Situations
There are instances when unique opportunities show up in business. Suppose you are operating in an emerging technology sector, you may not have complete details and benchmarks to base your opportunity cost, thus making opportunity cost analysis inapplicable in those situations.
5. Over-emphasis
While opportunity cost calculation looks like an interesting proposition, focusing excessively on them can lead to the undervaluation of benefits which may not be perceived instantly like social impact, workforce satisfaction or even ethical concerns.
What is An Example of Opportunity Cost?
Suppose a businessman has Rs.10,00,00 and he has two options to buy machinery. The first option is to import machinery from China, which has a production capacity of 10,000 units per day, but it can have an error rate of 5%. The second option is to buy a similar machine from an India-based company, whose production capacity is 9700 units and produces with very little margin of error.
At a 5% error rate, China machinery can produce up to 500 defective units. However, machinery purchased from India will likely produce 9700 defect-free units. So, the businessman has to weigh his opportunity cost whether to risk production of up to 500 units and repair defects by using a Chinese machine or have a definite quality production of 9700 units using an Indian machine. An accurate calculation of opportunity costs aids better decision-making.
Conclusion
Opportunity cost is a financial metric that allows business owners to weigh their options and decide between alternatives. While accurate calculation of opportunity cost can be challenging in certain situations, it is still an interesting metric to consider to minimize risk in decision-making.
Do remember to consider different types of opportunity costs in your analysis based on your short-term and long-term goals, including implicit cost, explicit cost and marginal opportunity cost to get a better understanding of allocating your resources effectively and maximizing your profits.
Also Read: Capital Budgeting : Meaning, Methods and Importance
FAQs
1. What is Opportunity Cost Definition?
Opportunity cost is a decision-making financial tool that helps businesses to choose the best alternative when confronted with multiple options to maximize their returns.
2. What Do You Mean By Opportunity Cost?
Opportunity cost means to forego other alternatives when one alternative is chosen.
3. What is the Importance of Opportunity Cost?
Opportunity cost aids business owners to refine their decisions by adding an extra metric when doing cost comparisons between alternate options.
4. What is Opportunity Cost Mean?
The benefits lost when one particular option is not chosen by preferring the other option is the opportunity cost of not considering that option.
5. Is it Necessary to Use Opportunity Cost in Business?
While it is not appropriate to include opportunity cost if you have insufficient data, considering opportunity cost data gives you more evidence to make better decisions.