What is MOQ?
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) is a limit imposed by manufacturers on the minimum number of units or the total order value of a product that wholesalers or retailers must purchase to complete an order so that the manufacturer gains optimum value and a minimum amount of profit margin on each transaction.
Businesses across the world use ERP Software to calculate MOQ, reduce the risk of overstocking, enhance cash flow, and increase profit margin. Setting a realistic MOQ helps them avoid wasting their resources on orders that bring too little value.
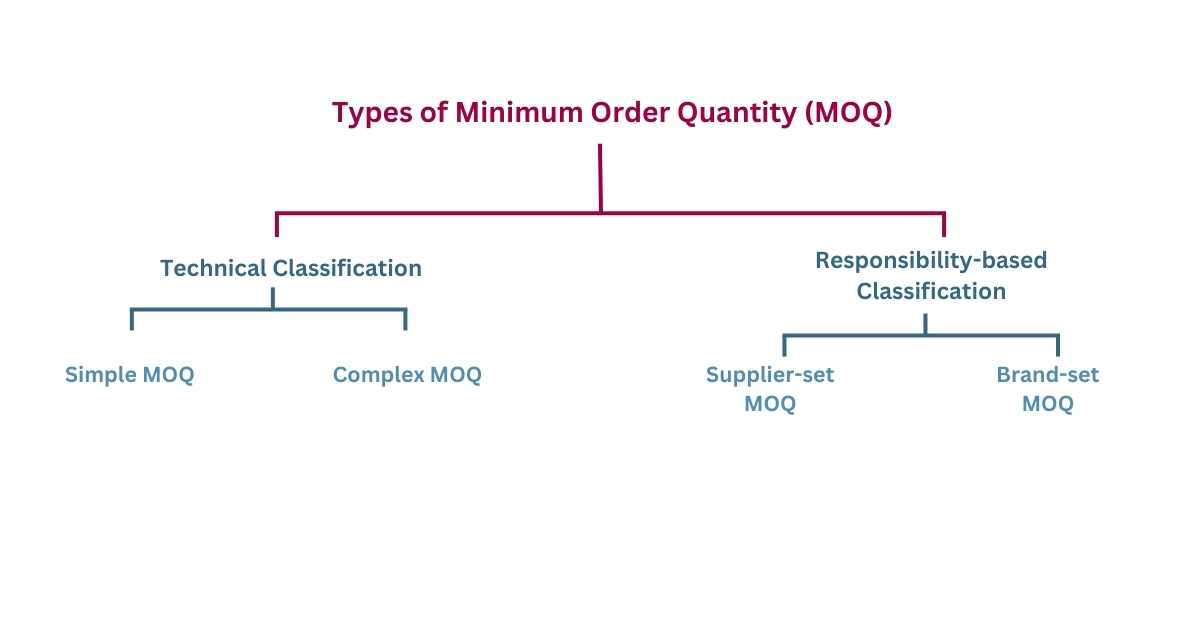
Different Types of Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
I. Technical Classification
1. Simple MOQ
This is a simple form of MOQ with no complex terms and conditions. In this type, your business is required to purchase a specific quantity of products to complete your order. Typically, when suppliers and retailers/ wholesalers enjoy a long-term partnership, the supplier might offer more flexibility and agree to reduce the MOQ.
2. Complex MOQ
This is an advanced form of MOQ where the supplier gives multiple requirements. For example, a supplier may require the wholesaler or retailer to buy a minimum quantity of products in addition to a minimum order value. The actual requirements may vary from supplier to supplier.
II. Responsibility-based Classification
1. Supplier-set MOQ
A Supplier-set MOQ is where the supplier narrates the minimum quantity of orders that one must purchase. The supplier imposes a minimum purchase restriction to meet their strategic business goals, uncover production costs, and align sales with the production cycle.
2. Brand-set MOQ
A Brand-set MOQ is determined by the brand rather than the supplier. It’s a common strategy among brands to set lower MOQ for newly launched products to get a glimpse of the market demand and the scope for expansionism.
Examples of Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Now that we’ve discussed what is MOQ, let’s take two simple examples to gain a better understanding of the concept of Minimum Order Quantity.
1. Units-based MOQ
ABC Ltd is a computer manufacturer based in Delhi, India. XYZ Ltd is a retailer based in Mumbai, who wishes to purchase 40 computers from ABC Ltd. However, ABC Ltd communicates that the Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) for the computers is 100 qty. In other words, XYZ Ltd must place an order for a minimum of 100 computers.
2. Total Order Value-based MOQ
In the same above example, ABC Ltd communicates to XYZ Ltd that they must give a minimum order of Rs. 40,00,000. In this example, the manufacturer (ABC Ltd) is not concerned about the number of units of the order. To place an order, XYZ Ltd will have to give a minimum purchase order of Rs. 40,00,000.
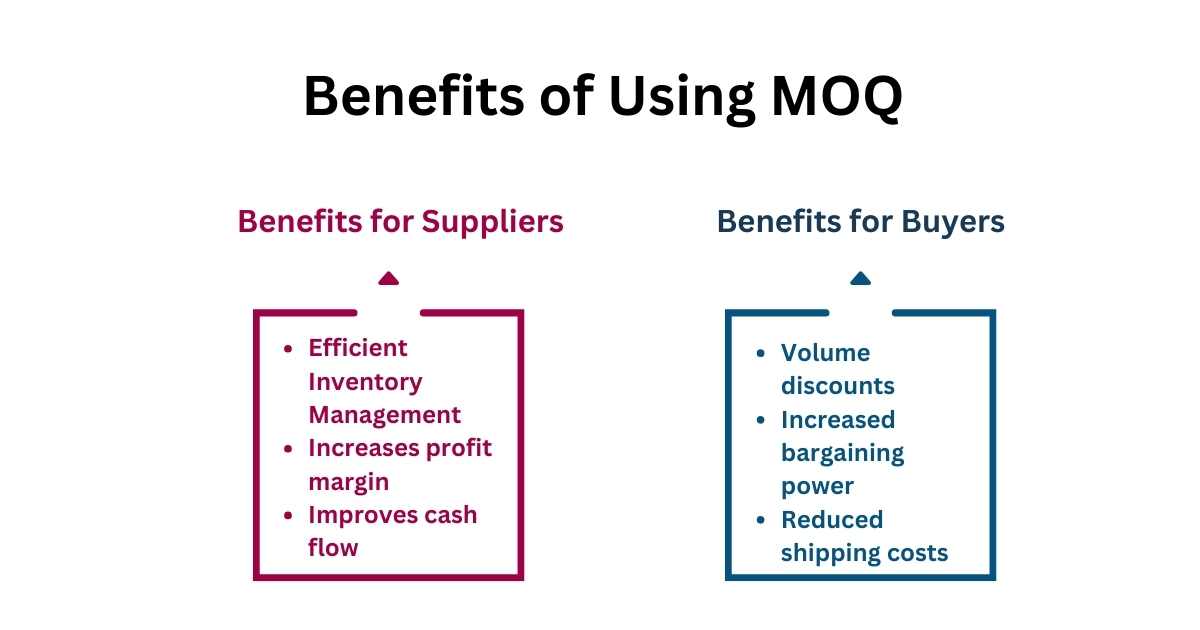
What are the Benefits of Calculating MOQ?
I. Benefits for Suppliers
1. Efficient Inventory Management
Excess inventory can cause various problems for businesses such as increased storage & insurance costs, and waste of organizational resources. Inventory Management System helps you set ideal MOQ, and plan inventory efficiently.
2. Increases Profit Margin
MOQ encourages manufacturers to produce goods at a large scale and sell them in large quantities. This helps them avoid wasting organizational resources on smaller orders that may not yield much results, and achieve their objective of profit maximization.
3. Improves Cash Flow
As we’ve discussed in what is MOQ, MOQ helps suppliers reduce excess inventory costs, they start earning larger revenues on each order. With more cash coming on, the company will benefit from enhanced cash flow, additional cash reserves, and stronger creditworthiness.
II. Benefits for Buyers
1. Volume Discounts
MOQ encourages buyers to purchase products at a larger quantity than they normally do. Businesses that purchase products in larger quantities maximize their profits and increase inventory turnover. Moreover, they are in a better position to resell products at competitive prices to the final user.
2. Increased Bargaining Power
Businesses that purchase products in bulk are in a better position to negotiate with the suppliers than those that purchase in smaller quantities. They can demand better discount offers, quality assurance, and payment terms.
3. Reduced Shipping Costs
Multiple recurring shipments can be more expensive than a single larger shipment of the same product. Businesses that give bulk quantities can track & schedule shipments more efficiently, and save a lot of time.
What are the Limitations of MOQ?
I. Supplier Perspective
1. Loss of Opportunities
A rigid supplier can set a very high MOQ, leading to little to no orders from small-scale businesses that may be willing to purchase the product in a smaller quantity in the beginning.
2. Spoil Business Relationships
If the supplier is very rigid and not flexible in terms of the MOQ, it may discourage existing business partners and impact long-term relationships.
II. Buyer Perspective
1. Higher Inventory Costs
Sometimes, MOQ can force wholesalers and retailers to purchase excessive quantities of products, leading to unsold sales and higher inventory costs.
2. Cash Flow Problems
By purchasing more stock than you need, your business may suffer from a negative cash flow statement. Your business capital will be tied up in unwanted inventory.
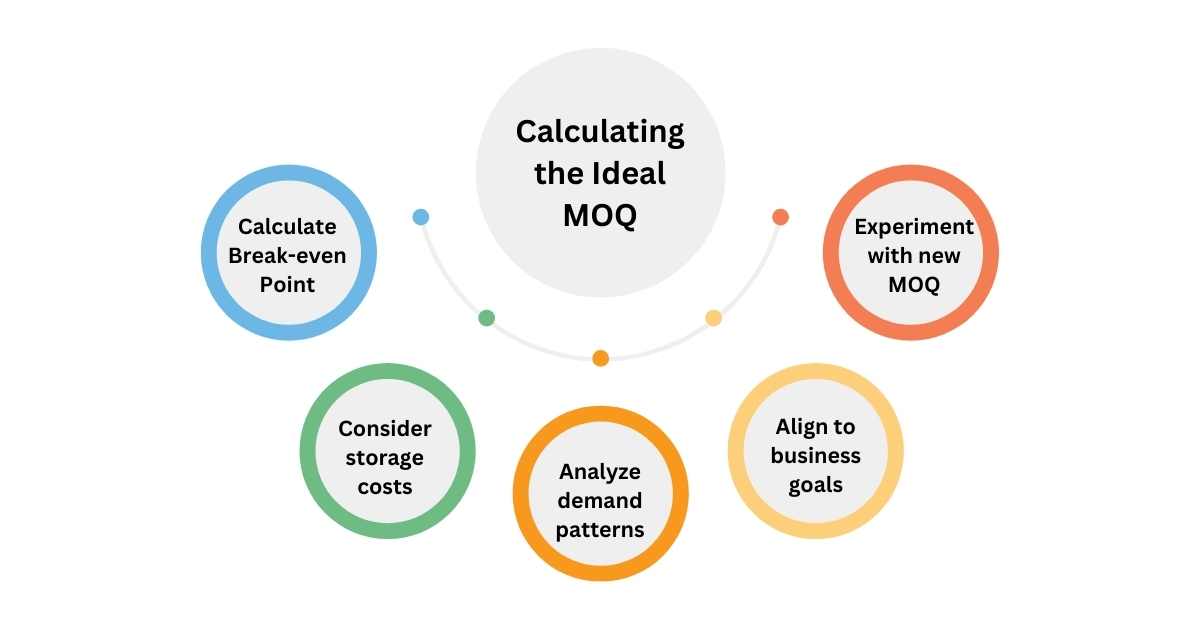
How to Calculate Minimum Order Quantity?
Manually calculating the ideal Minimum Order Quantity is not easy. That’s why, we suggest using an ERP Application that takes several internal and external factors into consideration, and simplifies the entire procedure.
Minimum Order Quantity MOQ Formula:
Minimum Order Quantity = Total Cost of Order / Unit Cost of Product
1. Calculate Break-even Point
Break-even Point (BEP) is the point at which the revenue generated from sales covers the total expenditure, and the business starts gaining revenues. Break even analysis is important to set a realistic MOQ.
2. Consider Storage Costs
Another factor that influences MOQ is the storage cost. Manufacturers of perishable products typically use the Best ERP Software in India to set a high Minimum Order Quantity, cover their additional storage costs, and reduce the potential risk of overstocking.
3. Analyze Demand Patterns
The next step is to perform demand forecasting for your products. If the demand is too high, your business may benefit from a higher MOQ. In contrast, if the demand for your products is too low, setting a higher MOQ can limit your growth and spoil partnerships.
4. Align to Business Goals
Be sure to set an MOQ that aligns with your long-term goals and strategic objectives. A poorly set MOQ can lead to more harm than good and act as a major hurdle in achieving your objectives.
5. Experiment with New MOQ
After evaluating all the above factors, it’s time to set your own MOQ. Be sure to perform A&B testing on a regular basis to increase conversions.
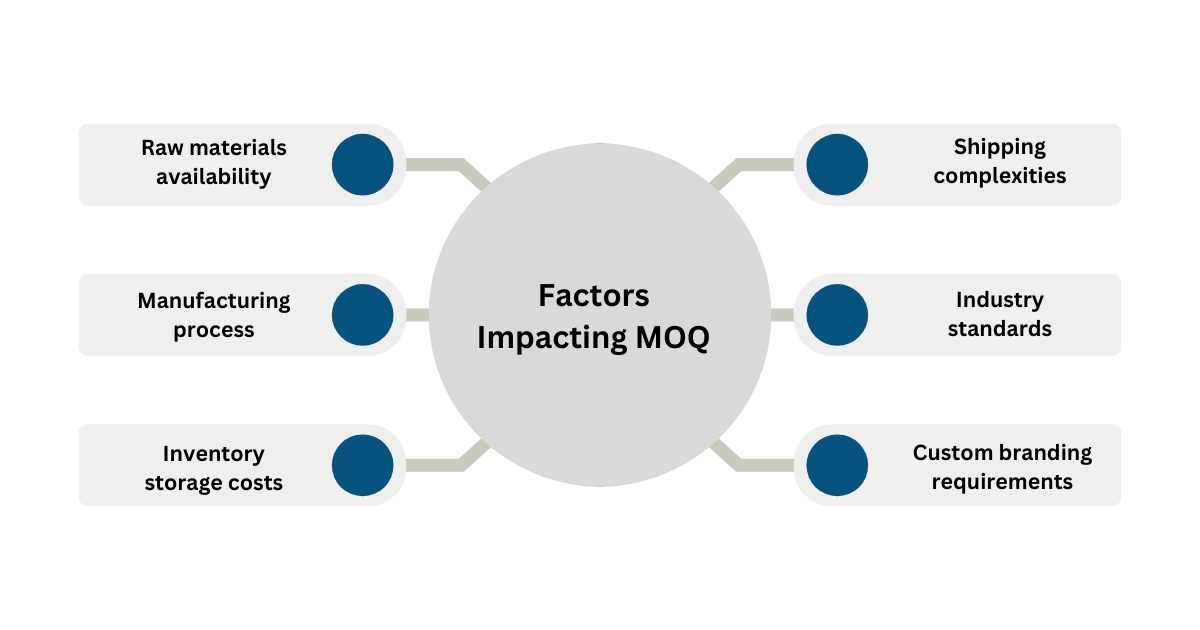
Different Factors Impacting the MOQ
As we’ve discussed the MOQ meaning, and its types, examples & benefits, let us discuss what are the different factors that can affect it.
1. Raw Materials Availability
Availability of raw materials is one of the important factors that affects a company’s MOQ. For example, some furniture manufacturing companies require purchasing raw materials in bulk. As such, they impose a higher MOQ for the finished products.
2. Manufacturing Process
Many companies operating in the pharmaceutical industry deploy advanced ERP for chemical manufacturing technologies such as robotics and automation for cost control and efficiency. Due to the nature and complexity of these processes, they must produce goods in a larger quantity, which ultimately upscales the MOQ.
3. Inventory Storage Costs
Think of the food industry where food producers have to ensure constant refrigeration of the food products to preserve the food quality & taste and ensure they are safe for human consumption. All of this adds up to the carrying cost. To avoid excessive storage costs, the company imposes a higher MOQ.
4. Shipping Complexities
Some products, especially, the large ones are difficult to transport from one location to another. Similarly, shipping products to remote locations can be a challenging task. To maintain a balance between the shipping cost and selling price, your manufacturer will impose a higher MOQ.
5. Industry Standards
Some industries (such as apparel & fashion, beauty & personal care, and custom merchandise) have a low Minimum Order Quantity than others. Thus, new entrants in the industry set lower MOQ to maintain industry standards and increase market share.
6. Custom Branding Requirements
Manufacturers often receive custom branding orders that require manufacturing products with custom packaging & logo, and a unique message for seasonal promotions. They may impose a higher MOQ to offset the additional costs and resources deployed to fulfill those demands.
Summing Up
There is no fixed MOQ applicable universally. Each manufacturer sets a unique MOQ that largely depends on their short-term objectives, demand for their product, payment terms, business size & type, and many other factors.
Sage X3 is a strategic tool that plays a vital role in setting ideal MOQ, evaluating supplier performance, and forecasting demand for products. It helps you avoid the risk of overstocking and control inventory efficiently. It is a must-have tool for businesses looking to nurture long-term relationships and mutually benefit.
FAQs
1. What is the MOQ Meaning in the Context of Product Ordering?
MOQ meaning in the context of product ordering is that it is the smallest number of units of a product that your buyers (whether wholesalers or retailers) must purchase to complete their order. Thanks to MOQ, your buyers benefit from significant discount offers on bulk purchases, and they are in a better position to negotiate and resell the goods at competitive prices.
2. What is the MOQ Full Form in Manufacturing Businesses?
In the context of manufacturing businesses, the MOQ full form is Minimum Order Quantity. It is a lower limit set by the manufacturer for order placement. There is no one-size-fits-all MOQ for businesses. It differs from industry to industry and even differs among different companies operating in the same industry.
3. How to Get a Lower MOQ through Vendor Negotiation?
Vendor negotiation and nurturing long-term relationships are keys to lower MOQ. Here’s how you can use them for your benefit:
- Most suppliers may agree to offer a lower MOQ for their first-time partners. Be sure to ask for it.
- Monitor and participate in early payment discount offers from various suppliers
- Reach out to multiple suppliers and negotiate for a favorable & mutually acceptable MOQ.
- If none of these work, consider paying a relatively higher per-unit price to get a favorable MOQ.
4. Can Suppliers Change the Minimum Order Quantity?
It’s a common practice among suppliers to set a lower MOQ for their long-term partners. This helps them promote long-term relationships and mutual profits. There is no single rate of MOQ. It varies from supplier to supplier and industry to industry. It can change due to changes in internal and external factors such as changes in the technology used for production, current market situations, industry standards, and the supplier’s financial conditions.
5. Are MOQ and EOQ the Same Thing?
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) and Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) are two different, yet highly inter-linked, concepts. MOQ is the minimum number of units or minimum total order value a manufacturer wishes to sell in a single order. In contrast, EOQ tells manufacturers an ideal and cost-effective order quantity or total order value that can cover their inventory holding costs, and derive a meaningful balance.
6. What are the Impacts of MOQ on Selling Price?
MOQ is one of the factors but not the only factor that affects a product’s selling price. For example, when your buyers agree to purchase large quantities of your products, they expect significant discounts and lower pricing. Similarly, small businesses that are not in a position to purchase larger quantities may not get discount pricing and are forced to purchase the product at a higher price.