Inventory is the most crucial component of any industry. It is one of the elements determining the profit and loss of the business. An optimised inventory reduces the items carrying costs.
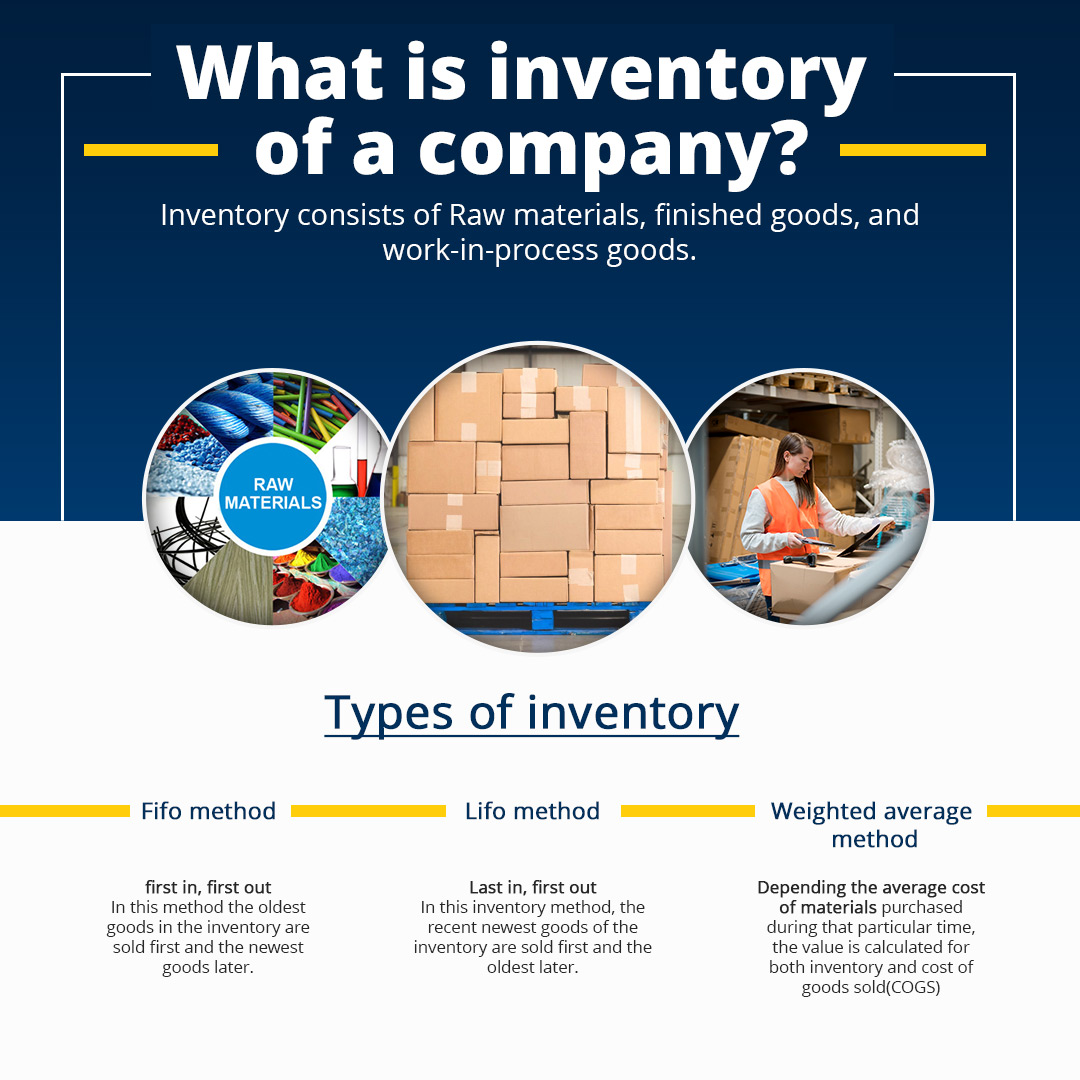
Inventory includes three main categories: – raw materials, unfinished goods and finished items. And these items are added as current assets in the company’s balance sheet.
Inventory management should be prioritized as it directly impacts the company’s revenue. To manage inventory seamlessly, real-time visibility of accurate data is vital. Leveraging technology is a boon to effective inventory management.
What is Inventory?
The inventory covers both the finished goods, the raw materials that are in the production process and the work-in-process(WIP) goods. The inventory of any company is significant as it is the major asset responsible for the company’s turnover as the inventory’s resources are the main source of revenue generation and money for the company’s shareholders.
The main goal of an organised inventory is order fulfilment, satisfying customer expectations, keeping track of items, and demand forecasting. Businesses must prioritise inventory to understand easily when there are excess stocks or when the stocks are less. A perfect inventory management system in place will be helpful in optimising it.
Inventory should be maintained efficiently to have enough stock to prevent any blocks in the supply chain system. The stocks should be moderately maintained as it determines the total inventory value.
Proper inventory control ensures flexibility in financials and meets customer orders.
⇒ Inventory methods can be valued in three ways :
First in, first out (FIFO) method
In this method, the oldest goods purchased are sold first. The cost of the sale of the latest purchased materials is taken as the carrying cost of the remaining inventory.
Last in, first out (LIFO)
This method focuses on selling the last unit of goods or the very recent ones. But the value of goods sold in the inventory depends on the earliest purchased materials.
Weighted average method
The value is calculated both for the inventory and Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) depending on the average cost of materials purchased in that duration.
Definition of Inventory Management
There are different ways to define Inventory management, it can be defined as the process of ordering, storing, using and selling goods or merchandise to earn profit. And for each industry, the definition of the term inventory changes slightly.
Manufacturing Industry
In the manufacturing sector, inventory comprises raw materials, semi-finished goods produced, items in the warehouse and finished products.
For example, a cake manufacturing company stores batches of finished items in the inventory, semi-finished cakes which aren’t packed or labelled yet and raw ingredients such as oil, flour, sweeteners etc are stored separately.
Service Industry
The service sector has no physical stocks to store in the inventory. So here the inventory stores the relevant data which is later sold to the customer.
For example, a research consultancy firm will sell information from its inventory. And a vacant room is the inventory of a hotel business.
What are the types of inventory?
There are four main common inventory types of inventory – raw materials, work-in-process(WIP), finished goods and materials repair and overhaul(MRO). Let’s discuss more inventory types below.
Raw materials
The raw materials that are used to make a whole finished good are stored in the inventory. These items are the components of either a work in progress or process or a finished good. Raw materials can be divided into two types-
Direct materials– The materials that are directly used in the finished products.
Indirect materials – These raw materials are a part of factory or overhead costs.
For example, in the production of handbags, the direct raw material is leather. Indirect raw materials are light bulbs, batteries etc that keep the business or the factories in operation.
Work in process WIP inventory
Items that are still in the making process are considered work-in-process (WIP) inventory. It comprises raw materials with labour costs sometimes that are still in the manufacturing process.
It includes both direct and indirect raw materials that are in the midst of the production process.
For example, a dress which is half done, the buttons, and the cloth piece together belong to the WIP work in the process inventory part. So at the end of the fiscal year, they are considered as unfinished goods.
Finished goods inventory
Finished goods are the most important asset to downright among the types of inventory. The items that your business listed on the website or sold directly to the customers are categorised under this inventory.
Overhaul/MRO
MRO can be expanded with inventory examples such as maintenance, repair and operating supplies. This inventory is used to assemble and sell the finished goods. These inventory items are not built into the product.
Based on your business policies, these items may be in a storage unit at the supplier, or in shipment.
An inventory example for this is the pen, pencil, paper etc can be categorised as MRO. Or the masks, gloves and caps used for packing a product are also considered as MRO inventory item.
Components
They are basically raw materials that are unnoticed after the product is finished. The best examples of these are lids, boxes etc.
Packaging materials
This inventory consists of three types of packing materials – The initial packing of the product is known as primary packing. The second package includes the packaging of the packed product including SKU and label information. The third package is the batch or bulk packaging that is done to load it into transport.
Decoupling inventory
This inventory is applicable to companies that manufacture goods. In this, the extra items are stored or it can also be WIP products that are in the production line to prevent any downtime or blocks.
Transit inventory
This inventory is also termed pipeline inventory. It moves in between manufacturers, warehouses and distribution centres. And it takes weeks to move among different facilities.
Excess inventory
It is also known as obsolete or dead inventory. It means a loss of revenue, if excess stocks are held in the inventory for a longer time, it diminishes its value. These are goods that are unsold and still the company bear the cost for its stays in the inventory.
Service inventory
It is a management accounting concept that measures the amount of service a business can provide in a particular duration.
Safety stock and anticipation stock
Safety stock is the extra goods component parts that the company stores in the inventory to meet any unexpected situation. These goods incur carrying costs but it fulfils customer demand.
Anticipation stocks are raw materials or finished goods that companies purchase to meet the required sales based on current trends.
Theoretical Inventory
In this type, a business requires a minimum amount of materials to be used for production without waiting for raw materials to arrive. It is also termed a book inventory. This inventory is used for production and the food industry.
For example, assume that a restaurant’s salad lettuce usage is 150 bags per week. But more orders are placed as safety stock in case of more sales or a few spoilt lettuces.
Its value is computed using the actual versus theoretical formula.
Significance of Inventory Control
Inventory management is pivotal for the business to maintain the right amount of stocks in the accounting period. Plus, a company’s right balance of inventory minimises storage costs, balances inventory levels and prevents overflowing stocks or too little inventory.
An organization’s inventory will have to pay the price for storing products for a longer time. So an effective inventory management system will reduce costs, fulfil orders on time and remove bottlenecks in supply chain management.
Inventory management helps in assessing current assets, financial reports and accounting balance. It helps in managing and balancing the company’s cost of goods sold too.
Inventory Best Practices
To successfully run a business, you must measure it, so you can find the best ways to manage it. Inventory and types of inventory have to be reviewed more frequently.
Invest in a cloud-based Inventory Management System
Implementing a cloud-based system will help in tracking the status of all the goods and SKUs in real time. This valuable data can be used for businesses to stay up-to-date and relevant. Globally, the inventory can be tracked with this advanced technology.
Carry safety stock
This inventory system technique of having a backup of extra items will help the company if the company depletes the resources sooner due to demand increase. It is also known as buffer stock.
What is Inventory Turnover?
The frequency in which a company sells its stocks or resources in a particular duration is termed inventory turnover. It can reveal if the report if your business has too much inventory.
⇒ Here is a formula to measure inventory turnover :
Average inventory = (Beginning inventory+ending inventory)/2
Inventory turnover= Sales + Average inventory
Conclusion
To wrap things up, a well-managed is necessary to meet the requirements of the business and meet the demands of the customer. There are distinct types of inventory with unique characteristics. Managing inventory efficiently is an ongoing process that requires frequent monitoring to ensure that the right products are at the right place and time.