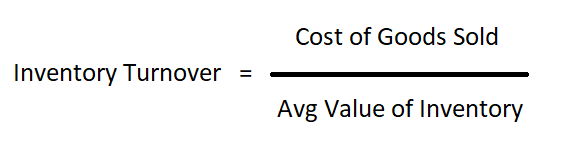What is the Inventory Turnover?
Inventory Turnover (also called, Stock Turnover) is a critical metric in the financial analysis that indicates how quickly a company sells and replenishes its stock over a period of time, and provides insights into the efficiency of the company’s inventory handling.
Businesses use ERP Software for sophisticated inventory planning, seamless movement of stock, and gaining agility in supply chain operations. Its plethora of modules enables companies to find cost-saving opportunities, minimize inventory costs, and sustain profits.
What is the Inventory Turnover Ratio?
Inventory Turnover Ratio is a ratio used by businesses and investors to measure the efficiency of the company’s inventory management, and compare the inventory levels to actual sales.
A lower ITR typically indicates lower sales and higher holding costs whereas a higher ratio typically indicates better sales and lower holding costs. However, there can always be exceptions. The ITR is also used to understand a company’s liquidity position.
Inventory Turnover Formula
The formula to calculate the turnover of inventory is simple and straightforward. Simply divide the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) by the Average Value of Inventory.
Here are the components of the Inventory Turnover Formula:
1. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) includes all the direct expenditures incurred during the manufacturing of your products such as the direct labor costs, direct material costs, and factory overheads, among others. Generally, as the nature and scope of a company’s activities increase, so does the COGS as the company needs to deploy additional resources to manufacture the goods. The COGS is recorded in the Income Statement (i.e. Profit & Loss Account).
2. Average Value of Inventory
The Average Value of Inventory determines how much inventory a business has exhausted over a specific timeframe. Calculating Average Inventory using Business Management Software helps you determine how much inventory you will need to support the operations of your sales team and ensure seamless order fulfillment.
Here’s the formula to calculate the Average Inventory:
Inventory Turnover Examples
Now, let’s walk through a few simple examples to better understand this concept in depth.
1. ABC Ltd, a Clothing & Apparel Retailer
ABC Ltd is a clothing and apparel retailer based in Pune, Maharashtra. In the past year, the retailer has incurred the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) of Rs. 28,000. Its Average Inventory during the same period was Rs. 15,000. Let us calculate the ITR.
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) / Average Value of Inventory
= 28,000 / 15,000 = 1.86
The ratio indicates that the company sold and replenished its inventory every 1.86 times during that year. It is not satisfactory given ABC Ltd is not operating in an industry targeting luxurious products.
2. XYZ Ltd, a Mobile Retailer
XYZ Ltd is a mobile retailer that incurred a COGS of Rs. 600,000 in the past year and had an Average Inventory of Rs. 20,000 during the same period.
ITR = 60,000 / 20,000 = 30
This is a very good ratio as it indicates that the company has sold and replenished its inventory every 30 times during that year.
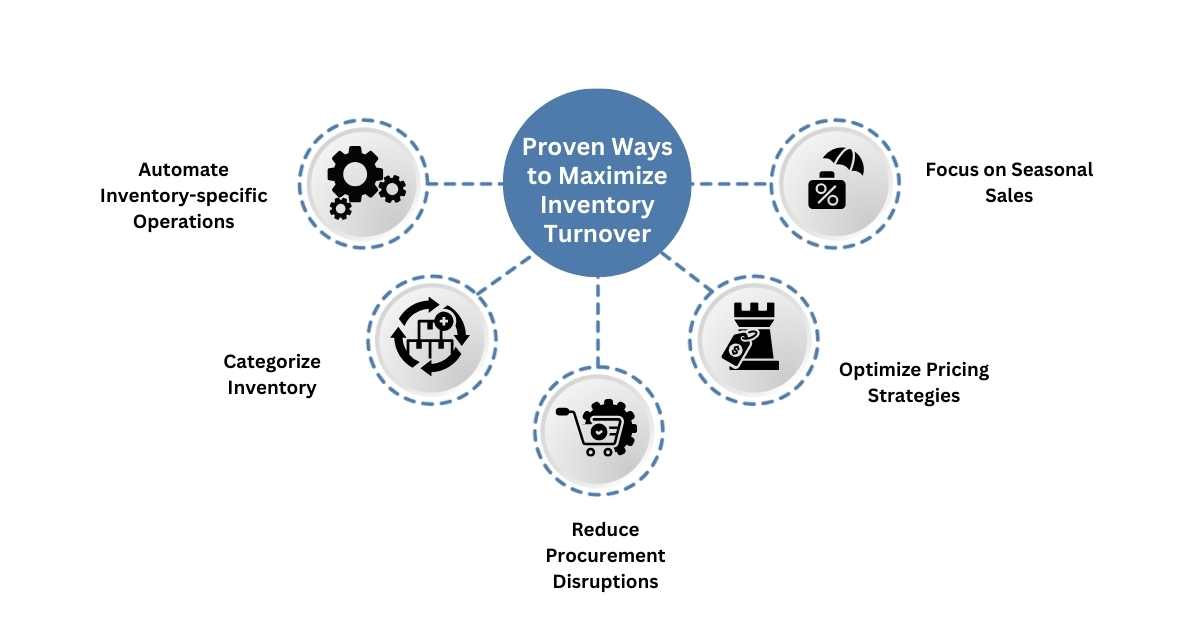
Proven Ways to Maximize Your Inventory Turnover
Now that we’ve discussed everything from Inventory Turnover meaning to its formula, let’s deep dive into the best strategies to achieve your ideal inventory level.
1. Automate Inventory-specific Operations
An Inventory Management System provides a platform to manage your entire inventory from a single place and stay in control of your inventory operations. Eliminate the hassle of misplaced or duplicate inventory, and focus on higher revenue growth.
2. Categorize Inventory
Categorize your inventory into different groups such as perishable items, non-perishable items, seasonal items, non-seasonal items, and so on. Depending on the nature of the inventory, deploy a relevant method (such as the FIFO method or LIFO method). Not only will this result in better turnover, but it will also expedite order fulfillment.
3. Reduce Procurement Disruptions
Some vendors may offer lower prices; however, they may not offer continuity in the supply of raw materials. To prevent unnecessary inefficiencies in your turnover and ensure timely delivery, negotiate with multiple vendors and deploy an Online Procurement Management System.
4. Optimize Pricing Strategies
Regularly perform A&B testing to understand the effectiveness of your pricing strategy. Use different sales channels and a robust Sales Management System to fine-tune your pricing strategy. With a revised pricing strategy in place, not only can you maximize your turnover, but also experience a surge in the profit margins.
5. Focus on Seasonal Sales
You can further boost your turnover rate by focusing on seasonal sales. Align your marketing strategies to drive quick sales during seasonal promotions, and boost your turnover ratio.
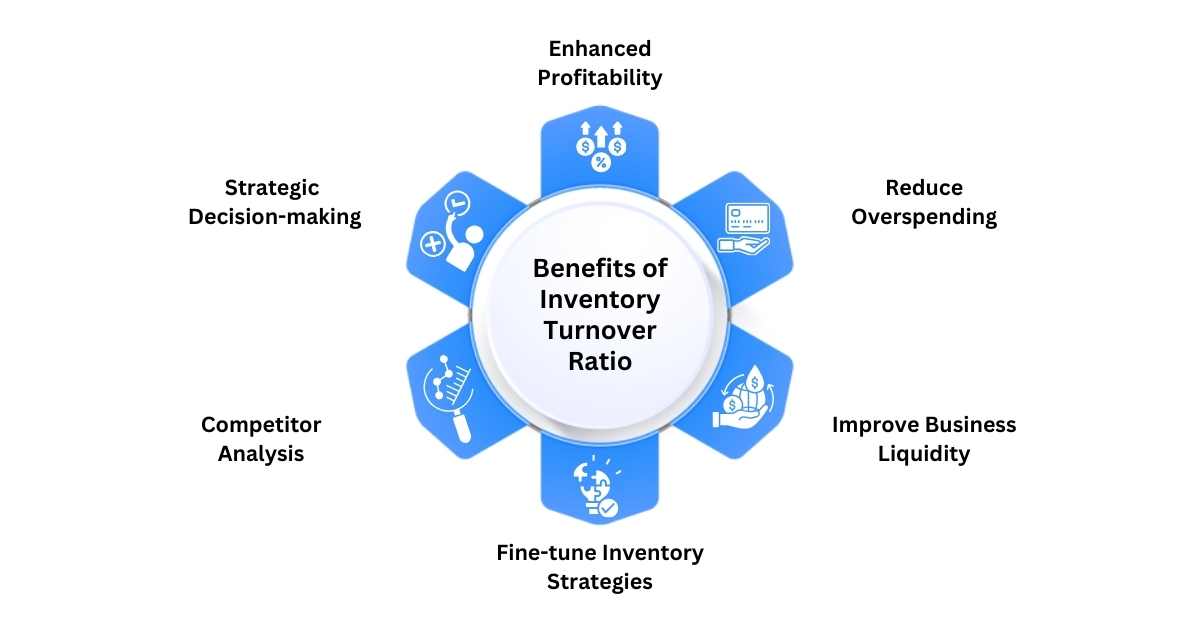
Benefits of Calculating Inventory Turnover Ratio
The turnover ratio of inventory is a valuable metric for businesses, especially manufacturing firms. Here’s why:
1. Enhanced Profitability
Typically, businesses with higher turnover tend to have lower inventory holding costs and better sales. Such businesses are more agile to rapidly changing market dynamics and capture new opportunities for profit maximization.
2. Strategic Decision-making
Get a better understanding of your inventory using the best Business Intelligence Tools, and identify any room for improvement (such as underperforming stocks). Make timely & informed strongly data-backed decisions rather than simply relying on your gut feelings.
3. Competitor Analysis
If you’re a food business, you can use an ERP for food industry to calculate the ITR of your competitors. Get remarkable insights about the effectiveness of their marketing & sales campaigns, and plan strategies for the advantages of your company.
4. Fine-tune Inventory Strategies
Identify the effectiveness of your current inventory management strategies, and tailor them to meet your strategic business needs. Accurately forecast your inventory requirements, minimize potential errors, and improve the effectiveness of your Demand Forecasting.
5. Improve Business Liquidity
Consistently lower turnover might indicate that excessive business capital is tied up to its inventory and the company is facing a cash crunch. To invest in new projects and innovations, the company will need to improve its turnover ratio using an ERP Application and sell unsold inventory.
6. Reduce Overspending
Let’s say you’re a manufacturer. You can invest in a Manufacturing ERP to regularly calculate your Inventory Turnover Ratio, better understand your inventory needs and accordingly fine-tune your strategies to reduce wastage of inventory. Reduced overspending directly translates into higher profits.
Limitations of Inventory Turnover Formula
While the Inventory Turnover Formula has its own benefits, it has certain limitations too.
1. Variations in Procurement Costs
Temporary fluctuations in the price and supply of raw materials can impact the accuracy of the interpretation of the turnover of the inventory.
2. Seasonal Demand Fluctuations
Temporary seasonal spikes or drops in the demand for a product may affect the accuracy of the interpretation of the turnover of the inventory.
3. Ignores Lead Time
The Inventory Turnover Formula ignores the Lead Time which can affect the accuracy of the decision-making.
4. Ignores Carrying Costs
The ratio also ignores inventory carrying costs which include the cost of inventory storage, insurance premiums, administration costs, and depreciation costs.
Wrap Up
Inventory Turnover Ratio is an important metric that helps investors get insights into your company’s efficiency at inventory handling, and understand the efficiency of the sales operations and the company’s overall liquidity level. A higher ratio is typically preferred while a lower ratio may imply lower sales and inefficiency at the inventory handling. However, there are certain exceptions.
Sage X3 is an exceptional solution that delivers the flexibility & scalability needed to manage your inventory operations and unlock the full potential of your business. Get easy access to analytical & reporting tools and benefit from robust supply chain operations.
FAQs
1. How Does Inventory Turnover Define in Modern Business Context?
In simple words, Inventory Turnover meaning is the number of times a company sells its inventory and replaces it with a new one. It is an important measure used by companies to get a better understanding of the efficiency of their inventory management. It may differ from industry to industry and even companies across the same industry.
2. What is the Ideal Inventory Turnover Ratio?
There is no single answer for the ideal ratio of inventory turnover. The ideal ratio may depend from industry-to-industry. Furthermore, as we’ve discussed in the Inventory Turnover meaning, it may also differ across companies operating in the same industry. Typically, a higher inventory ratio is preferred. However, this may not be the case for luxurious products and the construction industry as they deal with highly expensive products that are often difficult to sell. If you don’t have a good ITR, you can take a series of measures, including installing the Best ERP Software in India.
3. What Does a Higher Inventory Turnover Ratio Signify?
A higher turnover of inventory is typically a positive thing indicating an increasing demand for your company’s products due to various reasons ranging from effective marketing campaigns, and offering discounts to positive customer experience.
However, an unreasonably higher ratio may not necessarily be a good thing. It could also mean that you’ve got too little stock to fulfill your current market demands. However, it may not be sufficient enough to deal with an unexpected surge in demand or seasonal fluctuations. You can tackle such issues with a robust Warehouse Management System.
4. What Does a Lower Inventory Turnover Ratio Indicate?
A lower turnover of inventory is typically not favorable. It could indicate a variety of things, including:
- Decreasing demand for your company’s products. This may happen due to various reasons such as weak marketing & promotional strategies, poor customer experience, less demand for your products, or availability of a better substitute.
- Your company is incurring a higher inventory storage cost as you’re over-stocking your products and unable to sell them on time.
- Or, you have a significant portion of obsolete inventory tied up to your business capital. In today’s rapidly evolving technological environment, businesses suffer from this critical challenge.
5. Why is the Inventory Turnover So Important?
The turnover value of your inventory is important because it helps companies understand how effectively they manage their stock in relation to their sales. Inventory Turnover define as an important business metric that helps companies understand how quickly they sell and replace their inventory within a timeframe. Due to these advantages, the investors also consider the turnover value as the direct reflection of the efficiency of the company’s inventory management.
6. Does Inventory Turnover Ratio Vary from Industry-to-Industry?
Yes, the ITR varies from industry-to-industry. Moreover, it may not be the same for companies operating in the same industry.
Here are some common examples:
- The Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) industry typically has a higher ITR compared to other industries.
- In the retail industry, retailers often have to offset their low profit with a higher sales volume, which typically results into higher Turnover Ratio.
- Companies that sell luxurious products such as high-end automobiles, jewelry, and premium watches, typically have a lesser ratio
- The project completion time in the construction industry is often too high and prone to regulatory hurdles, resulting in a lower turnover ratio.