What is Goodwill Accounting?
Goodwill accounting is an accounting activity for assessing a company’s goodwill, an intangible asset comprising its market position, customer relationships, employee expertise and brand recognition, to determine the company’s purchase price when it is being acquired by another company.
In other words, goodwill is the premium value of a company above its fair market value, recorded as a non-current asset on the acquirer’s balance sheet. Goodwill is the amount you get after subtracting the fair market value from the purchase price of the business.
Importance of Valuation of Goodwill and its Accounting Treatment
Now that we know what is goodwill accounting, let’s find out why it is so important to calculate goodwill.
Firms have to perform goodwill accounting for various reasons, such as during mergers and acquisitions, or when the profit-sharing ratio of partners is changed, during the admission of a new partner, or the death and retirement of a partner. Accounting standards govern how goodwill is treated on financial statements, including how it is first recognized, measured, tested for impairment, and perhaps amortized.
Goodwill accounting plays a fundamental role in purchase price allocation(PPA), which is the allocation of acquired assets and liabilities in the balance sheet when one company purchases another company. According to the PPA study conducted by EY, 35% of the enterprise value of acquired companies was allocated to goodwill, indicating the growing role goodwill accounting has in the valuation of the firm.
Also Read: 3 Golden Rules of Accounting
How Is Goodwill Different From Other Intangible Assets?
The goodwill of a company is unique in the sense that it is subjective and it is only recognized in monetary terms when a company is being sold. Intangible assets in a goodwill like brand reputation, supplier and customer relationships can be difficult to quantify, however, the process can be simplified using modern ERP software, by assigning, tracking and analyzing values of various components of the goodwill of the target company and arrive at an informed purchase decision. On the contrary, other intangible assets like patents, copyrights, and licenses, have a definite value and are relatively easy to quantify.
What are the Different Types of Goodwill?
1. Purchased Goodwill
Purchased goodwill comes into being during the acquisition of a company by another company. It is quantified during the sale of the company and is recorded as an intangible asset on the acquirer’s balance sheet. Further, purchased goodwill is affected by impairment testing.
2. Inherent Goodwill
Inherent goodwill is the company’s reputation built over the years due to its long-standing market position, work ethic, customer base, and operational strengths. Inherent goodwill carries an intangible value which cannot be quantified. And it is not recorded on the balance sheet.
Difference Between Purchased Goodwill And Inherent Goodwill:
| Purchased Goodwill | Inherent Goodwill |
| Goodwill acquired through the purchase of a business. | Goodwill that develops internally over time within a company. |
| Recognized as an intangible asset on the balance sheet. | Not recorded on the balance sheet. |
| Based on the excess of purchase price over the fair value of net assets. | Difficult to measure; develops organically. |
| Arises during company acquisition or mergers. | Grows naturally through business operations. |
| Typically amortized over time (in some accounting standards). | Not subject to amortization as it is not recognized in financial records. |
What are the Challenges in Goodwill Accounting?
1. Valuation Difficulty
The value of goodwill can be difficult to comprehend as it is subjective. It can vary based on the accounting method chosen and accounting bias due to the market perception of the intangible assets of the business.
2. Overstatement Risks
As there is no tangible asset involved, goodwill runs the risk of being overvalued. This can unjustifiably inflate asset values and create anomalies in financial statements. Consequently, the firm may have to considerably de-value the assets during impairment testing.
3. Complicates Acquisition
Mergers and acquisitions deals can take a long time, sometimes years, to close. Part of the reason for the delay is the conflict of interest surrounding the goodwill of the target company, complicating the accounting process.
4. Valuation Collapse
Goodwill is highly susceptible to negative events. Whether it is a sudden dent in the owner’s reputation or the uncovering of a financial fraud, it can significantly reduce the goodwill of the company and lead to a drop in share price.
What are the Advantages of Goodwill Accounting?
1. Customer Trust
Goodwill in accounting strengthens trust among existing clients and attracts new clients, who would be willing to do business and form procurement contracts with your company.
2. Positive Perception
Goodwill is largely governed by the market reputation of the business. Higher goodwill creates a positive perception of your brand, making your business an attractive investment option.
3. Firm Valuation
Goodwill accounting helps in determining the true value of the firm, which may have been hidden till the time of its sale. A realistic valuation can help the company plan capacity expansion and diversification.
4. Creditworthiness
Goodwill increases the creditworthiness of your company among credit rating agencies and banks. Availing loans and fulfilling working capital requirements become easier with goodwill in accounting.
Which Factors Affect Goodwill of a Company?
A range of factors can affect the goodwill of a firm. Some of the key factors are as follows:
1. Business Reputation
Besides its product and service quality, how professionally a firm is run can influence its reputation, such as whether it uses advanced technology like manufacturing ERP software for efficient processes and professional decision-making.
2. Capital Availability
Businesses with sufficient capital for expansion indicate growth. Such businesses have an edge over those primarily dependent on external funds for development.
3. Business Scope
What is the future outlook of the business? Are there risks involved due to the nature of the business that can affect cash flow projection? What are its competencies like long-term contracts with customers and suppliers, patents etc.?
4. Business Location
A suitable location can influence goodwill in several ways. Is the manufacturing plant located near its clients and suppliers? Is an export-driven business located near a port? Do they have access to a pool of skilled talent?
What is the Positive And Negative Goodwill?
Positive goodwill occurs when the acquiring company is willing to pay a premium price over and above the fair market value of net assets identifiable in the company being acquired. Here, the target company is in a better bargaining position due to the strength of its intangible assets.
Negative goodwill, on the other hand, is when the purchase price is lower than the fair value of the target enterprise. It is an indicator of a distress sale and the target enterprise does not have the potential to improve its economic prospects due to declining reputation or future operational challenges.
Difference Between Positive And Negative Goodwill:
| POSITIVE GOODWILL | NEGATIVE GOODWILL |
| Increased brand value | Financial distress |
| Strong customer relationships | Undervalued assets |
| Employee retention | Declining reputation |
| Future growth potential | Future operational challenges |
What is Goodwill Impairment?
If the carrying value of the net identifiable assets of the company, including its goodwill, is more than the recoverable value from the sale of the company, the assets have to be impaired. According to Indian Accounting Standards IAS 36, companies are required to perform impairment testing at least once a year to determine if their fixed assets and intangible assets like goodwill are overstated and in need of impairment, which can be easily conducted using ERP software.
Impairment testing considers market factors like technological innovation, market trends or if the market capitalization of the company is lower than the carrying value of its assets. Likewise, internal factors like continuous decline in the performance of the assets, and overhauling of operations demand impairment testing. If the impairment loss is recognized, it is written off and marked as an expense in the P&L statement.
You Might Also Like: What is considered a Fixed Asset in Accounting?
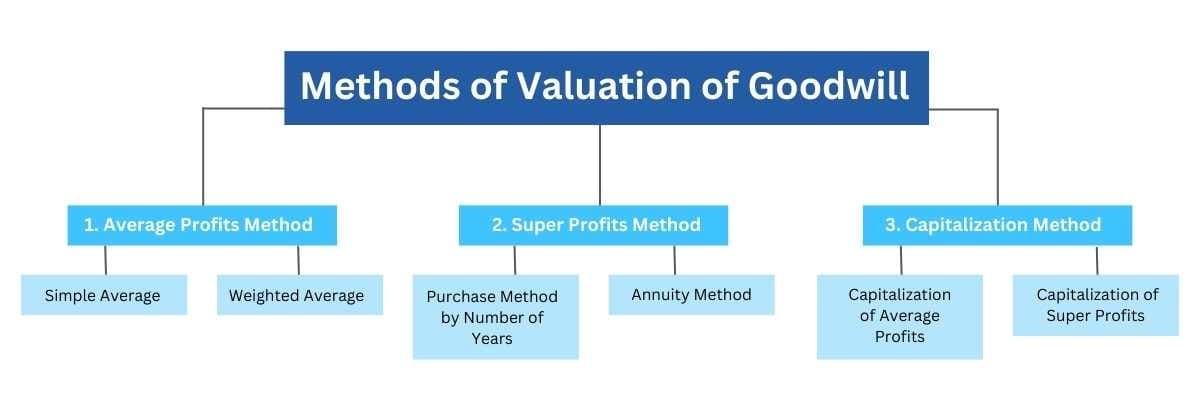
What are the Methods of Valuation of Goodwill?
Choosing the right methods of valuation of goodwill is important as it helps to determine the true value of the company’s assets using asset management software, in compliance with accounting standards and prevent impairment losses. Let’s look at the most commonly used methods to calculate goodwill.
1. Average Profits Method
In the average profits method, you calculate the average profits of the recent years and multiply the average profits by the number of years of purchase, which is the expected number of years for which the profit is likely to stay consistent and at par with recent years’ profits. Only the regular profits from core business operations are considered while avoiding one-time gains such as an asset sale.
There are two methods to determine the average profits using your ERP solution.
a. Simple Average
Here, we take a simple average of the profits of the recent years and multiply it by the number of years of purchase.
Simple Average Formula For Goodwill
Goodwill = Average Profit x Number of years of purchase
b. Weighted Average
In contrast, the weighted average method assigns more weight to profits earned in the latest years than the previous years.
Weighted Average Formula for Goodwill
Goodwill = Weighted Average Profit x Number of years of purchase
2. Super Profits Method
The super profits method is employed when the company has been earning higher profits year by year as compared to the industry standards and wants its goodwill value to reflect these super profits over the coming years.
There are two super profits methods for calculating goodwill.
a. Purchase Method by Number of Years
The purchase method determines goodwill as follows:
Normal Profit = Capital Employed x Normal Rate of Return
Normal profit is the profit the company expects to earn based on industry standards.
Super Profit = Average estimated profit – Normal Profit
Average estimated profit is the actual average profits the company earned in recent years.
Goodwill = Super Profit x Number of years of purchase
b. Annuity Method
The annuity method assumes that the future profits are not as valuable as the current profits due to the time value of money, and calculates the present value of the annuity for determining goodwill.
Goodwill = Super Profits x Present Value of Annuity
*Annuity value is calculated using discount rate and number of years of purchase.
3. Capitalization Method
The capitalization method of goodwill is used to determine goodwill when the company wants the goodwill to reflect its earning potential in the future. This is done by converting average profits or super profits into business value. The two methods of capitalization are as follows:
a. Capitalization of Average Profits
Goodwill = Business Value – Net Tangible Assets
Business Value = Average Profits × (1 / Normal Rate of Return)
Net tangible assets = Total assets – Intangible assets – Total liabilities
b. Capitalization of Super Profits
Goodwill = Business Value – Net Tangible Assets
In this case, Business Value = Super Profits × (1 / Normal Rate of Return)
What are the Steps For Calculating Goodwill?
Follow these steps using your ERP application to calculate goodwill.
1. Calculate Book Value
Calculate the net book value of all your identifiable assets and liabilities, including tangible and intangible assets, and accounting for asset depreciation.
2. Estimate Fair Market Value
Estimate the fair value of the company’s assets, i.e. the value the assets would fetch in an open market as compared with its net book value.
3. Fair Value Adjustments
Determine the difference between the fair market value of assets and the book value of assets to obtain fair value adjustments.
4. Determine Excess Purchase Price
Excess purchase is determined by calculating the difference between the actual purchase price and the net book value of assets.
5. Determine Goodwill
Finally, the goodwill of the company is calculated by deducting fair value adjustments from the excess purchase price.
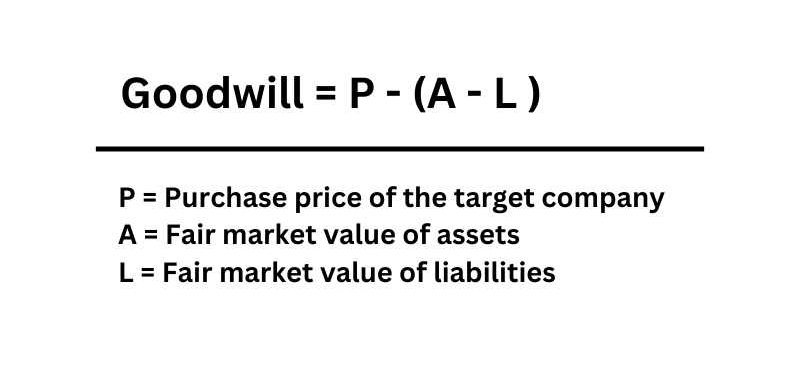
What is the Goodwill Formula?
Although the goodwill calculation requires thorough a determination of intangible assets, in simple terms, it can be calculated using the given goodwill formula.
Goodwill = P – (A – L )
Where,
P = Purchase price of the target company
A = Fair market value of assets
L = Fair market value of liabilities
What is the Best Example of Goodwill?
Let’s understand goodwill with the help of an example.
ABC Chemicals acquires XYZ Chemicals for Rs325 crore to expand its global footprint and product portfolio. After a detailed calculation utilizing the industry-specific capabilities of their ERP for chemical industry, ABC Chemicals found that the fair market value of assets and liabilities of XYZ Chemicals was Rs900 crore and Rs600 crore respectively. Therefore, the goodwill premium that ABC Chemicals paid to XYZ Chemicals is as follows:
Goodwill = 325 – (900 – 600)
Goodwill = Rs25 crore
Leverage Sage X3 For All Your Accounting Needs
As goodwill accounting takes center stage in corporate transactions, ascertaining the accurate value of goodwill becomes crucial. Multiple factors affect the value of goodwill and there are various methods available to calculate it, to meet different business objectives and comply with accounting standards.
Make impactful decisions for your organization with Sage X3 ERP, which provides holistic business management solutions, including advanced accounting functionalities, with actionable insights. Take your business efficiency to a whole new level by automating a range of routine accounting tasks using Sage X3.
FAQs
1. What Is Goodwill?
Goodwill is an intangible asset indicating the excess of the purchase price of an organization over the fair value of its net assets identifiable which are acquired in a business acquisition deal. Goodwill is built over time due to the brand reputation, market standing and customer loyalty, and is monetarily realized when a going concern is sold at a price higher than the fair value of its assets.
2. How Is Goodwill Calculated?
Goodwill is determined by subtracting the difference between the fair market value of assets and liabilities from the purchase price during the acquisition deal.
3. Why Is Goodwill Important In Accounting?
Goodwill in accounting helps determine the true value of the company beyond its core assets. Goodwill reflects the unique intangible capabilities of a firm, highlighting its growth prospects and its profit-making abilities.
4. Can We Call Goodwill A Current Asset?
No, goodwill is a non-current asset because its value lasts for many years in contrast to current assets which are expected to be monetized within one year.
5. How Is Goodwill Shown in Balance Sheet?
On the balance sheet, goodwill is shown on the assets side because it is a non-physical asset with the potential to increase a firm’s value over the years.