What is Work Order?
A Work Order is a comprehensive digital document that provides a detailed roadmap and information pertaining to different tasks that are required to be carried out at an organization, such as nature of the task, its location, contracting company, requirements for skilled manpower, and cost estimations, among others.
It is a part of a company’s Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) that creates a baseline for forming and executing its activities. Businesses use an ERP Software to draft a Work Order and clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each personnel involved in the activity and lay down the procedure starting with need identification to post-completion analysis.
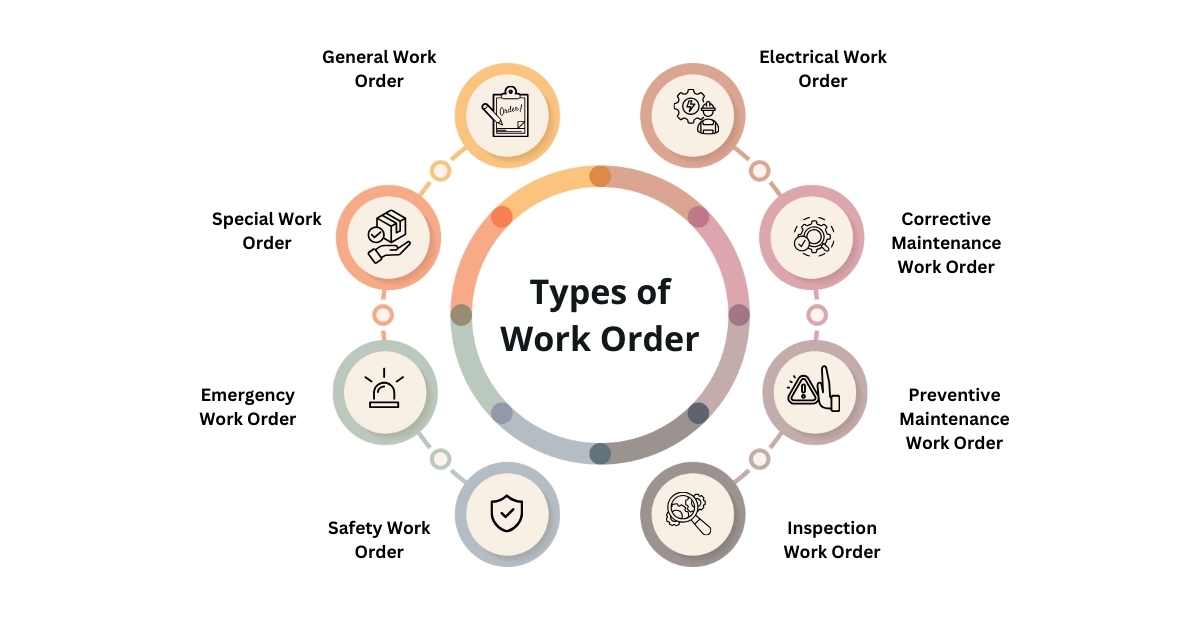
What are the Different Types of Work Order?
1. General Work Order
This includes various routine tasks that do not fit into a specific category. Let’s take a simple Work Order example: Checking the progress of a task, pest control activity, and painting at the company’s premises.
2. Special Work Order
It is created during special activities such as the upgradation of the company’s machinery, deployment of new assets, and so on. It is usually created for activities that are distinct from the regular ones.
3. Emergency Work Order
It is also known as an order for Reactive Maintenance. It is drafted whenever a technician detects a potential failure in an equipment or asset, requiring immediate repair to prevent disruption in the business activities.
4. Safety Work Order
As the name describes, this type of order is intended to safeguard the lives of the laborers involved in harmful & hazardous activities. It is intended to create a safe & secure environment for everyone and ensure minimal damage to the organization’s assets.
5. Inspection Work Order
It is drafted during the inspection phase. For example, it may be carried out during a Predictive Maintenance activity such as an assessment of the performance of an organization’s machinery. It helps detect functional issues and proactively build risk assessment strategies.
6. Preventive Maintenance Work Order
Preventive maintenance is an important part of an organization’s routine maintenance activities. It is intended to increase asset lifespan, prevent potential disruptions in manufacturing activities, and minimize costs of repair & replacement.
7. Corrective Maintenance Work Order
It is usually created by a technician after the identification of a problem during the inspection phase. It lays down detailed information detailing the resolution as part of the corrective maintenance.
8. Electrical Work Order
It is usually drafted by a company’s internal electrician. It provides detailed information with concise instructions to carry out installation or electrical repair & maintenance work. For example, inspecting the electrical panels, and carrying out wiring for a new appliance.
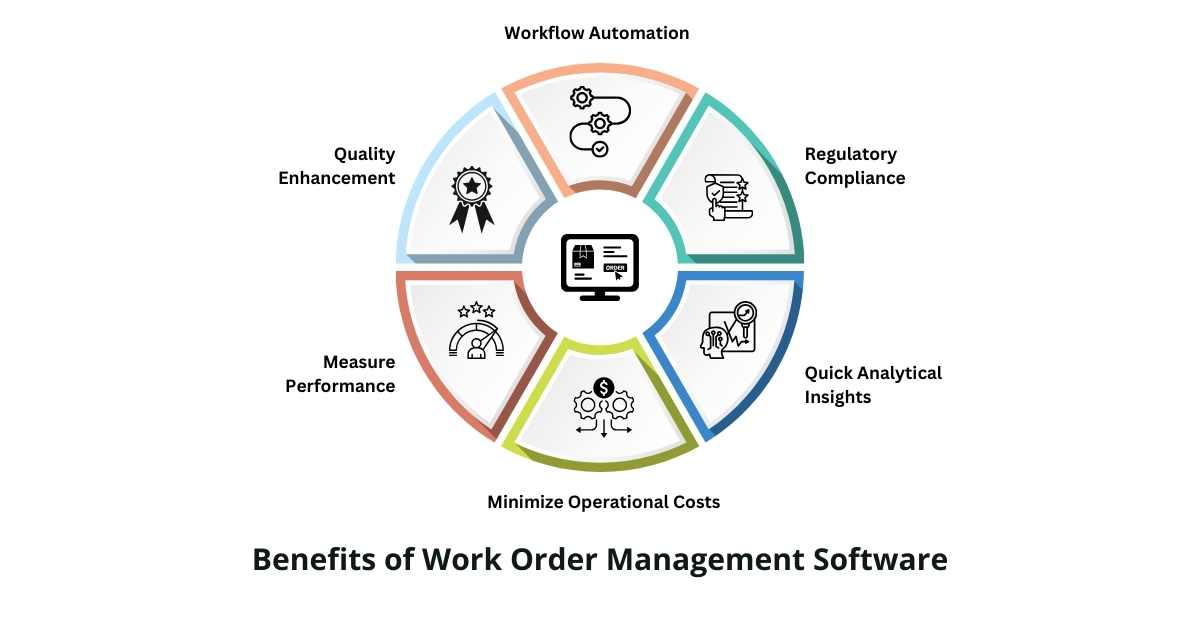
Benefits of Using a Work Order Management Software
1. Workflow Automation
Workflow Automation refers to the process of replacing manual labor work with autonomous tools that can independently carry out routine business processes. For instance, chemical companies use ERP for Chemical Industry to streamline routine tasks such as the generation of order, and benefit from innovation & technological transformation.
2. Quality Enhancement
The Business Management Software keeps a detailed log of all the operational challenges and documents everything in the order. Ensure adherence to the higher industry standards and consistency in the process for better results.
3. Measure Performance
Other advantages of ERP include tracking the work progress from its start to completion and managing multiple orders through a single unified solution. Regularly tracking your progress is important to identify potential bottlenecks and take corrective measures.
4. Minimize Operational Costs
One of the biggest benefits of deploying specialized Maintenance Software for it is cost efficiency. Automate your tasks, reduce dependence on manual labor, and reduce your operational expenses. Your employees can focus on more productive operations that warrant their attention.
5. Quick Analytical Insights
Turn long & complex data into quick analytical insights that aid instant & accurate decision-making. Make use of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (Ai) for data mining, predictive analytics, and gauging new market opportunities.
6. Regulatory Compliance
ERP implementation acts as the central repository of pan-organization-wide information which serves critical business insights for fast & accurate decision-making, and meeting audit requirements. It saves you from the hassle of unnecessary legal consequences such as fines, penalties, and lawsuits. Overall, it helps foster trust among external stakeholders such as your clients, suppliers, and partners.
Limitations of the Work Order Management Software
1. Upfront Costs
Small and medium-sized companies face the hurdle of significant upfront costs with On-premise ERP. Thanks to the evolution of cost-efficient Cloud ERP, it is no longer a big concern.
2. Employee Training
Merely implementing a Work Order Management software isn’t enough. You will need to train your employees, which may take a lot of your time, effort, and money.
3. Compatibility Issues
Before selecting your software for Maintenance Repair and Overhaul, make sure that you’ve done adequate research. Some low-quality software may not support integration with legacy tools and spreadsheets.
4. Unexpected Delays
Unexpected delays may also occur during the implementation phase. It’s common to encounter data conversion issues, and data quality & reliability issues which may delay the preplanned implementation.
Work Order Example
ABC Ltd is a pharmaceutical company involved in the production and distribution of pharma products. As a cost-saving measure, it has opted for hundreds of machinery on a rental basis from XYZ Ltd. At some point in time, a worker detects a malfunction with one of the machines and reports it to his immediate Manager, who generates an order using a Pharma ERP Software and submits the same to the machine owner. He gets an assurance that the repair work will be carried out soon.
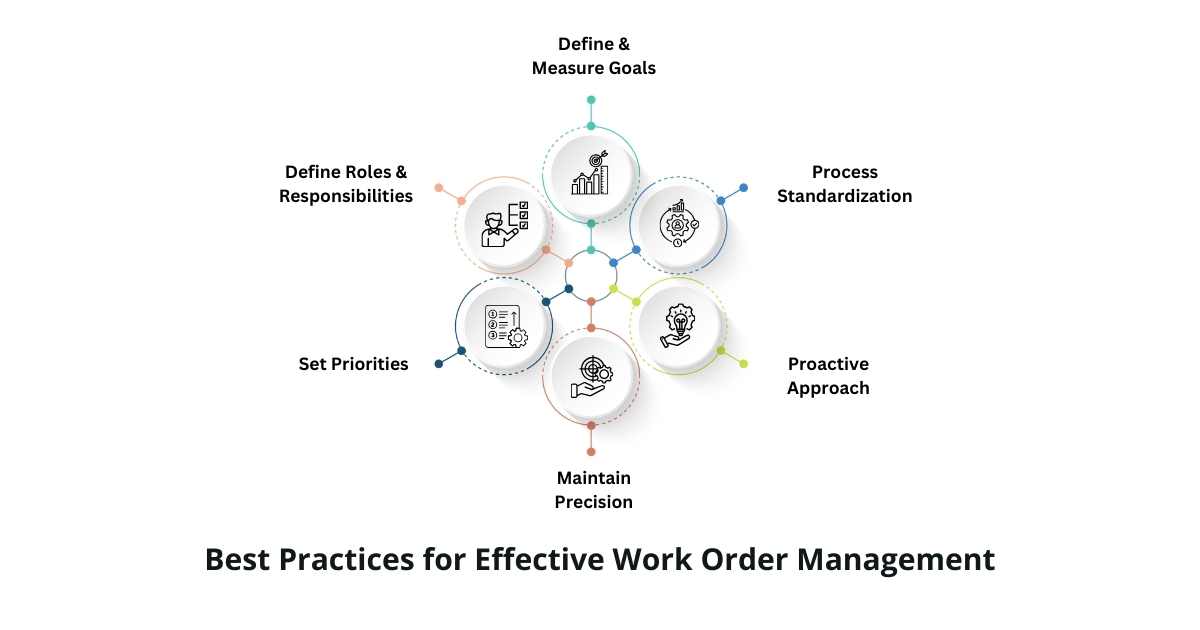
Best Practices for Effective Work Order Management
1. Define & Measure Goals
Setting up goals is important to ensure everyone’s working on a shared vision. Ensure your organizational goals and departmental goals are clearly defined. Regularly measure your work progress using various Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
2. Define Roles & Responsibilities
Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of the concerned parties to increase efficiency, avoid confusion & chaos, and set clear expectations. When the roles and responsibilities are not clearly defined, there is an added risk of duplication of work.
3. Set Priorities
Another important aspect of managing it is to set priorities among low, medium, high, and critical. Clearly establish a procedure for prioritizing them based on their nature & significance.
4. Maintain Precision
Make sure that your order is clear and specific to the points. Avoid using words or phrases that could lead to confusion or misinterpretation and derail the specific activity. For example, clearly specify the aim of scheduled maintenance and the specific machines that will undergo maintenance & upgradation.
5. Proactive Approach
Focus on building proactive strategies rather than reactive ones. For example, use a Manufacturing ERP to formulate strategies to plan Preventive Maintenance activity for your organizational equipment & machinery instead of waiting for an asset to break down and disrupt production activity.
6. Process Standardization
As we’ve seen, there are different types of orders. Standardizing them with a common format using an ERP Application will help you maintain quality and consistency, and ensure the message is clearly communicated to all the concerned parties accountable for the activity.
Difference Between a Work Order & Work Request
| Work Order | Work Request | |
| Concept | A Work Order is a digital document outlining the nature of a task and the complete procedure outlined for its smooth execution. | A Work Request is a formal request communicating the requirement for a task to be performed |
| Example | A maintenance manager approves a Work Request and compiles an order outlining the detailed plan, contracting company, repair date & time, and cost estimations. | A machine operator submits a formal Work Request to the relevant team or department requesting their attention after a machine malfunction. |
| Nature | Authoritative | Formal request |
| Issued by | Management or responsible authority | Employees or customers |
| Request Phase | The final stage after authorization | Initial stage before authorization |
| Next Stage | Actual Task/ Procedure | Authorization & Work Order |
Summing Up…
A Work Order plays a critical role in the planning and execution of a process such as regular asset repair or maintenance. It brings clarity to the entire process, sets roles & responsibilities, and ensures everything related to the task is well-documented.
Sage X3 is a single transformative solution that lets you take the benefit of innovation & rapid technological transformation to turn your business into a well-oiled machine. It comes with a host of features such as an intuitive user interface, extensive customization options, data analytics, Business Intelligence, and superior demand forecasting capabilities that build a strong foundation for your digital transformation & success.
FAQs
1. What is the Work Order Meaning in Simplest Words?
Work Order is an electronic document that provides detailed instructions for the execution of a business activity such as machine repair or maintenance. It serves technical details such as nature of the work, contracting technician, repair or maintenance schedule, and other information required for its smooth execution.
2. Who Creates a Work Order?
As we’ve already discussed in the “What is Work Order” section, it is created by anyone responsible for overseeing the completion of a specific work or activity. For example, a Production Manager responsible for overseeing the production activity may create it to ensure a machine breakdown gets fixed as soon as possible and doesn’t disrupt the production activity.
3. What are the Contents of a Work Order?
As we’ve seen in the “What is work order” section, it may contain hosts of information necessary to perform a specific task. Here are its contents:
- Details about the machinery or equipment requiring repair or maintenance
- A brief description of the problem (such as technical details about the machine failure)
- The nature of the diagnostic procedure required to be performed
- Task priority (low, medium, high, or critical)
- Task checklist (A list of all major procedures that must be followed from start to completion)
- Date of repair/ maintenance and estimated date of completion
- List of machine components that need to be repaired or replaced
- Requirements for skilled manpower
- Safety instructions pertaining to dangerous or high-risk activities
- Task assignee (internal employee, or contractual company)
- Pricing estimations (including repair/ maintenance costs, component replacement costs, and rental expenditures of special equipment)
4. What is the Purpose of Drafting a Work Order?
As we’ve already discussed in the “What is Work Order meaning?” section, it serves different purposes as outlined below:
- Increase asset longevity and performance
- Reduce potential machine breakdowns and production disruptions
- Comprehensive asset management and repair
- Minimize the cost spent on machine repair & replacement
- Preordering raw materials using supply chain management tools
- Ensure equipment & labor safety
- Compliance with industry norms and equipment safety
5. How is a Work Order Different from a Purchase Order?
A Purchase Order is typically issued to a vendor requesting the purchase of goods & services. It serves as a contract and is typically handled using an Online Procurement Management System. In contrast, as we’ve already seen in the “What is Work Order meaning?” section, it outlines how specific tasks or activities are required to be completed such as machine maintenance or repair during a specified timeframe. Anyone can serve it, including the Management, Product Safety Officer, or even customers. It serves only internal purposes, and it is not legally binding at all.
6. Can You Streamline the Work Order Creation Task?
Yes, it’s very much possible to streamline its creation task. In fact, as it has become the backbone of the company’s routine operations, a large number of businesses across India are adopting automation to avoid the labyrinth of paperwork and minimize administrative hurdles. The Best ERP Software in India has proven to be a game-changing solution for this.
7. What is a Work Order Lifecycle?
Its Lifecycle involves the following important phases:
- Problem Identification: This is the initial & most important phase that involves identifying the need for an activity (such as machine maintenance or repair).
- Work Order Issuance: The next step is to draft an actual order containing all the required information such as the problem description, location, estimated budget, etc.
- Timeline Scheduling: Schedule a timeline to execute your activity and allocate appropriate capital, and resources.
- Work Delegation: The next step is to assign the task or activity to the appropriate team or personnel and facilitate access to the required materials & tools.
- Notes Taking: Take the closing notes of your order as soon as it approaches closure. These notes may include information about the resources used, time spent, and any observations.
- Final Analysis: Perform a thorough analysis of the finished work to identify the scope for improvement and prepare notes for the Management’s consideration.