What is Material Control?
Material control involves the use of various methods to plan, procure, store, handle and consume raw material, aimed at controlling material costs, minimizing wastage and ensuring a smooth production run through continuous material availability while avoiding overstocking.
In other words, it optimizes inventory investment for a business by procuring the right quantity at the right time, thus improving its profitability and efficiency. The methods of material control involve demand forecasting, material purchase, storage, maintaining inventory records, and more.
What are the Objectives of Material Control?
According to the TERI report on ‘National Resource Efficiency Policy for India’, the share of average material costs in total production cost in Indian manufacturing setups is more than 70%, which is way higher than 40 to 50% average material costs in developed countries.
Given how material consumption impacts production costs, it highlights the need to adopt efficient techniques of material control and implement them with the robust support of modern ERP software.
Let’s look at the key objectives of material control:
- Production Continuity: Maintain a smooth production flow by ensuring the availability of exact material specs for different production lines and production stages, reducing the lead time.
- Cost Optimization: Tighten your hold over production costs by planning your material purchase, and avoid unnecessary cost escalation due to urgent and unplanned purchases.
- Reduce Wastage: Cut down on material consumption by minimizing wastage during storage and handling by tracking production and inventory errors in your ERP system.
- Prevent Shortage: Monitor the stock levels in your warehouse, forecast demand and ensure a regular supply of inventory, and also prevent overstocking.
- Maintain Quality: Set quality assurance standards by ensuring the usage of the right material during production, which meets the design requirements and is at par with industry benchmarks.
- Enhance Efficiency: Upgrade your existing material control mechanisms to reduce handling time, meet market demand and improve your production efficiency.
What are the Top 10 Techniques of Material Control?
A comprehensive understanding of various methods of material control makes sure you choose the one that aligns with your business objectives and production processes. Let us understand the meaning of different material control techniques and how it help you improve inventory control.
1. ABC Analysis
ABC Analysis is a material control technique where you place your inventory into three categories, namely, A, B, and C, based on how expensive they are and how frequently they are consumed in production. Items that fall under the ‘A category’ are the most valuable and they require accurate inventory control. ‘B category’ items are of moderate importance and require relatively less control whereas ‘C category’ are of less importance and do not require close monitoring.
The classification of inventory into the ABC category is automated through manufacturing ERP software, where you get a granular view of all the materials by value and consumption. The up-to-date data on each material helps you analyze and choose its category or change the category to align with changing order demand. As a result, you can prevent stock-outs of high-value items, take decisions on what to stock and save time and money in managing inventory.
Read more: What is ABC Analysis in Inventory Management System?
2. VED Analysis
VED Analysis is a method of material control to identify parts critical for maintaining production continuity. The raw materials are classified into Vital, Essential and Desirable categories. Vital parts are critical for operations and their stock-out can severely disrupt production. Essential parts, may not be as critical but their shortage can reduce production efficiency. Desirable items are those that improve processes in some ways, however, they do not affect operations in the short run.
Having the ability to classify materials into vital, essential and desirable categories gives you clarity on what needs to be purchased on a priority. With VED analysis, you can achieve better cost efficiency and minimize inventory shortage risks through adequate checks and alerts triggered via inventory management software. It makes sure that you have sufficient safety stock for critical items while paying close attention to their storage conditions and high-quality material procurement.
3. FNSD Analysis
FNSD Analysis groups the inventory based on their rate of consumption. FNSD stands for fast-moving, non-moving, slow-moving, and deadstock. Fast-moving items are very high in consumption, non-moving are consumed at moderate rates, usually within a year. Slow-moving items have a low turnover rate while dead stock lies idle for a long time with no foreseen demand.
The purpose of FNSD analysis is to set order priority based on the rate of consumption of items, how long they stay in storage and accordingly set their reorder point. It enables the identification and removal of dead or underperforming stock while helping you to plan better and make informed decisions on inventory.
4. Perpetual Inventory System
A perpetual inventory system is a method of managing inventories that allows for real-time updates and continuous tracking of inventory levels after each transaction. It improves reporting and inventory accuracy. This system can be easily integrated with purchase and sales systems to automatically document purchase and sales prices and determine the cost of goods sold.
With a perpetual inventory system, business owners can prevent low material supply situations, automatically modify reorder points, and stay continuously updated on inventory levels. It results in increased inventory efficiency and control by substantially reducing the need for physical inventory counts.
5. JIT Inventory System
Just-in-Time or JIT inventory system is a method of material control where goods are only received when they are needed for production, thereby enhancing production efficiency and increasing material turnover. This system requires perfect collaboration with suppliers as the suppliers need to be ready with the material when the manufacturer orders it.
Also called the pull system of inventory, the JIT system is executed via an ERP solution that helps manufacturers avoid the risk of obsolescence and significantly reduce storage space. Manufacturers focused on total quality management prefer this method of inventory control as they are frequently looking for better quality or innovative raw material to improve the quality of the final product.
You Might Also Like: What is Total Quality Management?
6. Double Bin System
One of the popular techniques of material control, the double bin or kanban system uses two bins to store inventory. The first bin contains the working stock and the second bin contains the reserve stock. The working stock bin caters to the current production demand whereas the reserve stock bin maintains the inventory level equivalent to the amount to be used until the new stock arrives.
This inventory replenishment technique ensures that there’s always sufficient material available for production. Manufacturing setups will relatively stable product demand prefer this system as it helps them reduce inventory ordering costs and ensure better inventory planning. Automating this ordering system via procurement software can generate significant cost savings for your company.
7. Inventory Costing
Inventory costing in material control is a technique used to determine the value of each stock item the company holds. Accurate assignment of cost using the ERP application gives the company a clear picture into their total costs associated with holding inventory, including the storage costs, labor costs, as well as ordering costs and the cost of raw materials.
Such cost-saving techniques of material control are excellent for financial planning and cash flow management. Giving transparency into the holding costs, the inventory costing method allows efficient tracking of inventory throughout the production and sales. It helps avoid excessive spending on inventory by optimizing new inventory purchases.
8. Level Setting
Level setting is a material control method to set different levels of inventory, helping you to closely monitor the consumption of inventory and timely order fresh supplies. It involves setting the reorder point, minimum level, maximum level, danger level, and average stock levels.
Level setting ensures what stock levels need to be maintained at any given point. As soon as a predetermined level is reached for any stock item, the ERP software sends an alert to the purchase manager and the company can consequently begin the purchase requisition process and automatically generate the purchase order.
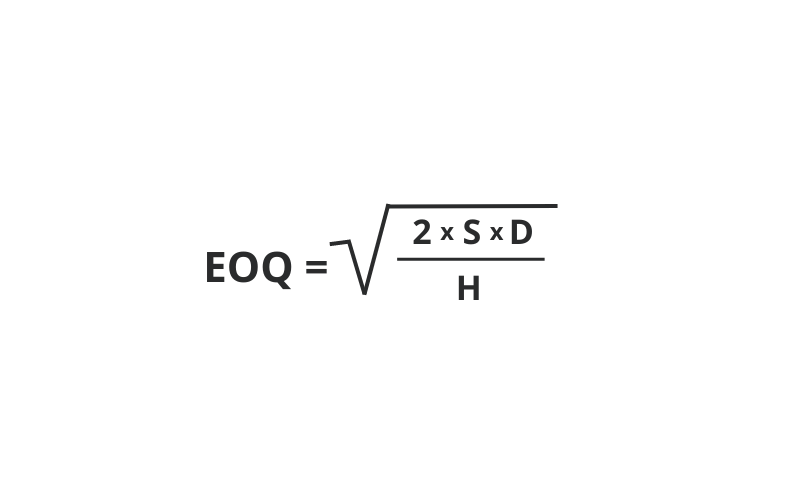
9. Economic Order Quantity
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is an inventory technique to identify ideal order quantity that meets demand without creating shortage of inventory. This method of material management is used to maintain healthy working capital by avoiding overstocking. Calculation of EOQ takes into consideration annual product demand, cost of ordering, and holding costs per unit.
The formula for EOQ is as follows:
Where:
D = Demand rate (units sold per accounting period)
S = Order cost (per order)
H = Holding cost (per unit per accounting period)
Your ERP software can automatically determine the economic order quantity for any product, thus helping you save time and maximizing profits.
10. Input Output Ratio
Input Output Ratio is part of the ratio analysis methods of material control where we determine the ratio of input raw material that goes into production and the standard raw material content of the output. This ratio helps you to determine the quantity of material being consumed and identify areas for improvement in production processes.
Besides controlling material consumption and saving costs, this ratio analysis technique also helps in improving product quality that comes with efficient production process. ERP for chemical industry keeps a detailed record of input-output ratios to help you track your material consumption and implement cost-efficient production methods.
8 Steps of Material Control
No matter what methods of material control you choose, follow these steps to ensure the success of your initiatives.
- Set Standards: Document the material specifications and quality standards that you aim to use in your production.
- Select Suppliers: Select the suppliers that align with your objectives and are capable of meeting your specifications and delivery timelines.
- Place Order: Begin the purchase process with purchase requisition within the online procurement management system to get approvals for material purchase and generate purchase orders.
- Receive Order: Make sure to inspect the material on receipt so that it complies with your quality standards and specifications.
- Store Material: Store the material in your warehouse as per storage guidelines for each product and implement a suitable technique to control inventory.
- Issue Material: Issue the material to the production department through a systematic documented procedure supported via ERP software to avoid misuse of material.
- Maintain Records: Maintain a thorough record of stock levels at various stages of production and generate reports within your ERP system to take inventory decisions.
- Assess Performance: Continuous review of your material control techniques allows you to implement improvement strategies and strive for higher inventory efficiency.
Benefits of Implementing Techniques of Material Control
Here are the advantages you get with implementing material control techniques.
- Avoid Production Delays : Implementing a suitable material control technique dramatically improves your production efficiency and reduces downtime due to inventory unavailability.
- Maintain quality control: Careful material control ensures that you use the right raw material for producing high-quality goods, meeting the specification requirements.
- Minimize inventory investment: Eliminate excess cash tied up in inventory and practice better cash flow management, thus ensuring liquidity of working capital.
- Reduce costs: Reduce storage costs and eliminate inventory waste associated with handling inventory and prevent risk of loss due to damaged or missing inventory.
- Improve supplier relationships: To ensure a steady supply of material, many material techniques require you to collaborate with suppliers, helping you to nurture long-term relationships.
- Enhance client satisfaction: Material control techniques give you real-time insights into inventory levels, improving your ability to accept new orders, meet demand and order timelines.
- Increase flexibility: Get the flexibility to respond to changing customer expectations whether it is new product development or increasing order size, helping you gain competitive advantage.
Challenges in Implementing Techniques of Material Control
Some of the common challenges you may face in implementing material control techniques are as follows:
- Recording error: Automate your inventory record system using the ERP system to prevent errors associated with repetitive manual entries.
- Supplier failure: Certain techniques like EOQ and JIT favor minimal stock levels, which can be counterproductive if your supplier delays the material supply.
- Technology integration: Multiple disconnected systems create data silos, reducing the effectiveness of material control methods. Bring all your operations and tools under a unified ERP application.
- Balancing inventory cost and service levels: Every material control technique offers unique benefits, however, choosing the wrong technique can impact your delivery timelines as you balance costs and stock levels.
Boost Your Inventory Efficiency with Sage X3
Different material control techniques have a unique set of advantages. Choose the one that aligns with your business goals. The implementation of these techniques through technology and automation gives you a competitive edge as it eliminates the need for manual inventory management.
Sage X3 ERP promises efficient control over your material through a range of features that meet the complex demands of the manufacturing industry. With industry-specific modules for procurement, inventory, production and warehousing, your operations achieve remarkable efficiency.
FAQs
1. What Are The Common Techniques of Material Control?
Common techniques include Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory, ABC Analysis and the Perpetual Inventory System. These techniques help in optimizing inventory levels, minimizing costs and ensuring that materials are available when needed without overstocking.
2. What Benefits Do Material Control Techniques Offer?
Implementing material control techniques leads to better inventory management by reducing waste, lowering storage costs, improving cash flow and ensuring timely availability of materials. These benefits contribute to increased operational efficiency and better decision-making.
3. What Challenges Arise in Adopting Material Control Techniques?
Challenges can include the complexity of accurate demand forecasting, integration with existing systems and maintaining the balance between reducing costs and ensuring sufficient stock levels. Additionally, reliance on accurate and timely data is critical for the success of these techniques.
4. How Do Material Control Techniques Match Business Needs?
Each technique serves different business requirements. For example, EOQ is ideal for businesses looking to optimize order quantity and reduce ordering costs, while JIT is suited for companies aiming to minimize inventory levels. ABC Analysis is beneficial for prioritizing control over high-value items, and Perpetual Inventory Systems are essential for businesses needing real-time inventory tracking.
5. What are the scopes of material control?
Material control covers a broad range of activities, including planning of materials, purchasing, receiving, inspection, storage, and issuing of materials. It makes sure that inventory is readily available when needed, while minimizing waste and maintaining accurate inventory records across operations.
6. What is the main objective of material control?
The main objectives of material control is to maintain a regular supply of required raw materials at minimum cost, avoid material shortages or excessive stock, and minimize incidences of dead stock.