What is Profit Maximization?
Profit maximization is a business strategy to achieve maximum profits by optimizing the product price, the level of output and the cost of production, while also ensuring that the firm does not earn profits by using low-quality raw materials. This approach significantly influences the decision-making process in an organization.
For any business to sustain and grow, generating profits is crucial. To maximize profits, it is essential to increase cash flow and improve business performance. To understand this concept better, it’s important to know the terms marginal cost of production and marginal revenue.
Understanding Marginal Cost and Revenue for Profit Maximization
What is Marginal Cost of Production?
Marginal cost of production is a key concept in managerial economics that helps businesses optimize their factory output to maximize profits. It is calculated by determining the change in the total cost of production that happens on producing one additional unit of goods.
Marginal Cost Formula
Marginal Cost = Change in Total Cost of Production / Change in Quantity of Goods Produced
What is Marginal Revenue?
Marginal revenue is a metric for businesses to estimate the additional revenue generated when a business sells one additional unit of goods. It is calculated by determining the change in the total revenue that happens on selling one additional unit of goods.
Marginal Revenue Formula
Marginal Revenue = Change in Total Revenue / Change in Quantity of Goods Produced
What are the Key Features of Profit Maximization?
Here are the key features of profit maximization that will help you to understand this process better.
1. Marginal Analysis
Profit maximization is achieved and analyzed by producing the quantity of goods where Marginal Revenue (MR) equals Marginal Cost (MC).
2. Revenue and Cost
Profit is calculated as the difference between Total Revenue (TR) and Total Cost (TC).
3. Market Models
The approach to maximizing profits differs depending on the market model being followed like perfect competition and monopoly.
4. Resources
The limited resources and their constraints that influence profitability have to be considered, including land, labor and master production schedule.
5. Market Dynamics
Product demand, variable cost fluctuations and competitor’s actions have to be taken into account to ensure long-term profitability.
What are the Objectives of Profit Maximization?
The objectives of maximization of profits are aligned with ensuring the long-term success of the business and protecting the vested interests of its stakeholders.
Let’s look at the various objectives.
1. Rational Goal
For any business owner, the reason to conduct a business is ultimately to earn maximum profits. So an ethical business strategy that leads to maximizing profits is justified.
2. Resource Utilization
Optimum utilization of resources ensures that a firm can earn maximum profit by keeping costs as low as possible while also ensuring strict quality control to avoid wastage and product recalls.
3. Business Performance
As the business grows, so does its desire to earn more profits. Real-time analysis of manufacturing operations with business intelligence software ensures that strategic business decisions are aligned with profit maximization goals.
4. Financial Growth
A business can grow faster only when it can generate high profits and the same are reinvested into new product development, capacity expansion and diversification.
5. Risk Mitigation
Businesses can leverage their profits to manage risks and uncertainties involved in running a business both in the short run and in the long run, including economic downturns, demand fluctuations, supply chain disruptions, etc.
Profit Maximization Formula
For a business to generate maximum profit, the difference between the total revenue earned on selling goods and the total cost of production of goods should be maximum.
The formula is as follows:
Profit (P) = Total Revenue (TR) – Total Cost (TC)
P = TR – TC
Profit Maximization Condition
Profit maximization occurs under two conditions: First Order and Second Order Condition
First Order Condition
Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost of Production,
i.e. MR = MC
The profit earned is maximum when the marginal revenue is equal to the marginal cost. In other words, the marginal revenue that a business earns on selling one additional unit of its goods should be equal to the marginal cost incurred in producing that additional unit.
Second Order Condition
The second order condition states that in the scenario where marginal revenue declines and marginal cost rises, the company must work towards fulfilling the first order of MC = MR to maximize its profits.
Profit Maximization Model
Depending on the market model being followed, the level of output at which a firm earns maximum profits can significantly vary. In the table below, notice the differences between two market models, monopoly and perfect competition.
| Profit Maximization | Price Setting | Level of Output (Quantity) | Marginal Revenue Curve | |
| Monopoly | MR = MC | Price setter | Less output at higher price compared to perfect competition | MR curve cuts the demand slope at a lower point |
| Perfect Competition | MR = MC | Price taker | More output at lower price compared to monopoly | MR curve cuts the demand curve at a higher point |
Let’s understand this with the help of diagram.
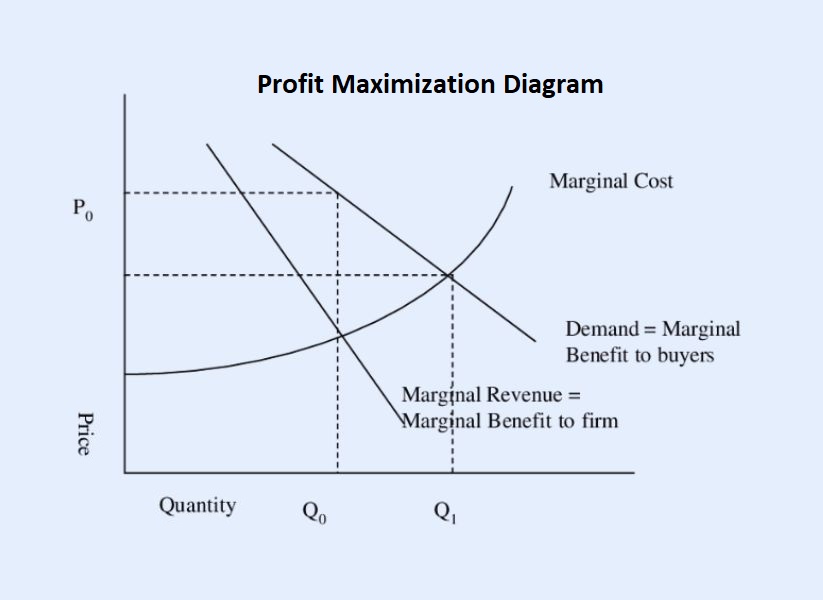
Profit Maximization Diagram
In a perfectly competitive firm, Marginal Revenue (MR) = Marginal Cost (MC) at the profit-maximizing quantity, Q1. In the diagram for perfect competition, MC curve intersects the demand slope line at Q1 (profit-maximizing quantity), where MR = MC.
So, Price (P) = Marginal Revenue (MR) = Marginal Cost (MC)
On the other hand, in a monopoly firm, MC curve intersects the demand slope line at Q0, thus MC = MR at Q0 (profit-maximizing quantity), but the monopoly firm can charge a higher price due to the lack of competition.
So, Price (P) > Marginal Revenue (MR) = Marginal Cost (MC)
For that reason, a monopolist will produce a smaller quantity than a perfectly competitive firm. Also, you’ll notice that the demand slope for monopolist is steeper because consumers are sensitive to a steeper price rise than a gradual price rise.
Thus, P0 > P1 and Q0 < Q1
What is the Profit Maximization Example?
Assuming that the product demand and product price remain the same, a firm can adopt various cost-saving strategies to maximize its profits. Here are some of the practical examples that businesses can use to reach their goal of profit maximization.
- Material Cost Optimization – Find cheaper alternatives to the existing raw materials without compromising on product quality and durability, although it may not be possible in some cases. Other methods to cut raw material costs include negotiating better prices with vendors, exploring cheaper shipping options, or looking for a vendor closer to production facility.
- Production Streamlining – Streamlining the flow of production line and assembly line reduces bottlenecks, minimizes idle time and increases the number of units produced per hour. As a result, it leads to higher resource utilization, improves operational efficiency and cost savings. Adding extra shifts is another way to maximize space utilization and increase production volume.
- Boosting Inventory Turnover – Businesses can adopt best inventory management practices like just-in-time to increase inventory turnover ratio. Accurate forecasting of demand using inventory management software helps to maintain the right inventory levels, minimizes holding costs and the risk of obsolescence, improving overall financial performance.
- Cost-efficient infrastructure – Invest in energy-efficient machinery, appliances and HVAC systems, and use renewable energy sources like solar panels to cut down electricity consumption. Consolidate operations by bringing multiple facilities under one roof. Sublet unused spaces to generate additional revenue. Optimize all your physical and digital assets using asset management software to maximize ROI.
- Employee Training – Training workforce to adopt cost-saving measures is an effective way to eliminate waste and optimize processes. Periodically training employees on best practices about quality control, efficient use of resources helps reduce wastage of materials and unwanted expenses. Educate them on preventive maintenance procedures to avoid costly equipment breakdowns and downtime.
Profit Maximization Theory and its Assumptions
The neoclassical economic theory of the firm states that the firm exists with the sole objective of generating profits. The goal of making more profits influences all decisions on resource allocation, production techniques, pricing levels and level of output. The theory of the firm is based on certain assumptions:
- The business operates as a single-commodity producer
- The entrepreneur makes rational decisions.
- The business owner also serves as the manager.
- Costs associated with different factors of production remain constant and predetermined.
- The market environment is not perfectly competitive.
- The theory assumes a fixed time frame without changes in trends over time.
- All units of the factors of production (like labor and capital) operate with consistent efficiency.
These assumptions is the reason why this theory is often criticized, because modern businesses operate in a dynamic and competitive environment with a focus to maximize profits in the long run and not just meeting short term business goals.
What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Profit Maximization?
As profit maximization theory is narrowly focused on maximizing profits, it certainly has some advantages, but there are also many disadvantages we need to be aware of. Let’s take a look at both.
Advantages of Profit Maximization
1. Lean Processes
Business processes like production line, assembly and storage are carefully planned to deliver peak performance, avoiding all wasteful practices.
2. Economies of Scale
Businesses have an opportunity to scale operations and increase production volume to the point where the cost of production per unit is minimal.
3. Financial Growth
High profits ensure high cash flow that can be smoothly tracked with financial management software, allowing businesses to plan expansions and ensure long-term success.
4. Resource Allocation
Allocation of manpower, machinery and raw material is performed most efficiently to extract maximum use out of limited resources.
5. High Productivity
Human resources are incentivized to be as productive as possible to maximize production levels, setting higher benchmarks for time efficiency.
Disadvantages of Profit Maximization
1. Short-Term Focus
For profit maximization in the short run, a business owner may overlook long-term growth strategies, causing the business to fall behind its competitors.
2. Reduced Employee Morale
The employees are constantly pushed to perform better than before, which may lead to dissatisfaction and lower their morale.
3. Ethical Issues
Serious ethical issues on the factory floor like labor exploitation, unsafe working conditions and environmental harm can hamper business reputation.
4. Increased Risk
Regulatory penalties, emerging technologies, change in customer preferences and demand fluctuations may lead to unforeseen events, causing business loss.
5. Customer Dissatisfaction
Inferior quality products and higher prices may turn the customers away from the business, and pursue better quality products offered by competitors.
Final Words
The condition to ensure maximum profit for a firm is to produce a quantity at which marginal revenue and marginal cost are equal. However, the profit-optimizing quantity for each firm will vary depending on which market model the firm is operating in.
Sage X3 ERP offers an effective solution to track your firm’s costs and revenue. This automated solution ensures that you don’t miss out on analyzing the critical financial metrics in real time and gain valuable insights into your business operations.
FAQs
1. What is the Profit Maximization Definition?
Profit maximization meaning is that it is a business strategy where a company determines the production levels, price levels and production costs at which it can earn maximum profits. It achieves this by analyzing the marginal cost and marginal revenue.
2. What do you Mean by Profit Maximization in Financial Management?
Profit maximization in financial management means taking all financial decisions with the objective of maximizing profit, considering the cash flow, investments and savings.
3. How to Achieve Profit Maximization?
A business can maximize its profit through efficient operations, increased sales revenue and cost-saving measures, all contributing to increased profitability.
4. What is the Profit Maximization Rule?
The common rule for profit maximization is that a business should produce sufficient goods to increase total revenue, where marginal revenue equals or is more than marginal cost.
5. What are the Conditions for Profit Maximization?
The conditions for profit maximization are:
Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost, i.e. MR = MC
Or Marginal Revenue > Marginal Cost, i.e. MR > MC