What is a Product Portfolio?
Product Portfolio is a high-level overview and a collection of all the products offered by the company, along with other supportive information such as their niche positioning, and contribution to the company’s overall strategic goals.
Product Portfolio enables your business to adopt a more customer-centric approach, stay focused on your goals, and make the most out of the market opportunities. It plays an important role in identifying the best and worst-performing products so that decision-makers can make informed decisions to align organizational resources and enhance profitability.
3 Popular Product Portfolio Examples
Now that we’ve discussed what is Product Portfolio, let us have a look at some of the most popular Product Portfolio examples.
1. Apple Inc.
When it comes to technology, Apple needs no introduction. Over the years, Apple has manufactured everything from an iPhone, iPad, iPod, MacBook, and Apple TV to the Apple Watch. Each of these products is very well-marketed and tailored to different consumer requirements.
2. Microsoft Corporation
The software giant has produced several remarkably diverse range of software products that cater to both individual and business needs. For example, Microsoft Windows, Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft PowerPoint, Microsoft Access, Microsoft Edge, Visual Studio, and Xbox Game Studios, among others.
3. Procter & Gamble (P&G)
Procter & Gamble (P&G) produces a variety of products for different consumer segments such as health care, beauty, grooming, and household. It focuses on building a strong brand portfolio and a global distribution network for the company’s growth & success.
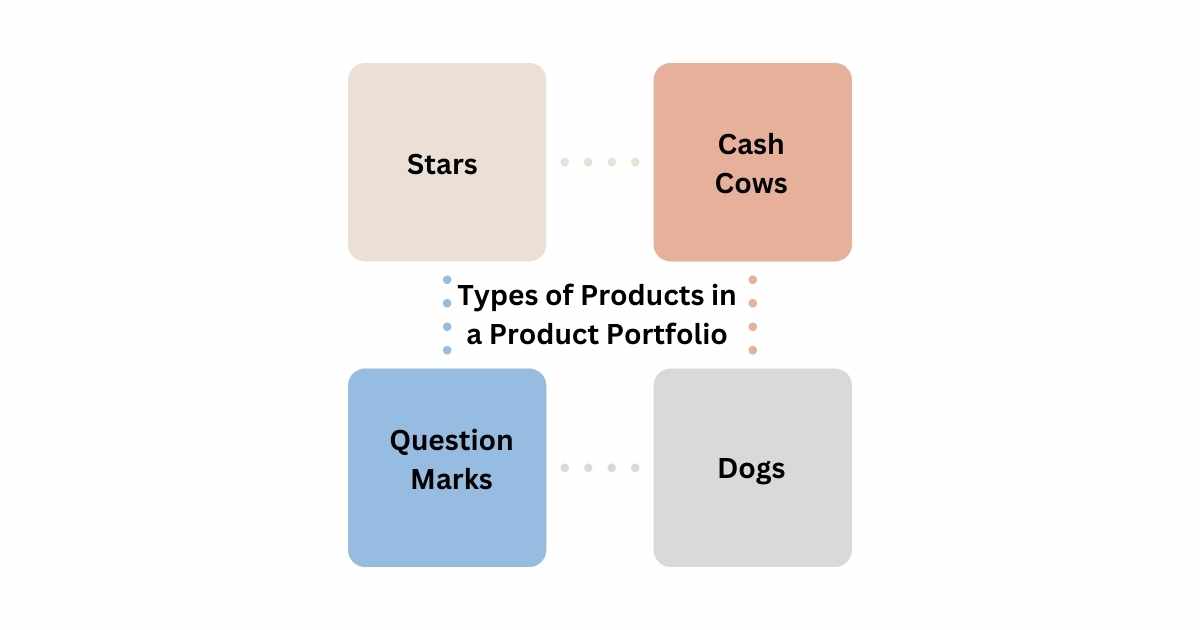
What are the Types of Products in a Product Portfolio?
Wondering what are the different types of products in a Product Portfolio? We’ve categorized them into 4 types based on their income generation.
1. Stars
Star products are typically high-income generating, yet costly products. They are typically launched in a highly competitive and rapidly evolving market.
2. Cash Cows
As the name implies, these products typically require a smaller investment and yield higher returns. This is because they still dominate industries that have already stopped growing.
3. Question Marks
The future of these products is uncertain. With the right strategic decisions and a sufficient resource base, these products have the potential to either generate significant revenue or fail.
4. Dogs
These products are typically a liability to the business due to their lower market share. Rebranding or redesigning them can help businesses focus on more profitable aspects.
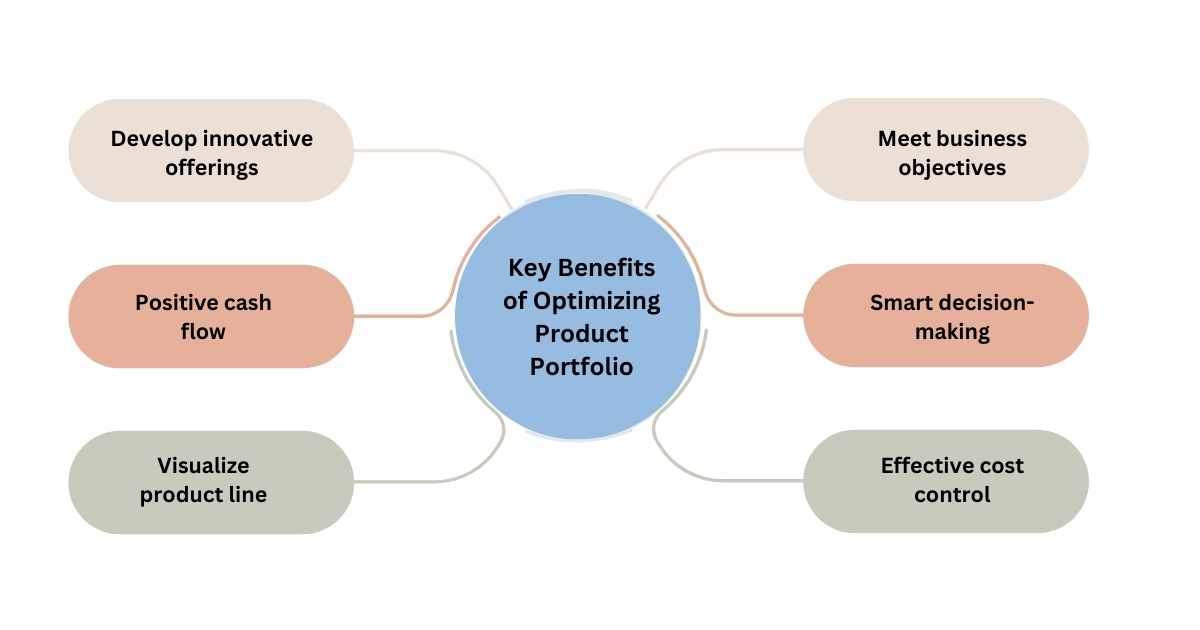
Key Benefits of Optimizing Your Product Portfolio
You might be wondering, why should you be spending your time and resources on managing and optimizing your Product Portfolio. We’ve got the answer:
1. Develop Innovative Offerings
Optimizing your portfolio helps you develop new innovative offerings that leverage modern technology & tools and provide value to the users. By consistently developing innovative products, your business will be able to distinguish itself from the competitors.
2. Meet Business Objectives
Merely setting up your business objectives isn’t sufficient. A comprehensive product portfolio will be able to help you align your products to your strategic business objectives. This is crucial for business sustenance and growth.
3. Positive Cash Flow
As we’ve already define Product Portfolio above, it’s clear that a strategically built Product Portfolio helps you maintain a positive Cash Flow Statement which eventually contributes to effective planning & coordination, business expansion, and profit maximization.
4. Smart Decision-making
Business executives will gain access to the most accurate & up-to-date information through your product portfolio. Eventually, they will be able to make the right decisions at the right time for the greater needs of the organization.
5. Visualize Product Line
Product Portfolio will make it easier to visualize your entire product line with a single glimpse and evaluate the overall effectiveness of your latest marketing strategies.
6. Effective Cost Control
In today’s time of higher inflation and challenges with the supply chain, cost control is imperative for businesses. A well-managed Product Portfolio helps you avoid overspending, save more money, and grow faster. If you haven’t guessed already, the Best ERP Software in India also provides you with robust tools & modules to cut costs and maximize your revenue.
Limitations of Product Portfolio Management
While effective Product Portfolio management is vital for every manufacturer, it has certain limitations too:
1. Dynamic Market Conditions
Market conditions are never static, they keep changing. Businesses have to keep their portfolio relevant to new market conditions. Otherwise, they risk becoming obsolete and they might lose their market share to the competitors. Worry not, you could overcome this limitation using an ERP application.
2. Inconsistency in Innovation
Another limitation of Product Portfolio Management is inconsistency in innovation. Businesses have to focus on innovation and make better use of new technology & tools to improve their product portfolio. A lack of innovation can lead to difficulties in selling the products.
3. Inefficient Use of Resources
Business resources are typically categorized into human, capital, and machinery. There is a need of better coordination between these resources to prevent portfolio imbalance which can have a long-lasting impact on your business.
4. Data Overload
One of the most common problems faced by organizations while managing portfolios is that of data overload. Excessive datasets can make the decision-making a sluggish & inaccurate process.
10 Proven Tips for Effective Product Portfolio Management
Do you want to master the art of effective Product Portfolio Management? Here are the 10 proven tips:
- SWOT Analysis: Perform a thorough SWOT Analysis of your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Identify Risk Tolerance: Identify your risk tolerance, i.e. the level at which you can tolerate risks. Accordingly, plan your strategies.
- Diverse Product base: Invest in numerous products to reduce the risk of over-exposure. Investing in multiple products will help you manage risk.
- Analyze Market Factors: Markets are dynamic, not static. So, consider the impact of seasonal demand spikes, changing consumer preferences, technological shifts, wars, and pandemics. It’s a good idea to regularly perform demand forecasting.
- Competitor Analysis: This is perhaps one of the most important ones. Perform a thorough analysis of your competitors, their strategies, performance, and risk tolerance.
- Prioritization of Products: Not all products generate equal revenue. Prioritize high-revenue generating products to make the best out of market opportunities.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate the right resources to the right product in the right quantity using a dynamic solution such as Sage X3. For example, allocate more resources to high-revenue generating products, and vice versa.
- Continuous Innovation: Stay innovative and invest in new technology & tools to leverage the cost-cutting benefits and provide a seamless experience to the user.
- Stay Updated: Regularly analyze your Product Portfolio. Please don’t risk it becoming obsolete or irrelevant over time.
- Stay Calm: Don’t react emotionally to sudden & unexpected changes in the market. Instead, hold your patience and make strong & data-driven decisions.
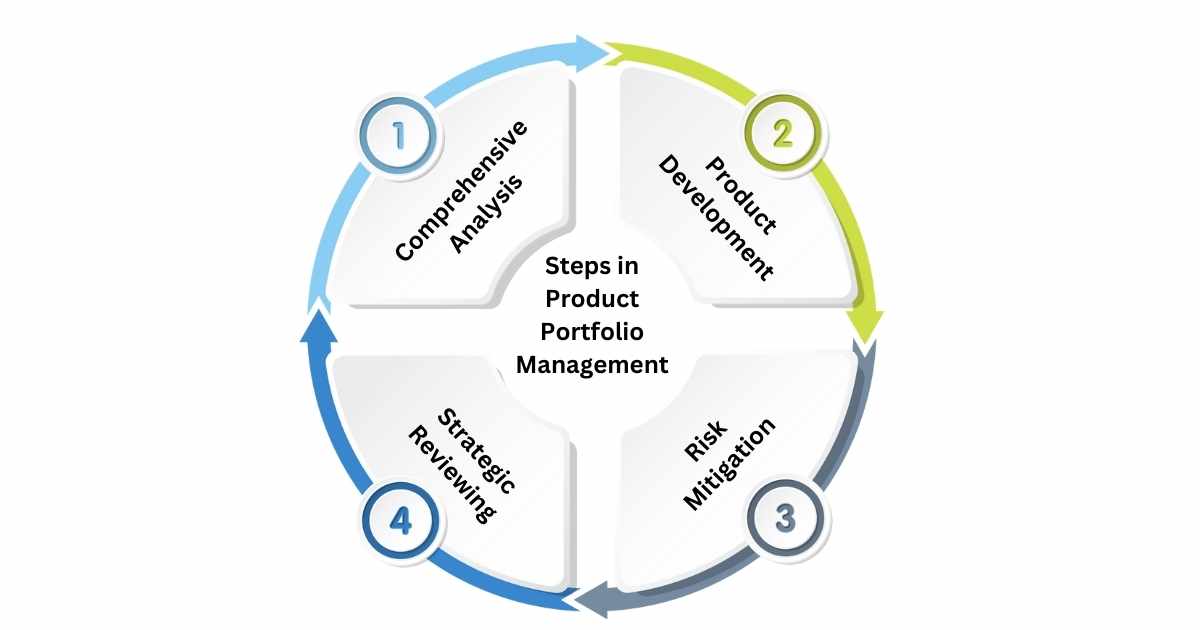
4 Simple Steps for Product Portfolio Management
Product Portfolio Management is a complex process that involves various steps given below:
- Comprehensive Analysis: Performing a comprehensive analysis of the company’s current products, market performance, and strategic goals & objectives. Here again, ERP Software will come to your rescue.
- Product Development: Building a diverse set of products that cater to the different requirements of the consumers. If the company is smaller, it will prioritize one product at a time.
- Risk Mitigation: Risk Mitigation is a strategy used by the company to ensure consistency in its revenue by building a mix of products.
- Strategic Reviewing: Observe the product performance, and make strategic decisions pertaining to continuity, and discontinuation of different products.
Wrap Up
A Product Portfolio is not just a simple list of the company’s product offerings. Instead, it is a comprehensive tool that provides vital information required for strategic decision-making, risk management, and sustained growth. A continuous evaluation of your Product Portfolio is crucial to understand how your products perform in different market segments & conditions.
Product Portfolio allows decision-makers to track the performance of each product and compare it against the changing market conditions. Based on the information in hand, they can make effective decisions to prioritize certain products, and invest additional capital & resources.
FAQs
1. What is the Definition of Product Portfolio?
Product Portfolio meaning is that it is a process of recording all the products sold by your company and performing a thorough analysis of their market performance and growth potential. The idea behind conducting a Product Portfolio Analysis is to understand how each product in your portfolio contributes to the company’s cash flow and make strategic decisions to improve its revenue stream.
2. Is the Product Portfolio Unique to Each Company?
Every company’s portfolio is different as each company’s strategic objectives, visions, and capital base, all differ. Some businesses may give more focus on diversified portfolios whereas others will focus on strategically important products. However, there may be certain similarities in terms of product, type, size & color.
3. What are the Contents of a Product Portfolio?
Generally, a Product Portfolio consists of the following products:
- The company’s primary products that consistently contribute to its income stream
- Company’s old products that may not contribute to its income stream as primary products, but are still not discontinued
- Newly launched products
- Any other complementary products sold as part of the cross-selling strategies
4. Who Uses a Product Portfolio?
Product Portfolio is used by different managers across different hierarchical levels for different purposes:
- Product Development Manager: They use the Product Portfolio to ensure the company’s human, asset, and capital resources align with its strategic goals.
- Senior Product Manager: They use the Product Portfolio to make decisions pertaining to the company’s investments, and compare the performance of each product compared to others.
- Product Portfolio Manager: They make high-level decisions to maintain a balance between the risk-reward ratio.
- Marketing Manager: They ensure consistency in the product’s branding and run tailored campaigns across targeted market segments & niches.
5. What are the Impacts of the Company’s Size on Product Portfolio?
Typically, the portfolios of large established brands are diverse in nature whereas the portfolios of new startups are shorter in size. This is because the established brands have had more time to develop a variety of products. They have gained a considerable revenue base and resources over the years.
6. Do the Product Manager and Product Portfolio Manager Play the Same Role?
No, the Product Manager and Product Portfolio Manager play different roles. Here’s why:
- Product Manager: The role of a Product Manager is to develop a strategic vision for a single product, look after its development & quality check, and ensure it adds value to the customers.
- Product Portfolio Manager: The role of a Product Portfolio Manager is to develop a smooth inter-relationship between the company’s products, and build a diverse set of products that cater to different customer requirements.