What is Inventory Holding Cost?
Inventory holding costs are the various costs a business incurs to store unsold inventory in a warehouse, which includes raw materials, work in progress inventory, and finished goods, and is calculated as a percentage of total inventory value to understand the true liability of holding inventory.
Your inventory holding or carrying costs have a direct impact on business profitability and operational efficiency. When you know how much does it cost to store your inventory, measures can be taken to optimize the cost, free up excessive capital tied up in inventory and divert funds towards strategic investments.
Why You Must Calculate Inventory Holding Cost?
According to the recent report published in the Economic Times, for Indian steelmakers, an inventory pile up of Rs. 89,000 crore has become a major cause for concern due to the import-export trade imbalance. This highlights how important it is to calculate inventory holding costs because unsold inventory can form a significant portion of working capital.
Now, let’s understand why you must determine inventory holding costs.
1. Financial Planning
Having an accurate cost of carrying your inventory with the help of ERP software allows you to draw long-term financial plans for your company. It helps you form a realistic operational budget, calculate tax liabilities, and assess the risk associated with holding inventory.
2. Inventory Levels
Are you one of those who generally keep higher inventory levels to prevent the risk of shortage? While having a safety stock is necessary, having too much of it significantly adds to your carrying costs. One of the most effective methods to optimize inventory levels is to know your carrying costs.
3. Profitability
As inventory carrying costs are non-production costs, they do not reflect in the cost of goods sold (COGS), which are direct costs associated with inventory production. Nonetheless, they have a profound impact on your profitability margins. You would surely want to keep them as low as possible.
4. Competitive Advantage
Inventory holding costs are part of your operational expenses, often hidden from plain view. Perhaps, your focus is completely on reducing the cost of production. However, you will be surprised that your competitors are able to offer better product prices by keeping their carrying costs low.
5. Informed Decision-Making
Decisions on holding inventory become even more crucial when inventory occupies large storage space and requires specific temperature and humidity conditions as in the case of chemicals. Using ERP for chemical manufacturing, chemical manufacturers can make more informed choices.
Also Read: Costing methods and techniques?
What Are the Challenges of Calculating Inventory Holding Costs?
1. Variable Costs
Inventory holding costs can vary significantly. Whether it is the storage costs of leasing a warehouse, labour wages or utility costs, keeping the costs updated in your ERP system ensures accuracy.
2. Estimation Errors
Your cost estimations can go wrong, especially when the cost is allocated towards shared resources. Possibly, you have a common warehouse for different business units with shared labor resources.
3. Inventory Loss Prediction
For many businesses, a portion of inventory does get wasted, like perishable food items. Tracking inventory waste can be difficult for multiple food items with different shelf life without a food ERP.
4. Data Integration
When don’t you have a single view of all your data across departments, carrying costs estimation is not easy. One of the foremost benefits of ERP is bringing data to a common platform for a unified view.
5. Inventory Valuation
Depending on what inventory valuation methods you use, such as FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average cost, your holding costs can differ accordingly. Whichever method you use, maintain consistency.
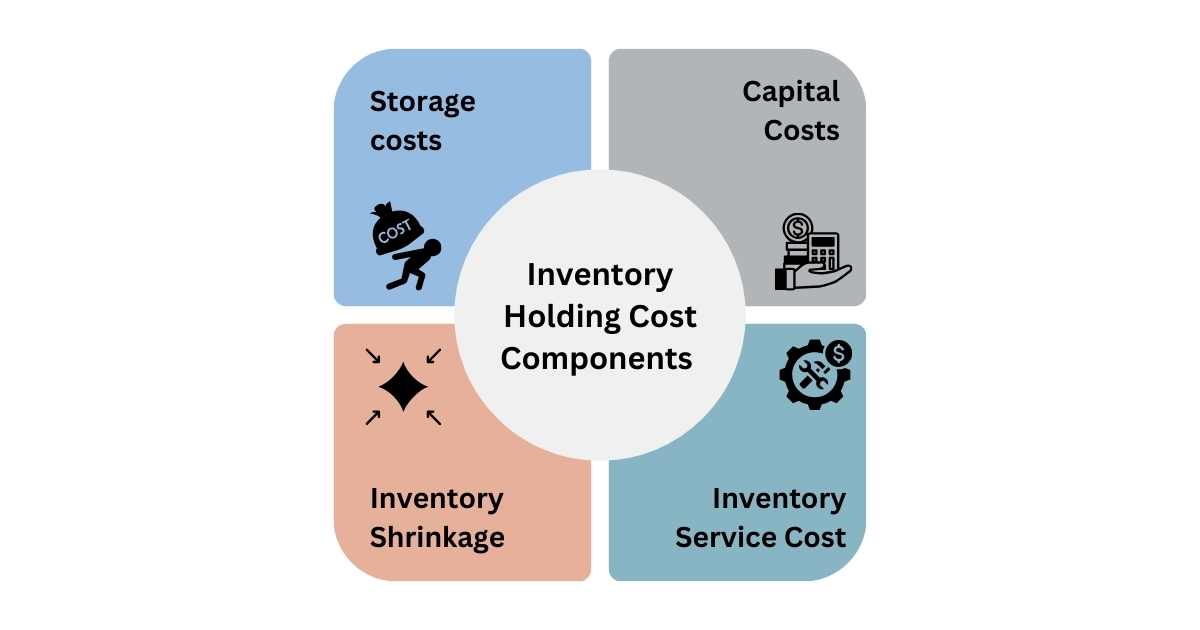
What Are The Key Components of Inventory Holding Cost?
There are four key components of inventory holding costs, whose understanding is necessary before you proceed to calculate your inventory holding costs.
1. Storage costs
Storage costs comprise warehouse expenses, which could be on rent or your own. Additionally, all costs associated with maintaining and operating the warehouse using a warehouse management system, labor and utility expenses are part of storage costs.
2. Capital Costs
Capital costs represent the opportunity costs of capital tied up in inventory. It’s the potential return that could have been earned if the same capital was allocated to other investments. Also, even if you borrow money from banks to buy inventory, the interest paid forms part of capital costs.
Learn everything about opportunity costs here and how to calculate it.
3. Inventory Shrinkage
Many businesses lose a significant amount of money due to inventory loss. It could be due to theft, damage to inventory during handling and storage, or missing inventory due to inventory recording errors. Inventory depreciation costs too are part of inventory shrinkage expenses.
4. Inventory Service Cost
Storing your inventory incurs expenses which are part of inventory service costs. It includes insurance premiums for financial protection against inventory loss or security measures you take to run your warehouse. In certain cases, your unsold inventory can incur taxes too.
How to Calculate Inventory Holding Costs?
Follow this step-by-step approach to calculate inventory holding costs.
1. Calculate Inventory Cost Components
Determine the value of every inventory holding cost component, including storage, capital, inventory service and shrinkage costs. Use your inventory management software to get accurate values.
2. Sum Up Inventory Cost Components
Adding the different components of carrying costs will help you arrive at inventory holding sum. Make sure you include every cost only once to avoid inaccurate financial insights.
3. Evaluate Total Inventory Value
Calculate the total value of your unsold inventory, including raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods, the data for which you will find in your inventory management system.
4. Calculate Inventory Holding Cost
To do this, divide the inventory holding sum calculated in the second step by the total inventory value in the third step. When you multiply this value by 100, you will get inventory holding costs.
Inventory Holding Cost Formula
Inventory Holding Costs (%) = (Sum of Inventory Cost Components / Total Inventory Value) x 100
Example of Inventory Holding Costs
Let’s understand inventory holding costs with an example from the pharmaceutical industry. For a pharmaceutical company, the types of inventory holding costs typically include the following:
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: Pharmaceuticals must comply with strict regulatory standards, which may require additional testing, record-keeping and storage protocols to maintain product integrity.
- Storage Costs: Medicines often require special storage conditions, like temperature-controlled environments, adding to warehousing costs.
- Insurance Costs: Coverage for high-value inventory against risks like theft, damage and product spoilage.
- Capital Cost: These are the opportunity costs of capital tied up in inventory, which could otherwise be invested in research and development, or other expansion plans.
- Obsolescence Costs: Medicines and other pharmaceutical products have a limited shelf life, leading to potential losses if inventory expires before being sold.
So, if the sum of all the above components of inventory carrying costs is Rs. 2 crores and the total value of the inventory is Rs. 10 crores, the inventory holding costs as a percentage of the total value of inventory is 20 per cent. Managing the carrying costs is crucial for profitability due to the sensitive and high-value nature of pharma products.
Also Read: What is Push and Pull Strategy in Manufacturing?
Why Inventory Holding Costs Increase?
There are several reasons why your inventory holding costs increase. The main reasons are as follows.
1. Expired Inventory
Inventory if left unsold can get expired. For a pharmaceutical company, ensuring the right amount of inventory using pharma ERP software is key to minimizing losses due to storage of medicines with a short shelf life.
2. Demand Fluctuations
Demand for your product can vary due to changing customer preferences or poor market sentiment. For a manufacturer, whether following a push or a pull strategy in manufacturing, accurate demand forecasting is essential.
3. Overstocking
Overstocking can significantly affect inventory holding costs. You might have to consider leasing extra warehouse space to store unsold inventory. Moreover, excessive capital locked in inventory can impact the financial health of your company.
4. Supplier Uncertainty
Another external factor that leads to inventory holding cost escalation is the uncertainty of supply. With high supplier lead times, you again tend to overstock. Plus, a significant portion of your supplementary raw materials may stay underutilized until you get the essential item from your supplier.
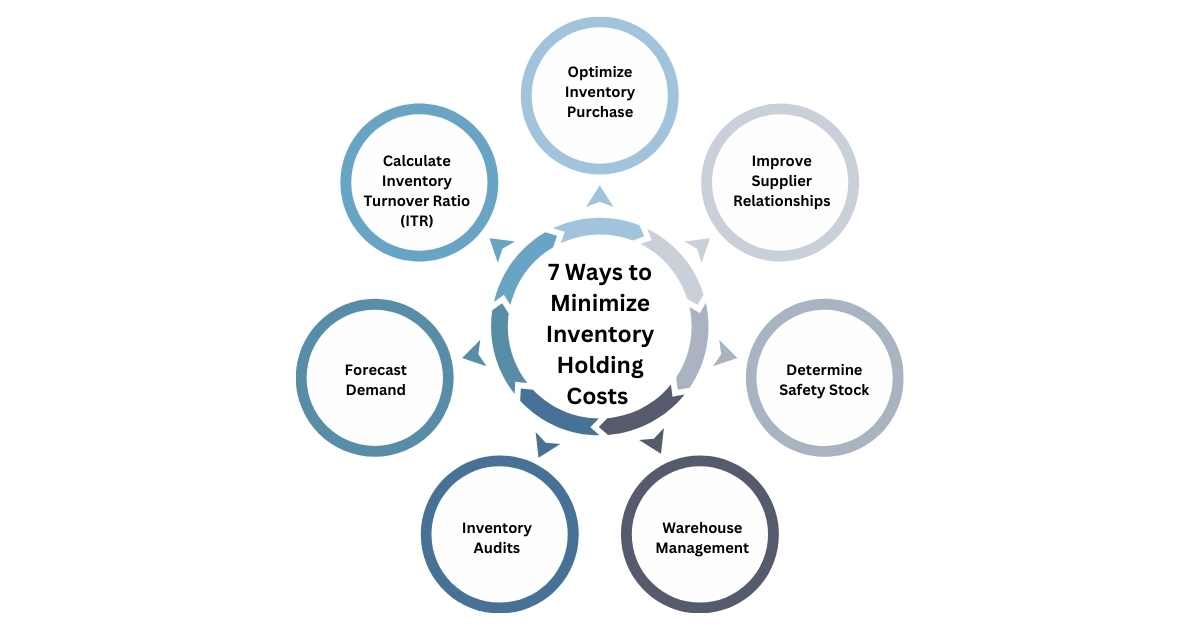
How To Minimize Inventory Holding Costs?
With properly implemented strategies using the best ERP software in India, you can drastically reduce inventory holding costs. Let’s look at the most effective methods to reduce these costs.
1. Optimize Inventory Purchase
Ordering the right quantity of inventory is one way to minimize inventory holding costs. Many manufacturers use Economic order quantity (EOQ), one of the top techniques of material control, using their ERP software to accurately match order frequency and volume with demand.
2. Improve Supplier Relationships
Maintaining a strong relationship with suppliers ensures that your suppliers are willing to make adjustments based on your demand. That means they can assure shorter lead times by sending smaller order volumes frequently, thus reducing the need for you to store surplus inventory.
3. Determine Safety Stock
Safety stock is the buffer stock you keep to meet inventory demand till you receive new stock from your suppliers. Your ERP solution helps you maintain safety stock for every item and it also helps you set automated reorder points when the inventory falls below threshold levels.
4. Warehouse Management
Attain significant cost benefits by efficiently managing your warehouse using WMS. Implement vertical storage to optimize storage space. Besides your picking, packing and shipping processes are streamlined, reducing the handling time and expenses to manage your inventory.
5. Inventory Audits
Frequently inventory audits of your warehouse and production facility make sure that you eliminate excess inventory. It gives you an opportunity to identify slow-moving inventory and find ways to optimize that inventory. For example, a perpetual inventory system allows real-time inventory tracking.
6. Forecast Demand
Demand forecasting feature in top manufacturing ERP software allows you to make informed decisions about resource allocation, production planning and determine optimum inventory levels. As a result, there is a considerable reduction in inventory storage needs and its carrying costs.
7. Calculate Inventory Turnover Ratio (ITR)
The inventory turnover ratio is a metric to determine how your inventory is performing, which is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold by the average inventory. A lower ratio is a signal that your inventory movement is slow and you must take steps to improve inventory management.
Revolutionize Inventory Management with Sage X3
Inventory holding costs are the price you pay to store inventory. So you would always want to know how to minimize such costs by knowing your opportunity costs. Can you free up capital tied in inventory to invest in something more productive? But you would also want to ensure that you have sufficient safety stock to service customers on time.
If you need to boost inventory efficiency, you must have real-time control over your inventory, which helps you minimize inventory holding costs. Sage X3 ERP solution offers real-time inventory tracking along with all other essential ERP modules such as AP & AR automation, financial management and business intelligence, offering you comprehensive business control and in-depth insights.
FAQ
1. What is Inventory Holding Cost and Why Is It Important?
Inventory holding costs are all expenses incurred towards the management of unsold inventory. It consists of expenses such as capital costs or opportunity costs of investing in inventory, storage costs, insurance costs and inventory service costs. It is vital to calculate as it directly impacts business profitability and cash flow.
2. How Is Inventory Holding Cost Different From COGS (Cost of Goods Sold)?
Holding cost is the ongoing expense a business incurs for storing unsold goods. On the other hand, COGS represents the direct costs of producing the inventory sold. And when you price your products, you must take into consideration both inventory holding costs and COGS.
3. Is There A Specific Formula To Calculate Inventory Holding Costs?
Yes, holding costs of your inventory are often calculated as a percentage of the total value of your inventory, including storage, capital and depreciation costs. The formula for inventory holding cost is as follows:
Inventory Holding Costs (%) = (Sum of Inventory Cost Components / Total Inventory Value) x 100
4. What Role Does Inventory Management Software Play In Controlling Holding Costs?
Inventory management software optimizes inventory levels, reduces inventory overstocking and automates tracking, helping lower storage and capital costs effectively.