Evolution of ERP
ERP Through the Ages: The ERP Journey Unfolded
What is an ERP?
An Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is an end-to-end system and a fluid framework that integrates different business processes and provides complete oversight & control over your business operations.
ERP Software revamps traditional business practices such as juggling between different spreadsheets and legacy tools. It acts as a Single Source of Truth that provides 360-degree visibility across all departmental operations. It enables decision-makers to make smart & quick decisions, effectively use the organizational resources, minimize costs, and capitalize on new business opportunities.
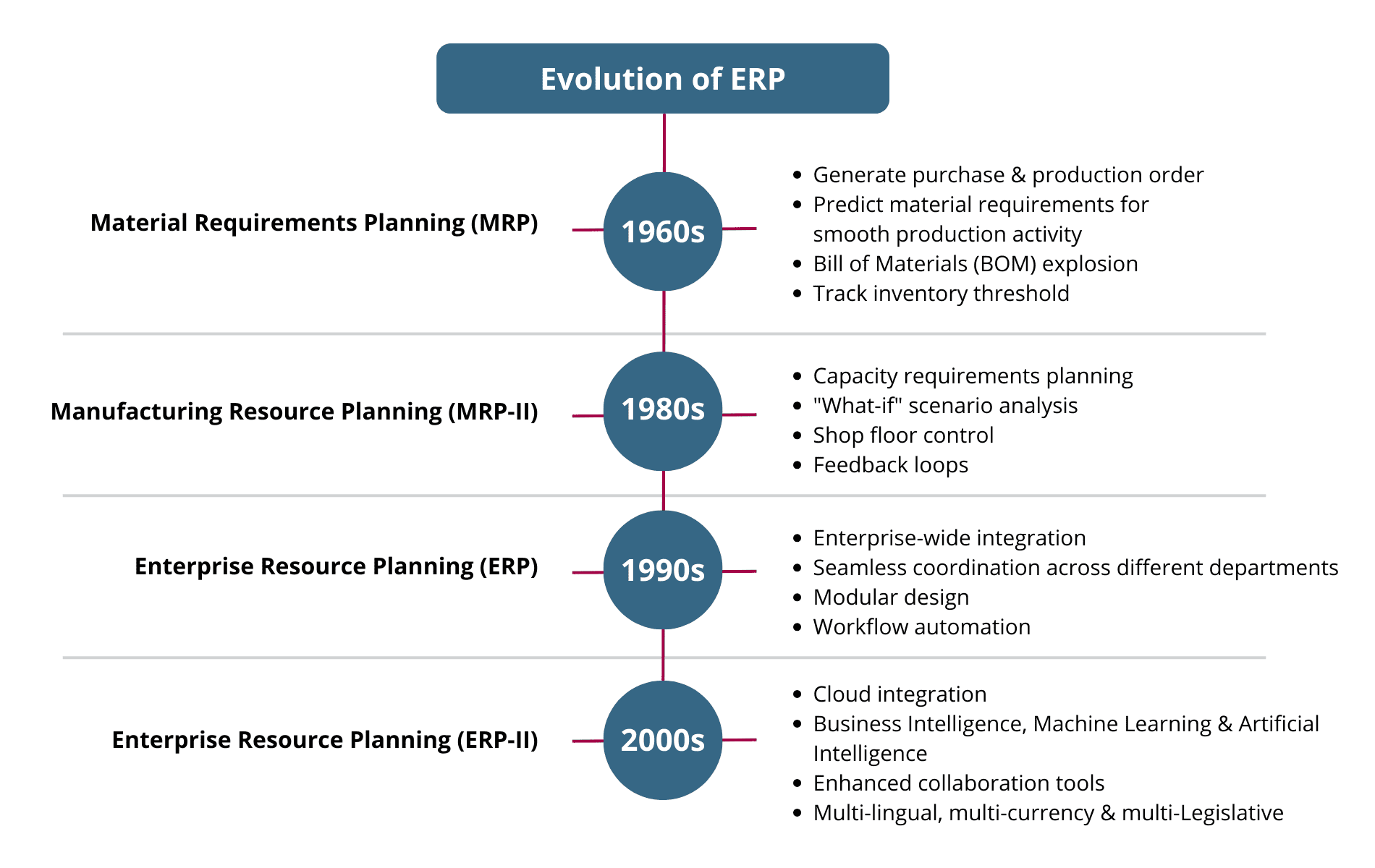
The Evolution of ERP
1. Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) was originally invented in the early 1950s by an IBM engineer, Joseph Orlicky. However, it was never commercialized until 1964 when it was “reinvented” to cater to the needs of the manufacturing companies. Black & Decker was the first company to implement it. The MRP only supported monitoring production resources, in addition to demand forecasting and purchase management.
2. Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP-II)
Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP-II) came into existence in the 1980s. It empowered manufacturing companies with resource optimization tools to allocate labor & machinery to reduce cost and maximize production efficiency. It enabled them to manage their inventory, visualize & develop precise production schedules, and deal with manufacturing-specific challenges.
3. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
The first true ERP came into existence in the 1990s with the introduction of a first-ever multi-functional system that went beyond basic manufacturing & inventory management capabilities and supported broader business functions. However, it was only limited to internal business processes.
4. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP-II)
ERP-II is considered a significant upgrade to the ERP throughout the evolution of ERP. It covered external business processes and came with powerful collaboration capabilities, integration between different business departments, and several other add-on features such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM System), Supply Chain Management (SCM), and financial management module.
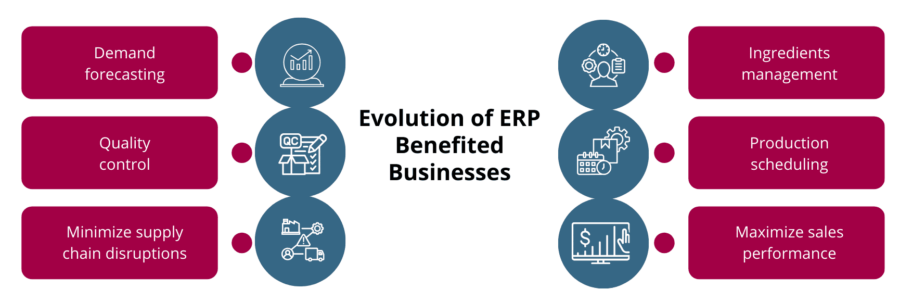
How has the Evolution of ERP Benefited Businesses?
1. Demand Forecasting
Forecast demand for your products & analyze consumer buying patterns. For example, ERP for furniture manufacturing allows furniture MSMEs to predict future demands for their products.
2. Ingredients Management
Other benefits of ERP include its ability to create & manage production formulas/ recipes. For example, pharmaceutical companies use Pharma ERP Software to track and combine the ratio of ingredients to produce safe and effective tablets and capsules.
3. Quality Control
The quality assurance process is conducted at all levels of the production process to produce high-quality, safe, and reliable products and maximize consumer satisfaction. Consistently producing quality goods translates into better goodwill and higher market share.
4. Production Scheduling
Align your production management process to meet changing business needs and market scenarios. ERP Application helps you minimize production waste, minimize costs, and ensure responsiveness to changing market conditions.
5. Minimize Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply Chain Management tools optimize the shipping process, prevent bottlenecks in the supply chain, and ensure a smoother order fulfillment process. This results in lower overhead costs and higher efficiency rates.
6. Maximize Sales Performance
Sales Management System optimizes sales-specific activities by streamlining order placement, lead management, analysis of past sales, and trend identification.
What is the Difference Between MRP-II and ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is considered the successor of the Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP-II) in the ERP evolution. Today, ERP has become an everyday part of business life.
Here’s how both of them differ in concepts:
| MRP-II | ERP | |
| Definition | Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP-II) is a standalone tool used by manufacturers to plan and optimize production activity | Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is an all-encompassing tool used by companies across all industries to manage & optimize all aspects of their business operations. |
| Uses | MRP-II is primarily used by manufacturing companies | ERP is used in companies across all industries |
| Cost | Cheap (Limited feature set) | Expensive (Broader feature set) |
| Implementation Complexities | Easier to implement | Time-consuming & resource-intensive |
| Level of Customization | Offers limited customization options | Offers a wider range of customization options |
| Scope |
|
|
| Integration | Limited or no external integration support | It can be integrated with legacy tools & spreadsheets |
Usage of ERP Across Different Industries
ERP helps businesses across all industries move beyond traditional spreadsheets and legacy tools, and benefit from streamlined growth across all departments.
1. Manufacturing Companies
Manufacturing ERP Software enables manufacturers to schedule their manufacturing activities, manage resources, meet quality & industry standards, and avoid poor inventory management.
2. Retail Outlets
Enterprise Resource Planning enables retailers to monitor stock levels in real time, deliver personalized services to their customers, and improve store operations.
3. Alcohol Industry
ERP for alcohol industry allows alcohol manufacturers to monitor the manufacturing process at all stages, reduce wastage, create & manage formulas, and forecast demand for their products.
4. Food & Beverage Industry
ERP for food industry gives businesses a complete view of the food production process, streamlines the procurement of raw materials, and optimizes key business processes.
5. Chemical Industry
ERP for chemical industry enables chemical manufacturers to monitor batch production at a large scale, ensure strict quality compliance & regulatory adherence, and leverage modern technology & innovation to gain a competitive advantage.
6. Medical Device Manufacturers
ERP for Medical Device Manufacturers helps reduce complexities in the production & distribution of medical devices, enhance compliance with Govt regulations, and produce safe & reliable equipment.
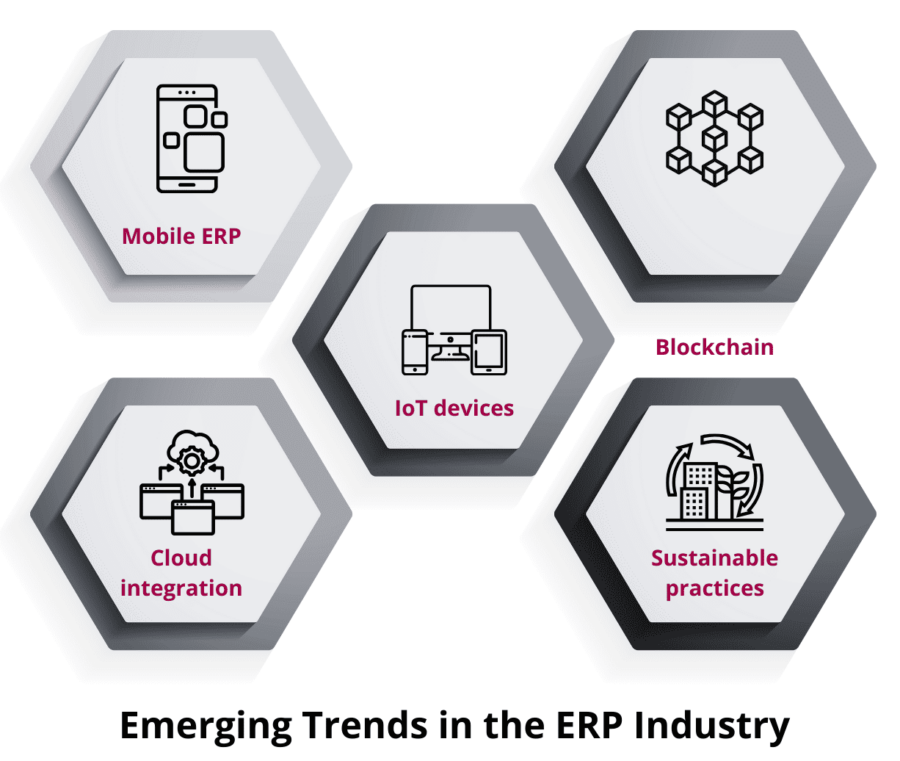
What are the Emerging Trends in the ERP Industry?
1. Cloud Integration
The cloud has enabled businesses to store their data on the vendor’s servers and gain flexibility and remote accessibility. Cloud ERP eliminates the need for a significant cost at the beginning of the implementation period.
2. Mobile ERP
Mobile-based Enterprise Resource Planning tools provide on-the-go access to business-critical data and allow employees to work remotely. Whether it is checking the status of an activity or approving it, Mobile ERP streamlines both the front-end & back-end activities.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
Internet of Things (IoT) devices capture data using sensors, and share it in real-time with other devices for better shop floor performance, operational efficiency, and higher accuracy.
4. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology builds a secure & transparent network to facilitate real-time tracking of goods, reshape supply chain activities, and combat various modern-day business challenges.
5. Adopting Sustainable Practices
Thanks to growing awareness about the need for environmental preservation & energy saving, the Best ERP Software in India aligns with sustainable & environment-friendly business practices.
Fuel Your Business Success with Sage X3
Over the last few decades, the evolution of ERP has completely transformed the way companies operate. From its invention as a simple inventory management tool to an all-comprehensive tool, ERP has become an indispensable part of the company’s day-to-day operations.
Sage X3 is a strategic tool that goes beyond a traditional ERP tool to support a wide range of legacy tools and offers a comprehensive suite of features, alongside best-in-class collaborative capabilities. It is built keeping in mind the needs of global organizations that require multi-country, multi-lingual, multi-currency & multi-legislative support.
Top Industries Leveraging ERP Software
Food & Beverage
Alcohol
Pharmaceuticals
Advertising
IT Services
Furniture
Manufacturing
Auto Ancillary
Pharma Trading
Packaging
Medical Device
Chemical
Plastic
Brewery
Logistics
Automotive
Related ERP Articles
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Who Developed the First Ever ERP?
Joseph Orlicky, an engineer working at IBM, is known as the original developer and pioneer of Material Requirements Planning which ultimately became Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) as we know it today. He built the foundation of ERP in 1964 by commercializing the concept of what he called, Material Requirements Planning (MRP).
2. What were the Earliest ERPs be like?
In the history of ERP, the earliest ERPs were limited in scope and functionality. They supported only specific business functionalities such as the production process. Unlike modern cloud-based ERPs, they require a huge upfront investment. Before the ERP evolution, companies incurred a significant cost in setting up and maintaining their own dedicated IT infrastructure & workforce, software license costs, and maintenance & upgrade costs, among others.
3. How is ERP-II Different from ERP?
ERP-II is considered as the successor of the ERP-I which primarily focuses on internal business processes related to specific business functions. The ERP-II goes beyond internal processes to cover various other external aspects such as managing customer relations, suppliers, and e-commerce to build strong & meaningful relations. Moreover, it empowers your business with strong analytical capabilities and demand forecasting for smart decision-making.
4. How is Artificial Intelligence (AI) Transforming the ERP Industry?
Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing the world, and Business Management Software is no exception. Here’s how:
- Demand Forecasting: Gain comprehensive insights into the market dynamics for strategic planning, resource optimization, and making accurate decisions with AI-powered Business Intelligence Tools.
- Process Large Dataset: AI’s ability to process vast amounts of information supports quick & accurate decision-making, which improves the company’s agility.
- Sustained Market Advantage: AI in supply chain lets you develop proactive strategies to respond to sudden market changes, and mitigate supply chain risks.
- Robotic Process Automation: Automate smooth flow of workflows, data extraction, and transmission from inter-connected devices and bots.
- Proactive Risk Management: AI-powered Financial Management Software enhances fraud detection algorithms and shifts the focus of the risk management strategy from reactive to proactive.
5. How has the Cloud Revolutionized the ERP Industry?
The introduction of cloud technology has allowed ERP vendors to host business data on their servers. Unlike On-premise ERP implementation, it doesn’t require an upfront investment. You can start using it by paying a monthly or annual subscription fee. Your employees can access business data no matter where they are without needing to be physically present in the office.
Schedule Product Tour
"*" indicates required fields