Top 6 Components of ERP
Flip the switch on innovation & gain an edge over competitors with the right combination of ERP components

What are ERP Components?
ERP Components are integrated modules or capabilities that provide a clear view of business activities and allow you to manage them to meet evolving market demands prudently, plan & schedule activities, gain actionable insights, and make strategic decisions.
ERP Software comprises numerous modules that address specific operational needs and provide visibility into different aspects of your business operations. With the right ERP components, you can turn a vast trove of information into bite-sized, quick & powerful takeaways, and use custom features tailored to your business needs.
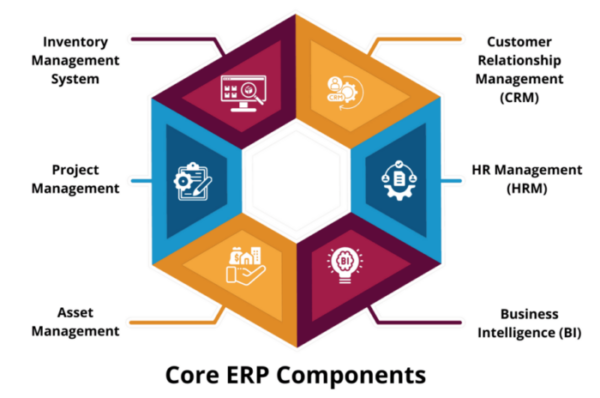
What are the Core ERP Components?
1. Inventory Management System
The Inventory Management System assists businesses with the management and distribution of inventory in real time. It provides real-time visibility into your inventory threshold and automatically notifies the concerned personnel every time the stock level reaches a certain threshold.
2. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
The CRM minimizes the efforts required in customer data management. From tracking & filtering quality leads to reducing the time in the order fulfillment, it improves the overall business efficiency and customer acquisition cost. The Lead Management System analyzes & nurtures leads, and converts them into actual sales.
3. Project Management
Business Management Software includes powerful Project Management capabilities that facilitate realistic planning, budgeting, cost control, and inter-departmental collaboration. By analyzing and planning every aspect of your project from the idea generation to completion, you can avoid bottlenecks, improve quality, and mitigate project risks.
4. HR Management (HRM)
Traditionally, managing employee databases, payroll, and workforce planning, were conducted manually. ERP functions reduce the burden of the HR department and facilitate automated tools for payroll management, financial planning & budgeting, and tracking employee recruitment & employee onboarding.
5. Asset Management
The Asset Management module frees up your staff from routine asset management operations and automates asset tracking, maintenance & performance monitoring. ERP acts as a maintenance software that maximizes the lifespan of your assets and ensures they are always in good & working condition.
6. Business Intelligence (BI)
Business Intelligence is one of the most important extended ERP components. ERP implementation helps decision-makers gain actionable insights, track the effectiveness of the sales and marketing campaigns, and forecast sales & demands for their products. Companies can monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to visualize new trends and make data-driven decisions.
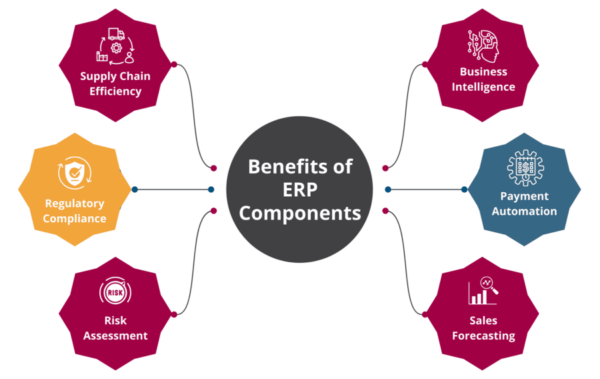
Strategic Benefits of Using ERP Components
1. Supply Chain Efficiency
The Best ERP Software in India transforms the traditional Supply Chain management process with the help of modern tools & technologies that facilitate real-time tracking of stocks, efficient warehouse management, optimizing organizational resources, automated order placement, vendor management, managing work schedules, and better responding to customer problems.
2. Business Intelligence
The Business Intelligence Tools facilitate real-time data analysis, data visualization, strategic planning, and smart decision-making. It enables businesses to make strongly data-driven decisions that are based on the most accurate & reliable information through intuitive charts, reports, and customized dashboards.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Manual compliance tasks are not only complex and time-consuming but also prone to various human errors. The main components of an ERP monitor changes in the regulatory landscape and automate various compliance operations to prevent fines, penalties, and non-compliance.
4. Payment Automation
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) automates the management of the company’s money inflow and outflow and reduces the time & complexities in the Accounts Payable & Receivable processes. For example, AP Automation automatically extracts data from supplier’s invoices using their Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology. In contrast, AR Automation makes the manual collection process quicker & easier.
5. Risk Assessment
Other advantages of ERP include risk assessment. Several internal and external risks can affect your business performance, customer experience, market reputation, and compliance. ERP provides powerful tools and mechanisms to effectively identify and mitigate these risks.
6. Sales Forecasting
Forecasting your sales is not an easy task. Thanks to ERP, businesses gain realistic estimates about the market demand for their products and nearly accurate predictions about future sales so that they can prepare for changing circumstances.
Limitations of ERP Components
ERP Application provides numerous benefits to businesses. Nevertheless, it has certain limitations too.
1. Upfront Investment
For small businesses, ERP cost is often a big concern. You can avoid the hassle of significant upfront investment by subscribing to a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) based Cloud ERP.
2. Implementation Time
Company-wide ERP implementation can take time as you will need to integrate multiple data sources, convert your data, and ensure compatibility with your existing systems.
3. Employee Reluctance
Some employees may be reluctant to adopt the new system and prefer the traditional way of working. It can be a hurdle in achieving the intended objectives of the implementation.
Diverse Usage of ERP Components Across Different Industries
ERP serves different industries to manage key aspects of their operations and ensure ease of business.
1. Manufacturing Companies
Manufacturing ERP Software helps manufacturers plan their production activities, allocate resources efficiently, and make the best out of their manufacturing capacity. It also helps them automate routine tasks, and lower the production cost.
2. Pharma Companies
Pharmaceutical companies use Pharma ERP to gain just-in-time inventory insights, track the expiration of medicines, gain operational efficiency, and comply with government regulations.
3. Food Companies
ERP for Food Industry provides a centralized platform for food companies to manage their food formulas, manage food safety & quality assurance, plan & optimize their inventory, and fulfill customer orders on time.
4. Automotive Companies
Automotive ERP transforms the traditional processes in automotive companies and allows decision-makers to gain a bird’s eye view of the entire manufacturing, Supply Chain Management (SCM), and other processes.
5. Wholesale Distributors
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) empowers wholesalers with end-to-end inventory analysis. They use it to track & manage inventory, improve inventory turnover, and shorten order-to-cash timespan. Other ERP modules help wholesalers automate the supply chain and overcome various business challenges.
6. Retailer Distributors
With the emergence of e-commerce platforms, retailers are leveraging the main components of ERP to provide a seamless shopping experience to their customers. It provides distinctive features to integrate shopping carts, reduce cart abandonments, and improve conversion rates.
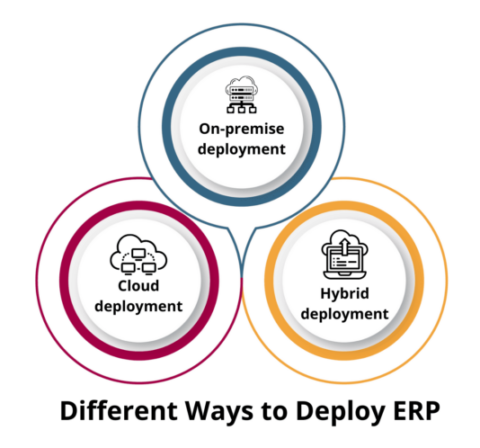
Different Ways to Deploy ERP
1. On-premise Deployment
On-premise ERP is a type of ERP that stores your data in the company’s internal IT infrastructure. Typically, this deployment method is preferred by large companies with a huge capital base and internal IT infrastructure. They can securely store their confidential data, and gain from extended customization abilities.
2. Cloud Deployment
Cloud ERP is a type of ERP that securely stores your data on the vendor’s IT servers. Your vendors provide distinct user interfaces. Cloud-powered ERP empowers your business with endless possibilities. It provides a responsive user interface (UI) to fit your needs across different devices including desktop, tablet, and mobile. Your employees can work remotely and the data will be accessible in real-time.
3. Hybrid Deployment
Hybrid ERP is a combination of both On-premise and Cloud deployment. Hybrid is often considered “the best of both worlds” because it provides the advantages of both the On-premise and Cloud deployment methods into a single platform.
Start Your Journey to Success with Sage X3
ERP components play a vital part in managing all aspects of your business from providing a sweeping overview of your business operations to facilitating insight-driven data for smart decision-making. There are numerous modules, and it’s important to choose the right ones.
Sage X3 reduces the complexity of your business operations and equips decision-makers with untapped potential for their journey to growth & success. It facilitates business-critical tools, actionable insights, and a robust array of features so that decision-makers can focus on key operational domains and achieve their strategic targets.
Top Industries Leveraging ERP Software
Food & Beverage
Alcohol
Pharmaceuticals
Advertising
IT Services
Furniture
Manufacturing
Auto Ancillary
Pharma Trading
Packaging
Medical Device
Chemical
Plastic
Brewery
Logistics
Automotive
Related ERP Articles
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do I have to Purchase All the ERP Components?
2. What are the 5 Widely Used ERP Components?
Companies across different industries and sizes use numerous ERP components. Here are the 5 widely used main components of ERP:
- Business Intelligence: This component navigates through the complexities of the business environment and provides actionable insights to make data-driven decisions.
- Customer Relationship Management: This component helps businesses manage customer data, identify trends, and derive meaningful insights.
- Inventory Management: This is a crucial component that allows real-time inventory tracking, and ensures your business never runs out of inventory or faces excess stock.
- Human Resource Management: The HRM component assists businesses with employee record management, payroll management, performance evaluation, and various other HR tasks.
- Financial Management: The Finance module in ERP automates the company’s financial operations, sales order management, invoice generation, payables & receivables management.
3. Which ERP Components are Mostly Used by Business Executives?
Business executives may use different Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) components based on the nature and scope of their business and their specific requirements. Here are the most commonly used ones:
- Business Intelligence: Decision-makers can sift through multiple data sources, and leverage robust data intelligence networks to increase profitability and achieve sustainable revenue growth.
- Risk Management: Executives can use the end-to-end risk management tools to reduce operational and compliance risks, and ensure adherence to the best industry standards.
- Financial Management: It provides insights into the company’s financial health, and allows decision-makers to track business performance and analyze profitability.
- Sales Management: The Sales Management System aids in analyzing market trends & patterns, and forecasting demand for the company’s products.
- Customer Relationship Management: It helps you maintain healthy relationships with your customers and contribute to the growth and success of your company.
4. What is the Role of the Supply Chain Component of ERP?
Supply Chain component plays a critical role in the growth and success of your organization. It lets you:
- Analyze demand for the company’s products
- Manage the flow of goods and services
- Streamline supply chain activities and timely fulfill customer orders
- Increase the company’s responsiveness
- Deal with ever-changing market circumstances
- Reduce operational costs and increase profit margins
5. What Factors Should I Take into Consideration while Selecting ERP Components?
Selecting the right components of ERP is key to remaining competitive and profitable, and making the best out of your ERP investment. Here are the factors that you should take into consideration:
- Problem Analysis: Perform an intricate analysis of the internal and external problems faced by your company, and how ERP will tackle them.
- Functional Fit: Make sure that your ERP components align with your strategic business needs and long-term objectives.
- Industry Experience: Make sure that your vendor has extensive knowledge and experience to keep up with the industry requirements and latest technological changes.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Measure the financial return you can expect from your investment in the ERP and make it a more profitable one.
- Scalability: Can your Enterprise Resource Planning adapt to changing business needs and accommodate new changes? Be sure to check that out.
Schedule Product Tour
"*" indicates required fields