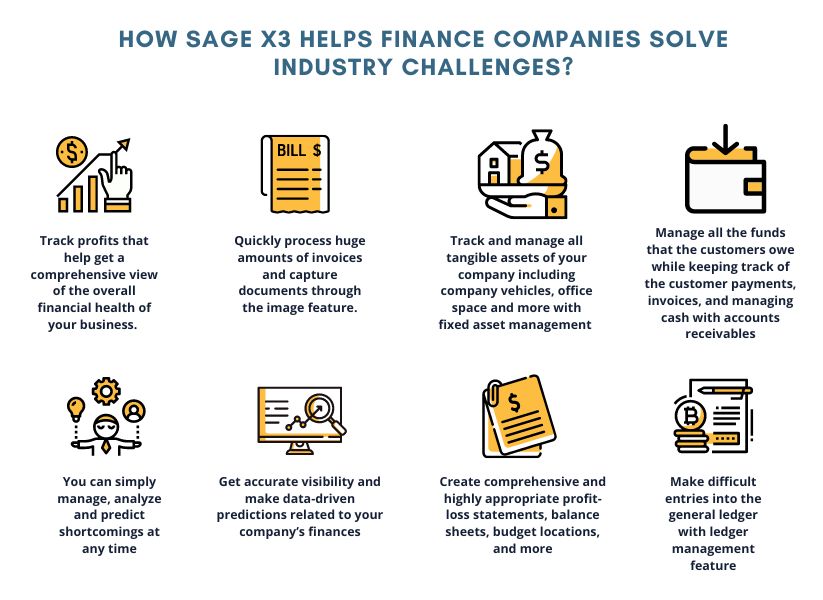
Summary: Fixed Asset is a constituent part of your business. Fixed assets are long-term assets that a company owns to generate income through business operations. They cannot be converted into cash in the short term. Let us learn more about the characteristics and many aspects of fixed assets.

An asset is a valuable resource you purchase, expecting a continuous flow of benefits and income. Anyone can own assets – companies, individuals and the government. In a company, the assets are recorded on the balance sheet. An entity must record two types of assets on the balance sheet – Fixed and current assets.
What is Fixed Asset?
Fixed assets are tangible properties or equipment a company uses to generate profits. These assets provide financial gain to the business for the long term. The company owns fixed assets for a long time for more than a year. The value of these assets is later depreciated, and they can be converted to cash after a year.
Fixed assets are recorded in the balance sheet under the property, plant and equipment (PP&E) category.
Fixed assets are also known by the terms capital assets or non-current assets.
Examples of Fixed Assets
Suppose a furniture company purchases an office building with industrial equipment for 25 crores. Here the land, building and industrial equipment are examples of fixed assets. All these assets can be used for more than one year and contribute to generating revenue. These assets are registered on the balance sheet as fixed assets.
Listing some examples of fixed assets below :
Property, plant and equipment (PPE)
- It includes buildings and even under-construction buildings. Upon completion, an under-construction building will automatically be transferred under the right fixed asset category.
Land
- Buildings and leasehold improvements, including interiors.
Vehicles
- The truck, used to carry goods and other company vehicles, comes under the fixed asset category.
Furniture and Fittings
- Furniture such as desks, cupboards, chairs, and conference tables come under the fixed assets category. Fittings like office equipment, mirrors, light and art are classified under fixed assets.
Machinery
- Industrial machinery and tools used for manufacturing processes are considered fixed assets.
Computer equipment and software
- Computer equipment such as servers, desktops, laptops, iPads and others.
- Cloud-based applications are considered a fixed asset. Enterprise packages and platforms also come under this category.
Types of Fixed Assets
There are two types of fixed assets :
Tangible assets : Assets which has a physical form are denoted as tangible assets. Assets such as land, industrial machinery, buildings and many more are categorized under tangible assets.
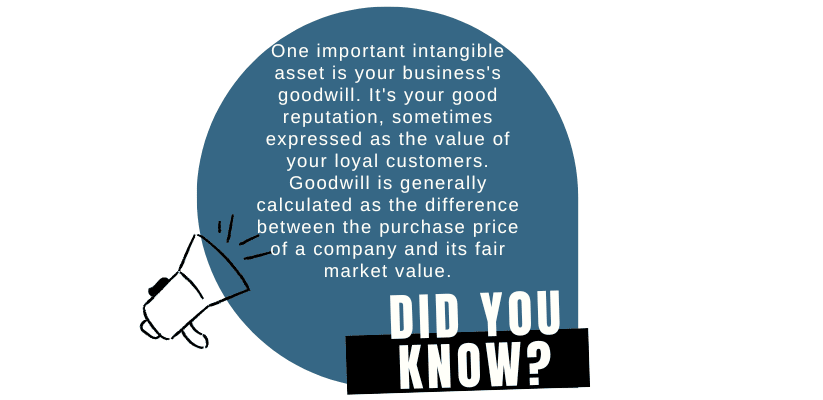
Intangible Assets : Intangible assets don’t have a physical existence. Intellectual rights, goodwill, trademarks and copyrights are some examples of Intangible assets.
Benefits of Fixed Assets
A company has to record its assets to create accurate financial reporting, business valuations and in-depth financial analysis.
Fixed assets are significant for the company to conduct business operations and make a profit.
A fixed asset is crucial because the investors closely inspect a corporate’s assets to decide if they should invest in that specific company.
Capital-intensive industries like manufacturing that own large property, plant and equipment require an accurate record of fixed assets.
The value of fixed assets depreciates over a period of time. As the company records the depreciating value of fixed assets over time, the investors will get an indication that the company is growing.
Accounting for Fixed Assets
In a company, fixed assets are recorded to clearly understand transactions for the same.
Balance Sheet :
In the first step, a purchased fixed asset and its value is recorded on the balance sheet. If the fixed asset is purchased in credit, it would be classified under the account payable category. A fixed asset is capitalized in the balance sheet as it is used for a more extended time to generate revenue.
Income Statement :
Fixed assets are depreciated after a year as property plants and equipment are used to conduct business operations. After a certain time, these assets will incur wear and tear charges.
For example, a building has to be repaired by maintaining the interiors. Office equipment has to be serviced every six months or every year, which is an expense for the company. The company’s net income is calculated after depreciating the value of fixed assets. Later the fixed assets are scrapped or sold and converted to cash.
Statement of Cashflow :
All business transactions are registered on the balance sheet. So purchase or selling of fixed assets is recorded in the investing activities section of cash flow statements. A fixed asset purchased is an outflow of cash and is classified under capital expenditures. The sale of fixed assets is an Inflow of cash categorized under proceeds from the sale of property and equipment.
Fixed Asset Accounting Cycle
-
Acquisition
All the costs, including the fixed asset price, shipment, installment and service charges, are entered into the balance sheet. Even if you are paying instalments or via an exchange is also registered in the journal entry.
2. Depreciation
The value of the fixed assets is depreciated periodically for tangible assets and amortization for intangible assets.
3. Revaluation
Entries you make should reflect the current market value of the asset. Ensure that the revaluation causes any gain or loss in the accounting entries.
4. Impairment
The period when the market value of an asset is lower than the valuation mentioned on the balance sheet. It is also known as writing down.
5. Disposition
After an asset’s lifecycle is complete, it is sold, traded or scrapped down. Here you calculate the gain or loss of the asset. Then that specific asset is eliminated from the accounting entry.
<<<Also read: The Scope of Financial Management>>>
Depreciation in Fixed Asset
Fixed assets have a useful life of more than one year. They cannot be easily converted to cash as they help generate income. Each year the value of fixed assets deflates, which will be reflected in the balance sheet. This deflation of assets is known as depreciation.
The company knows the entire life cycle of fixed assets before they purchase them. We can say that the value of fixed assets keeps on depreciating each year, but on the other side, revenue will increase. One of the methods to measure the depreciation of these assets is straight-line depreciation.
For a year, fixed assets function relatively well. Later the company have to pay for the wear and tear charges. So the worth of the fixed assets depreciates each year, and they are later replaced with new ones.
Non-depreciable fixed assets
Fixed assets whose value cannot be depreciated yearly are non-depreciable assets. Land’s value cannot be depreciated anytime. Most of the time, land’s value keeps on increasing. In comparison, the value of the building keeps on declining every year.
Difference between Fixed Assets and Current Assets
What are a company’s assets ? A company’s assets are things they own to monitor and control business operations and generate revenue.
Generally, a company’s financial accounts are categorized into distinct divisions. Fixed assets and current asset is a part of that accounts.
Fixed assets are capital assets, also known as property, plant and equipment(PP&E), which are assets used by the company for more than one accounting period.
Current assets are items such as cash and inventory that are used or sold before an accounting period completes. It can be easily converted to cash. Inventory, cash, cash equivalents, and accounts receivable are current assets. The value of the current assets cannot be depreciated.
Challenges of Fixed Asset Accounting
- Manually managing, tracking and monitoring asset transfer is critical for a company. As a result, there will be inaccuracy in financial accounting reports.
- Real-time data visibility is significant here to avoid errors and confusion.
- Changes in tax implementation affect fixed asset accounting.
- Recording the accurate cost of depreciating value of fixed assets is substantial.
Benefits of Automation for Fixed Asset Accounting
- ERP software provides accurate data for the accounting of fixed assets.
- Simplified business processes and access information anytime.
- Highly secured data can be accessed by accounting professionals or those who are trained for it.
- ERP software helps to track, monitor and maintain the data of fixed assets of the company. And it also tracks if the asset is purchased within the budget.
- Automation improves efficiency and saves time. It’s easy to calculate accounting without any errors.
- ERP system can easily measure the precise lifespan and depreciation and predict fixed asset maintenance costs.
- ERP software is compatible, and the specialities or features can be customized based on the company’s needs.
<<<Also read: Asset transfer from CWIP to Fixed Asset>>>
It is crucial to understand the fixed asset value of your company. Maintenance of fixed asset accounting up to date is not easy. Rely on an accounting expert or automated software to get the accurate value of your fixed assets. As the fixed asset has a useful life of more than one accounting period, it’s vital to know and calculate the net book value periodically.
The disposal of fixed assets is complex. Therefore, the right business decisions must be taken when purchasing a fixed asset. A robust record keeping has to be maintained to track and manage all the fixed asset accounting.
Sage Software Solutions is a leading IT company with an array of advanced ERP software solutions. Our proprietary products — Sage X3 and Sage 300 will help you cut your operational expenses, improve business productivity, increase operational efficiency, forge robust customer relationships, and strengthen association with vendors, suppliers, and distributors. So, if you are looking to reinforce your business fundamentals and emerge as an industry leader, then please schedule a call with one of our sales representatives.